Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) is a vascular condition that impacts arteries, leading to hypertension, strokes, or aneurysms if not properly managed.
What are the main causes of Fibromuscular Dysplasia?
- Genetic predisposition plays a role, as Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) is more common in individuals with a family history of vascular diseases or arterial irregularities.
- Hormonal factors may contribute, particularly in women, as Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) is often diagnosed in females between the ages of 20 and 60.
- Abnormal cell growth within arterial walls leads to narrowing, blockage, or aneurysm formation, disrupting normal blood flow through affected vessels.
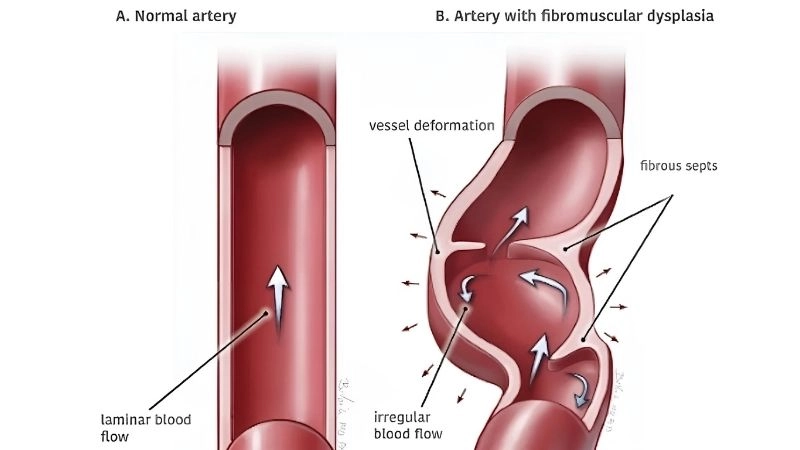
Fibromuscular dysplasia symptoms affecting arteries
>>> See more: Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) causes and care
Key symptoms of Fibromuscular Dysplasia to watch for
- High blood pressure is a frequent symptom when renal arteries are affected, making Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) a common cause of secondary hypertension.
- Headaches, dizziness, or ringing in the ears often occur when Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) impacts arteries in the brain or neck region.
- Stroke-like episodes, including vision changes or weakness, may develop if blood flow to the brain becomes severely restricted by Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD).
How can you prevent Fibromuscular Dysplasia effectively?
- Regular check-ups and early screening help detect vascular irregularities, allowing timely intervention and reducing the risks of Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) complications.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including balanced nutrition and regular exercise, supports vascular health and lowers overall risks linked to Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD).
- Avoiding smoking and controlling blood pressure with medical guidance can significantly decrease the progression and severity of Fibromuscular Dysplasia.

FMD treatment options for better patient outcomes
>>> See more: Pulmonary hypertension risk factors and management
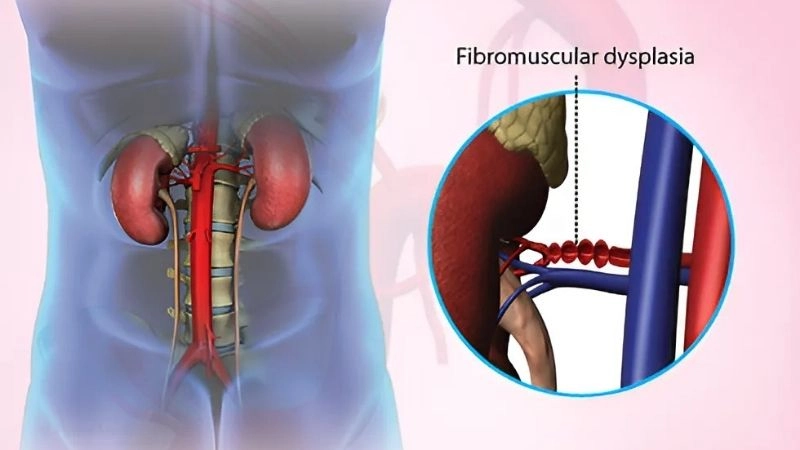
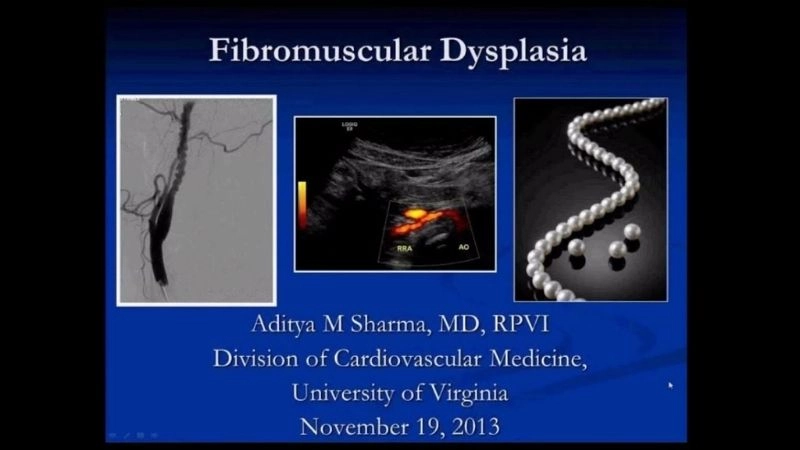
Images visual examples of Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Visual examples of Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) typically highlight twisted arteries or a “string of beads” appearance in imaging scans.
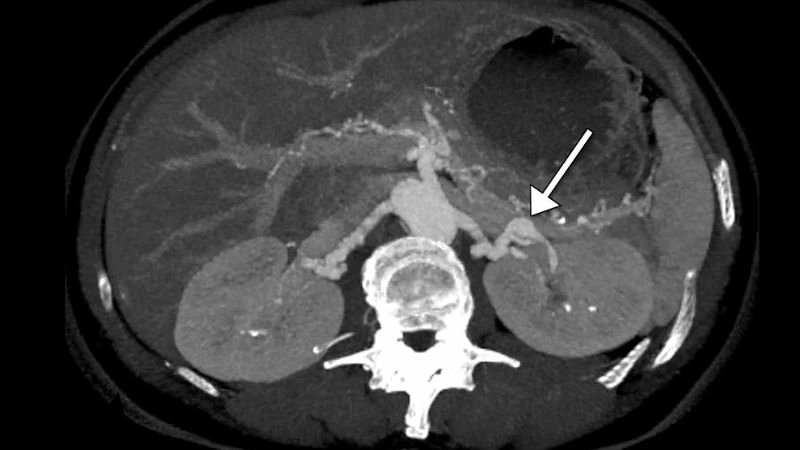
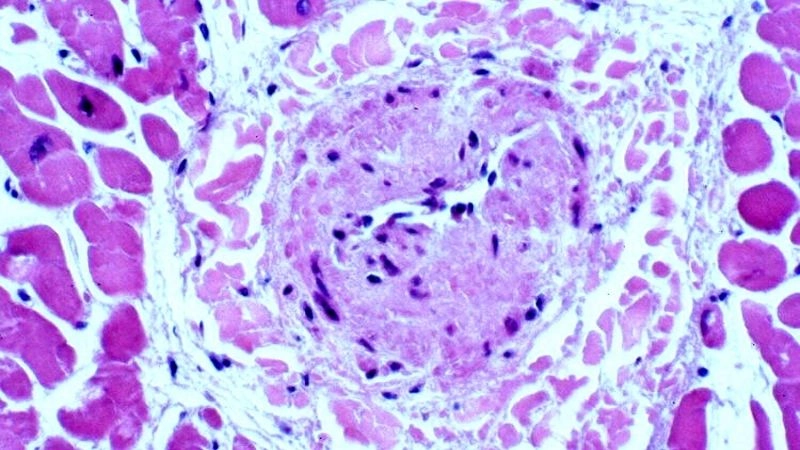

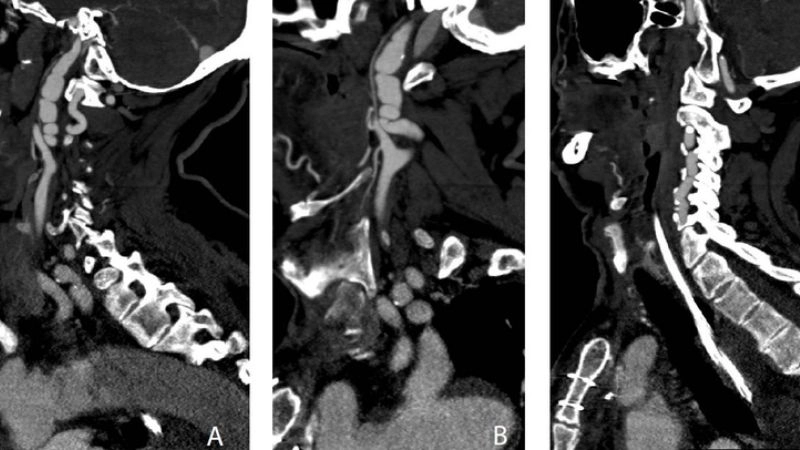
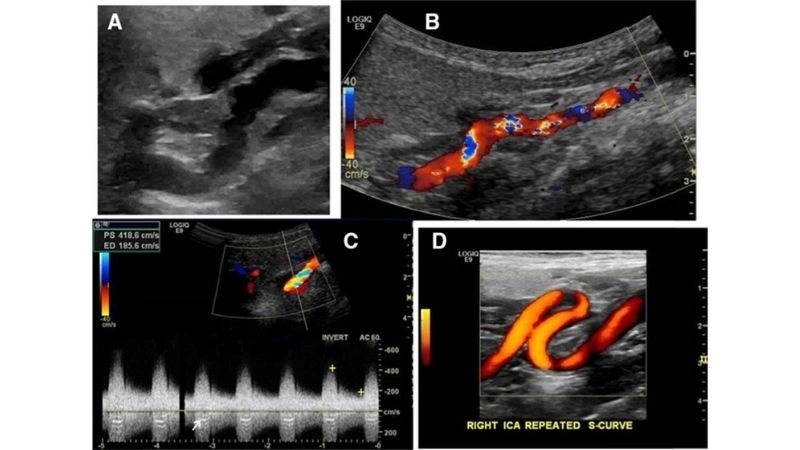


>>> See more: Kawasaki disease causes symptoms and complications
Understanding Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) helps patients recognize symptoms early, seek treatment, and improve long-term vascular health outcomes.