Worried about a suspicious rash? Understanding impetigo is the first step to fast relief and preventing its spread. Don't let this contagious infection disrupt your family's health and learn the key signs to watch for and how to protect your loved ones.
What are the main causes of impetigo?
- The primary cause is bacterial infection, typically from Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes entering the skin through cuts, insect bites, or other breaks.
- This highly contagious condition spreads easily through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person or by touching contaminated items like towels, bedding, or toys.
- Warm, humid environments can increase the risk, as bacteria thrive in these conditions, making impetigo more common during hot summer months or in tropical climates.
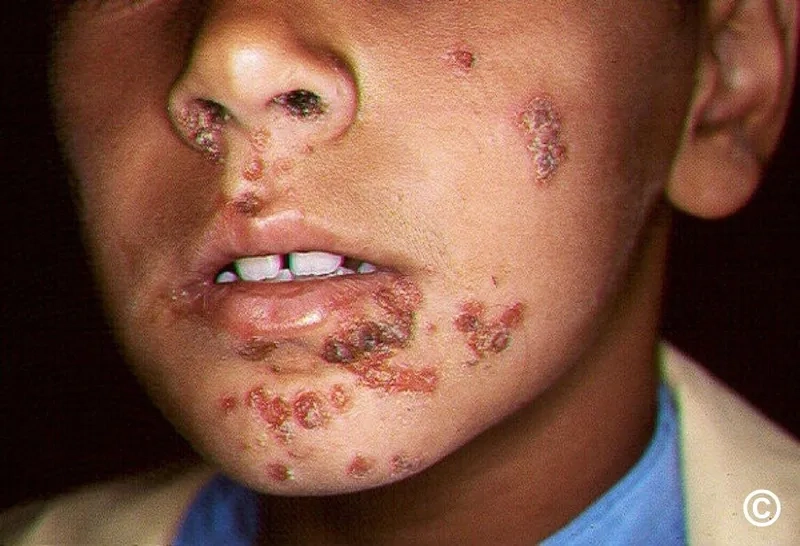
Key symptoms of impetigo to watch for
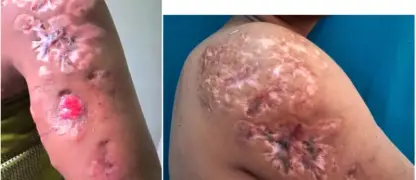
- Look for red sores, often around the nose and mouth of toddlers, that quickly rupture, ooze for a few days, and then form a honey-coloured crust.
- A less common form, bullous impetigo, involves larger, painless, fluid-filled blisters that appear on the trunk, arms, and legs of infants and young children.
- The affected areas may be itchy and occasionally sore, but the infection is generally superficial and does not cause a fever or significant systemic discomfort.
How can you prevent impetigo effectively?
- Practise good hygiene by washing hands regularly with soap and water, especially after touching any sores, to prevent spreading the bacteria to other people.
- Keep any cuts, scrapes, or insect bites clean and covered with a bandage to stop bacteria from entering the skin and causing an initial infection.
- Avoid sharing personal items like towels, clothing, or razors with someone who has impetigo until their infection has fully cleared up after starting treatment.
>>> See more: Hookworm infection - Causes, symptoms, and modern treatment
Image of the disease impetigo
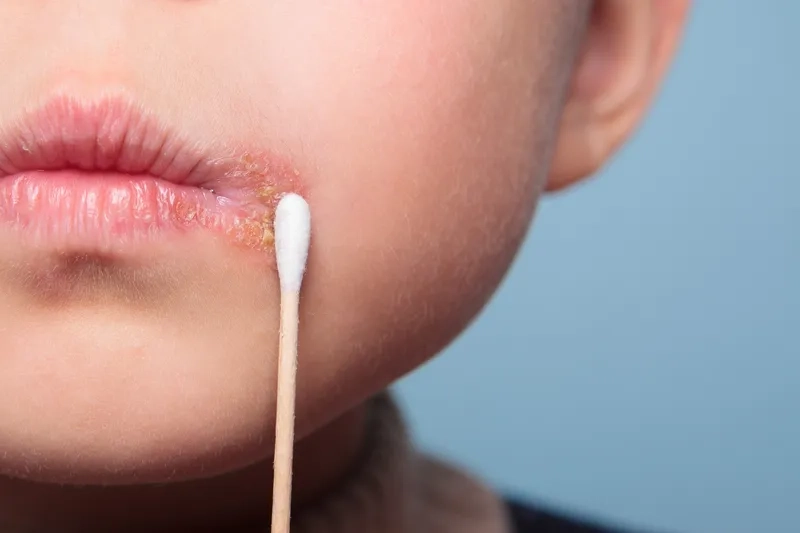




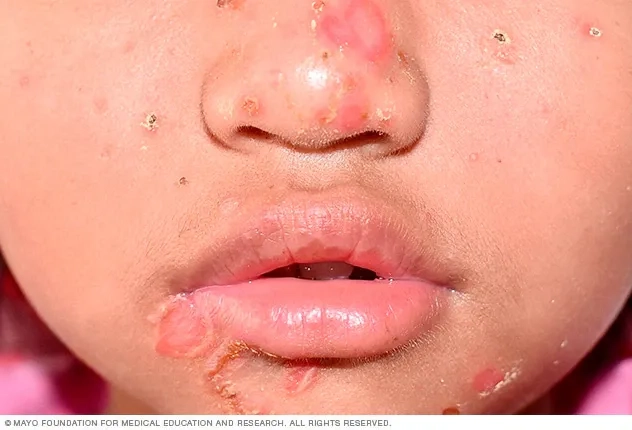


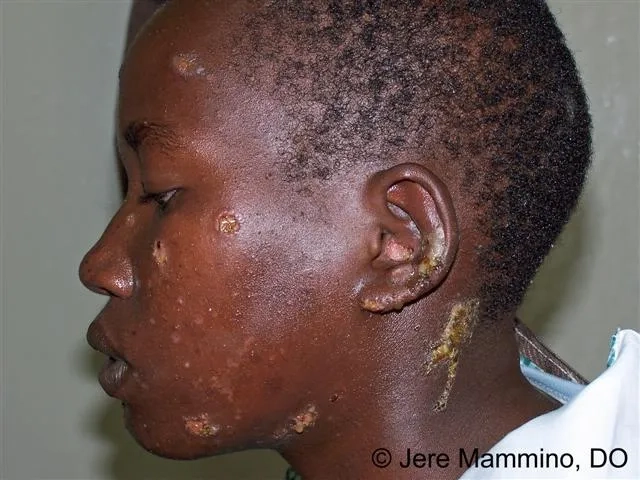
>>> Read more here: Human bocavirus - A common cause of respiratory illness in kids
Early detection and proper hygiene are key to managing impetigo. If you suspect an infection, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and effective impetigo treatment cream options.
>>> Details at: Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection - A guide to symptoms, vaccines, and cancer risk