Understanding Nocardiosis is vital, especially for those with weakened immune systems. Early detection can prevent severe complications like brain abscesses and ensure effective treatment. Don't overlook these critical signs of a Nocardia infection.
What are the main causes of Nocardiosis?
- Nocardiosis is caused by inhaling dust or soil contaminated with Nocardia bacteria, leading to a serious infection, most often in the lungs.
- The infection can also occur when contaminated soil enters an open wound, resulting in a localized skin infection known as cutaneous nocardiosis.
- It is important to understand that nocardiosis is not contagious and cannot be transmitted from one person to another through casual contact.

Key symptoms of Nocardiosis to watch for
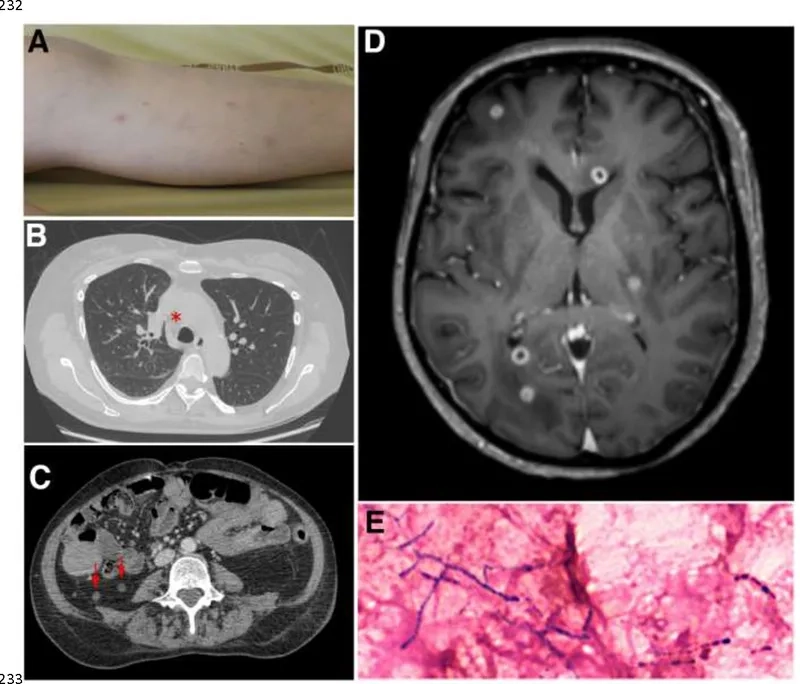
- Pulmonary nocardiosis, the most common form, presents with symptoms like cough, chest pain, fever, and night sweats, often mimicking pneumonia.
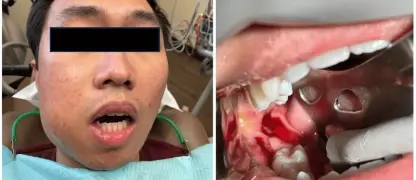
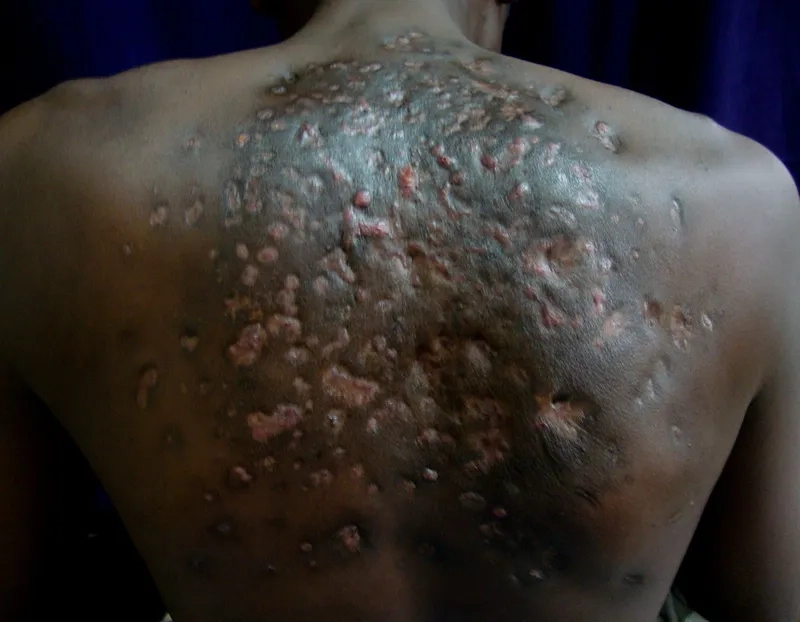
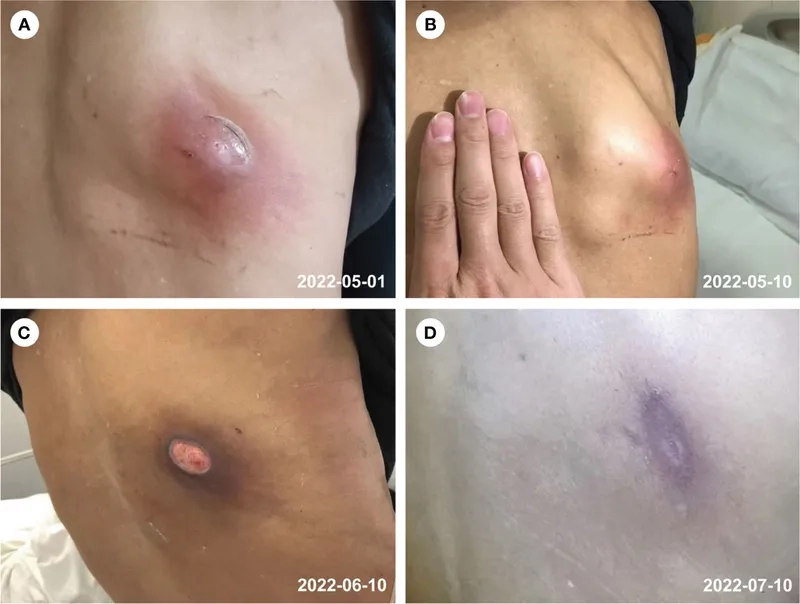
- Cutaneous nocardiosis can appear as skin ulcers, nodules, or abscesses that are slow to heal, particularly after a minor skin injury.
- When a brain abscess from nocardiosis occurs, symptoms may include severe headaches, confusion, weakness, and seizures, requiring urgent medical care.
How can you prevent Nocardiosis effectively?
- The best nocardiosis prevention for immunocompromised individuals is avoiding exposure to soil and dust by wearing masks and gloves during gardening.
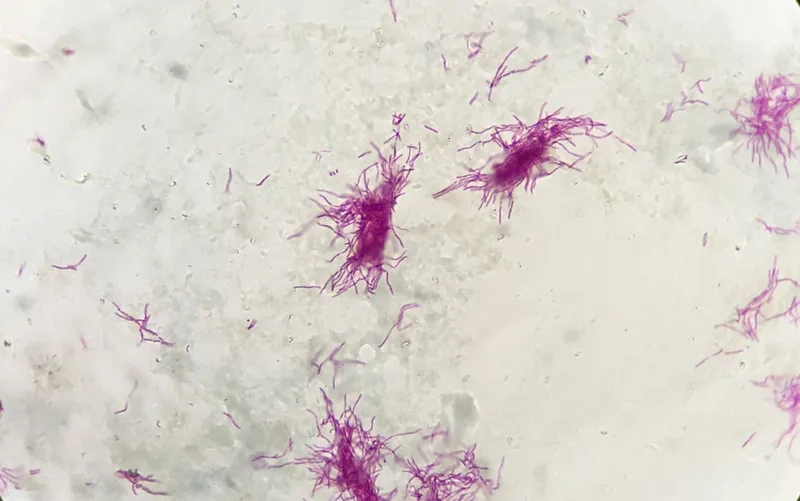
- An accurate diagnosis of nocardiosis is crucial, typically involving laboratory analysis of tissue or fluid samples to identify the bacteria.
- Successful nocardiosis treatment requires a long course of specific antibiotics for nocardiosis, sometimes for six months or more to clear the infection.
>>> See more: Glanders - A rare but serious bacterial disease explained
Learn about through Nocardiosis medical images
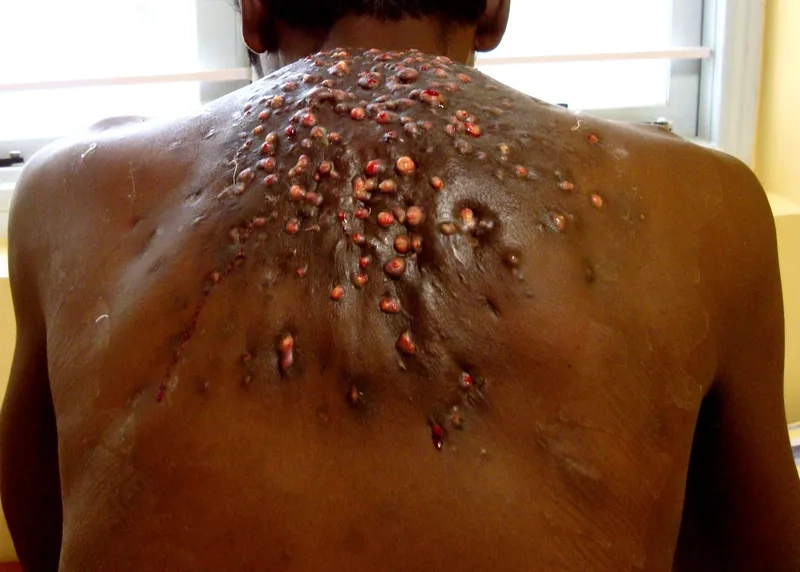


>>> Related articles: Fusospirochetal disease - Understanding trench mouth
Recognizing the risk factors for nocardiosis is the first step toward protection. If you suspect any symptoms, seek immediate medical consultation for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
>>> Don't miss: Fournier's gangrene - Recognizing this medical emergency