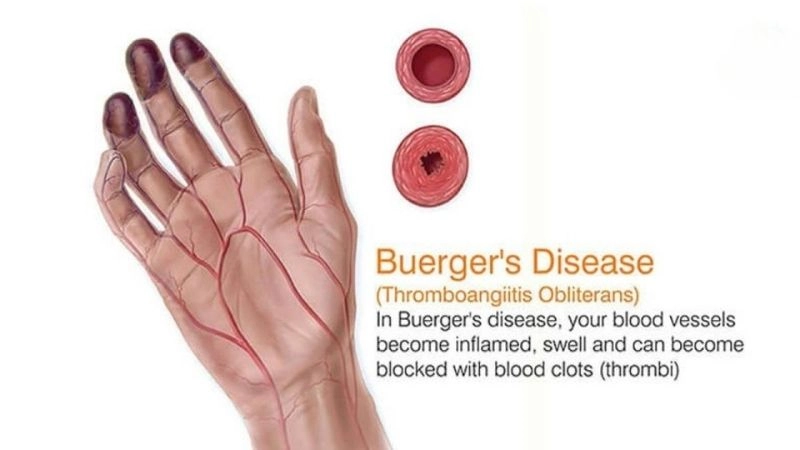
Thromboangiitis Obliterans (Buerger's Disease) affects small and medium blood vessels, leading to severe pain, ulcers, and circulation problems in limbs.
What are the main causes of thromboangiitis obliterans?
- Chronic tobacco use is the strongest risk factor, directly damaging blood vessels and triggering inflammation in arteries and veins.
- Genetic predisposition increases vulnerability, making certain individuals more likely to develop the disease when exposed to environmental triggers.
- Immune system dysfunction contributes to vessel inflammation, narrowing blood flow and accelerating tissue damage in the extremities.
Thromboangiitis obliterans treatment options explained
>>> See more: Understanding about aortic aneurysm thoracic abdominal
Key symptoms of thromboangiitis obliterans to watch for
- Persistent pain in hands or feet, often worsening during rest, signaling compromised blood circulation and vessel obstruction.
- Non-healing sores or ulcers on fingers or toes, caused by reduced blood supply and poor tissue recovery.
- Numbness, tingling, or skin discoloration in extremities, reflecting nerve involvement and chronic circulation problems.
How can you prevent thromboangiitis obliterans effectively?
- Quit smoking immediately, as it is the most crucial step to halt disease progression and improve circulation.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle through balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and hydration to support vascular function.
- Protect extremities from cold, injury, and infection to reduce complications and improve overall limb health.
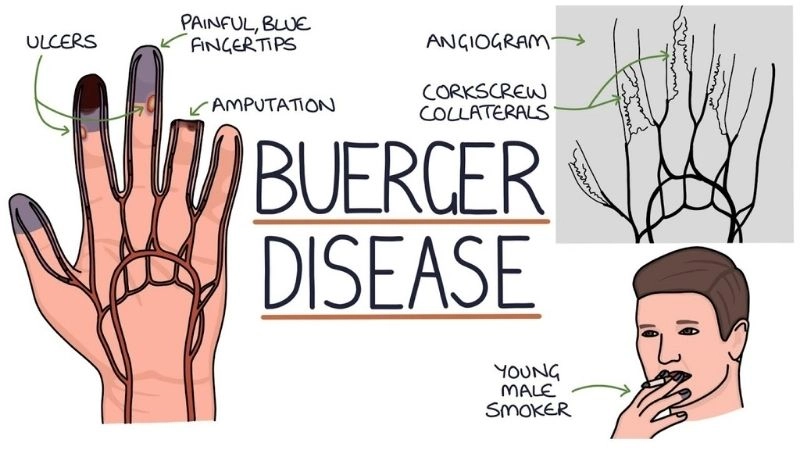
Accurate Buerger's disease diagnosis for early care
>>> See more: Aortic dissection causes symptoms and risk factors
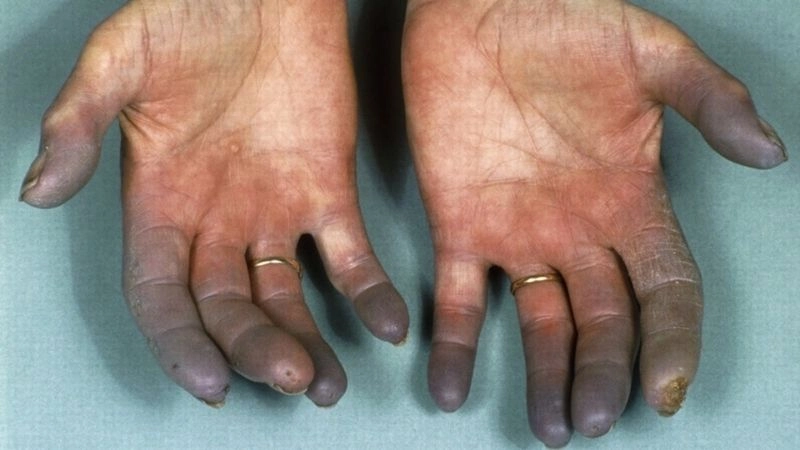
Images visual examples of thromboangiitis obliterans
Thromboangiitis Obliterans (Buerger's Disease) often presents with visible symptoms such as ulcers, skin discoloration, and tissue damage in the fingers and toes due to reduced blood flow.


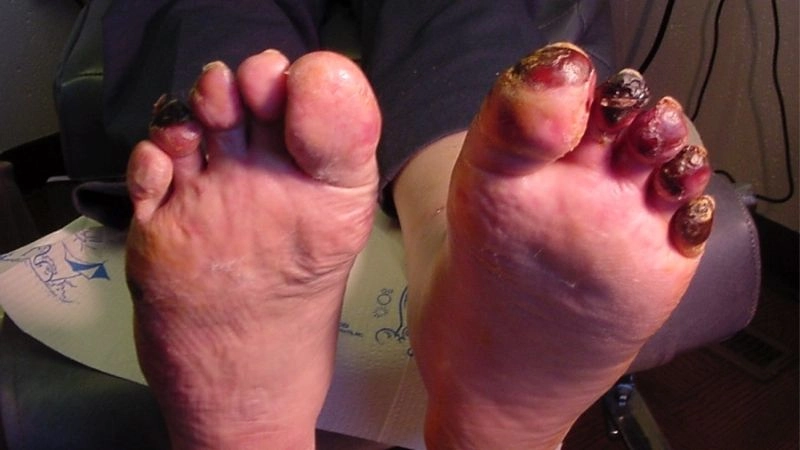

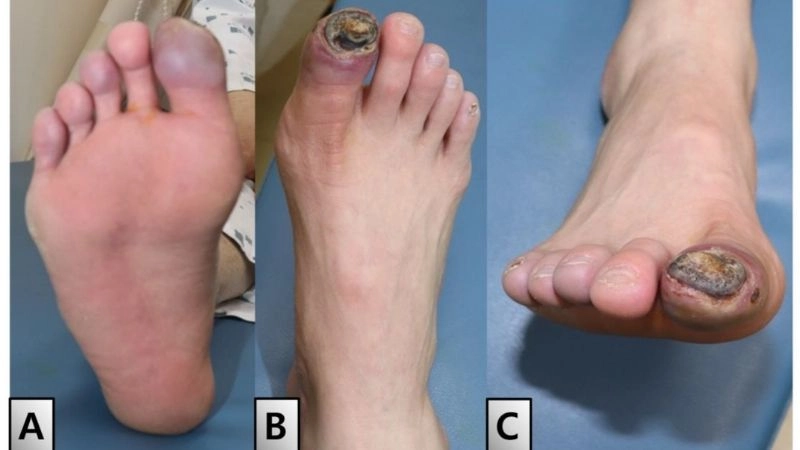

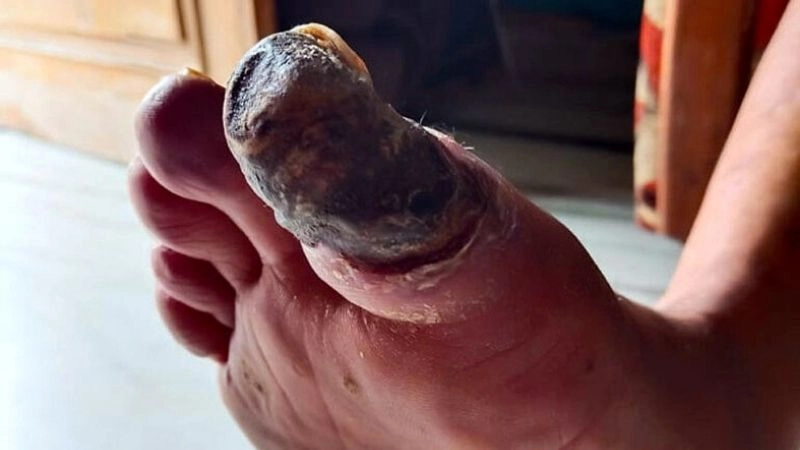
>>> See more: Subclavian Steal Syndrome what you need to understand
Thromboangiitis Obliterans (Buerger's Disease) requires early diagnosis and lifestyle changes to reduce pain, protect vessels, and improve quality of life.