This common bacterium is a major cause of hospital-acquired infections and can be antibiotic-resistant. Understanding how a Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection occurs is the first step toward protecting your health and recognizing the risks in both community and hospital settings.
What are the main causes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection?
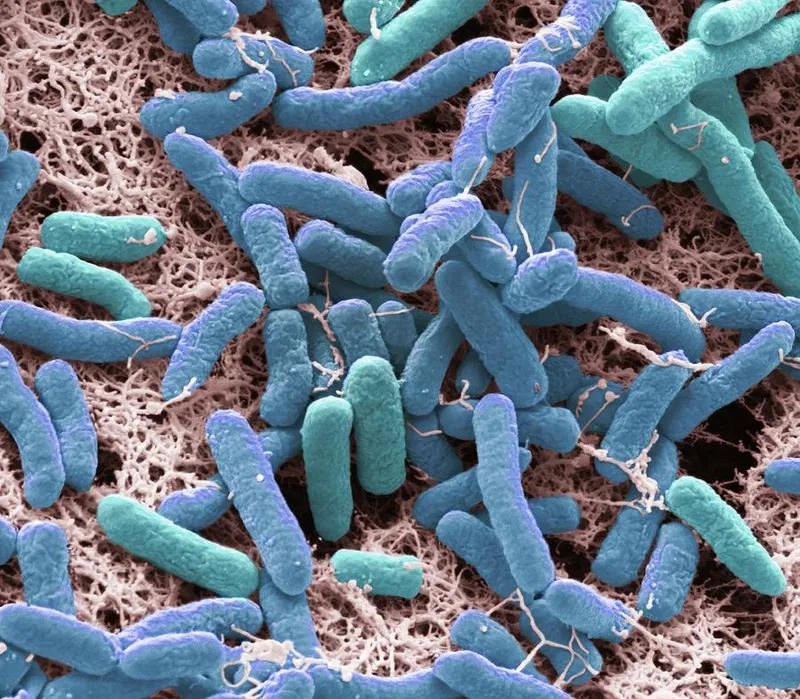
- The infection is caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a versatile gram-negative bacteria found in soil, water, and on plants, thriving in moist environments.
- It typically enters the body through weakened defenses, such as surgical wounds or catheters, making it a common and serious hospital-acquired infection.
- Exposure can also occur through contaminated water sources, leading to conditions like hot tub folliculitis or swimmer's ear (otitis externa) in healthy individuals.
Key symptoms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection to watch for
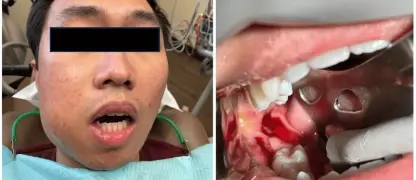
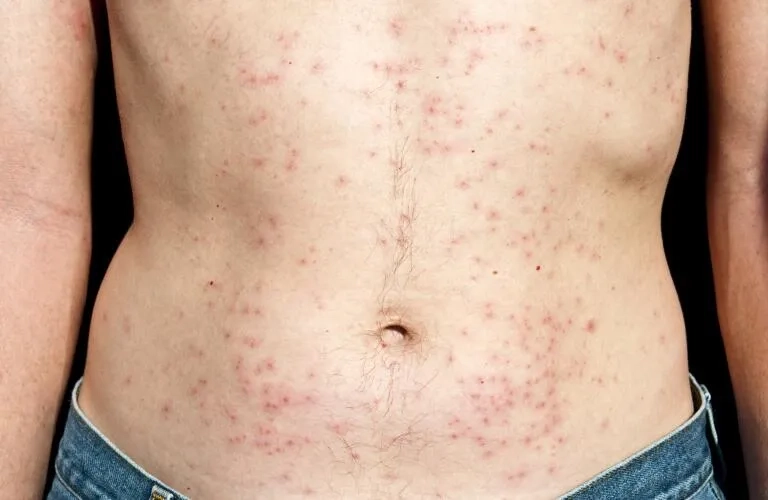
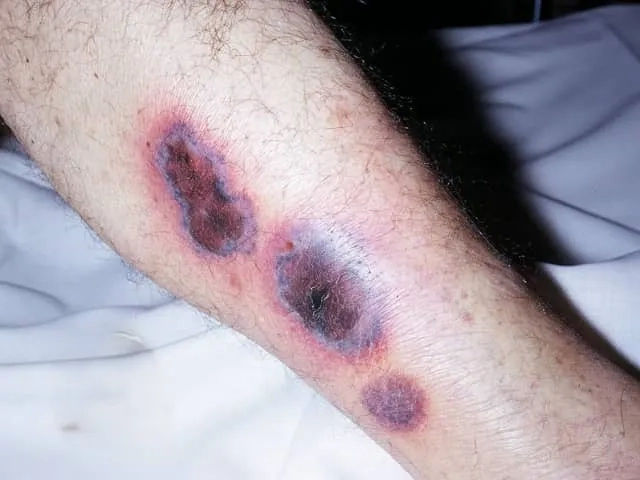
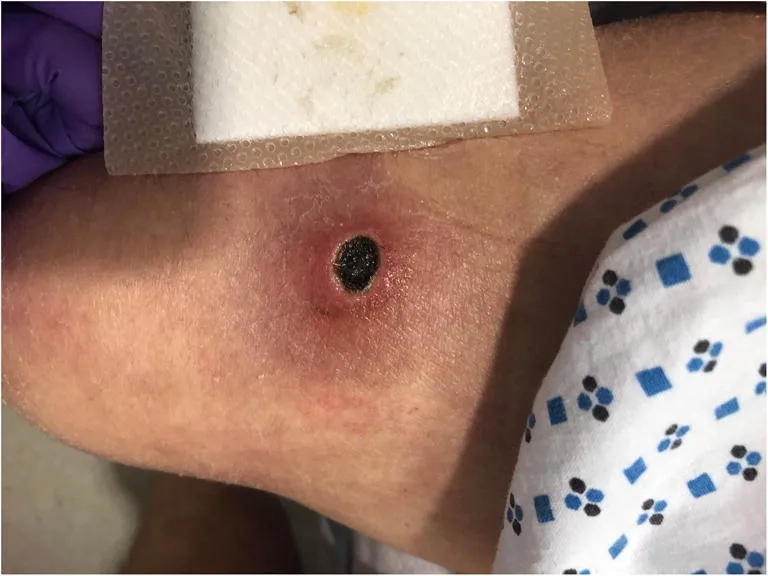
- Localized infections, such as a wound infection or swimmer's ear, can cause pain, green-blue pus, swelling, and a distinct fruity odor at the site.
- When it affects the lungs, causing Pseudomonas pneumonia, symptoms may include high fever, chills, body aches, and severe difficulty with breathing.
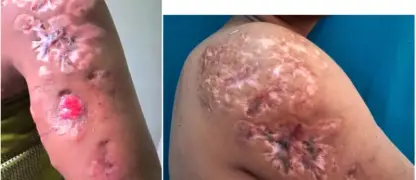
- A skin rash known as hot tub folliculitis presents as an itchy, bumpy red rash and is a common symptom after exposure to contaminated water.
How can you prevent Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection effectively?
- Rigorous hand hygiene is the most effective prevention method, especially in healthcare settings, to stop the spread of this multidrug-resistant organism.
- Keep all wounds, especially burns or surgical sites, clean and properly covered to prevent the bacteria from entering and causing a serious infection.
- Ensure that swimming pools and hot tubs are properly chlorinated and maintained to prevent skin infections and swimmer's ear from contaminated water sources.
>>> Related articles: Nocardiosis - A serious infection for the immunocompromised
Image of the disease Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection
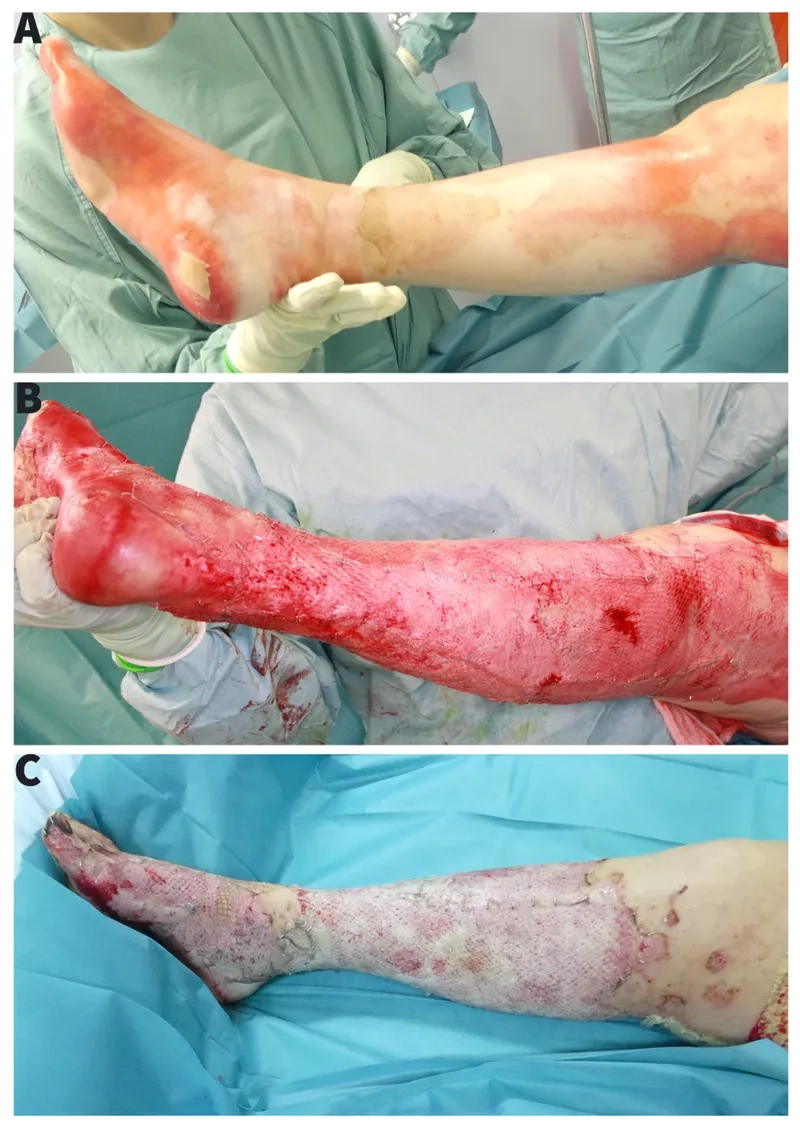
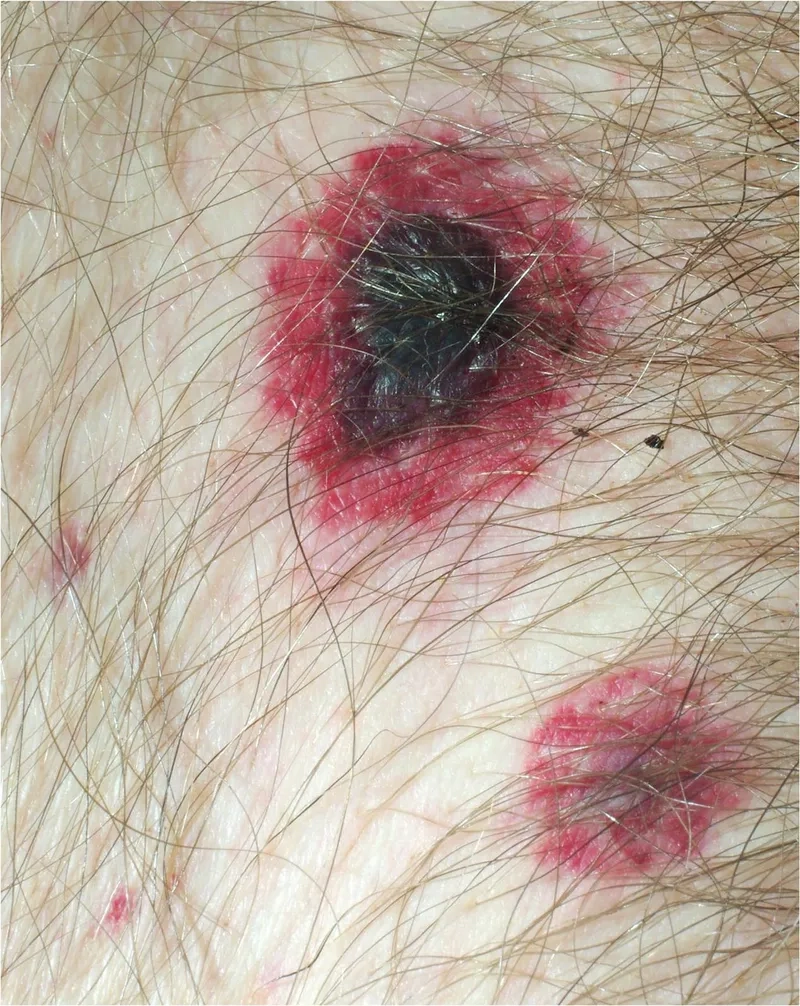
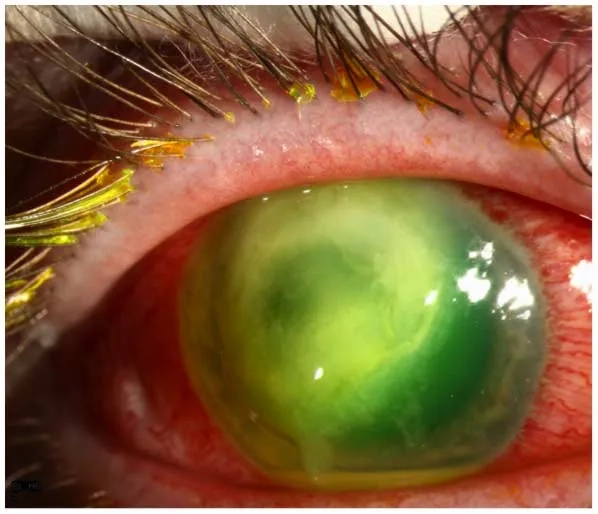

>>> See more: Necrotizing fasciitis - The flesh-eating bacteria explained
Due to the risk of antibiotic-resistant Pseudomonas, prompt diagnosis and treatment are critical. If you suspect an infection, consult a healthcare professional immediately for proper care and management.
>>> Learn now: Mycoplasma pneumoniae - The cause of walking pneumonia