A simple cut could lead to a life-threatening infection. Understanding what is tetanus and its prevention is not just good knowledge—it's a critical step in protecting yourself and your family from this dangerous bacterial disease. This guide covers the essential information.
What are the main causes of tetanus?
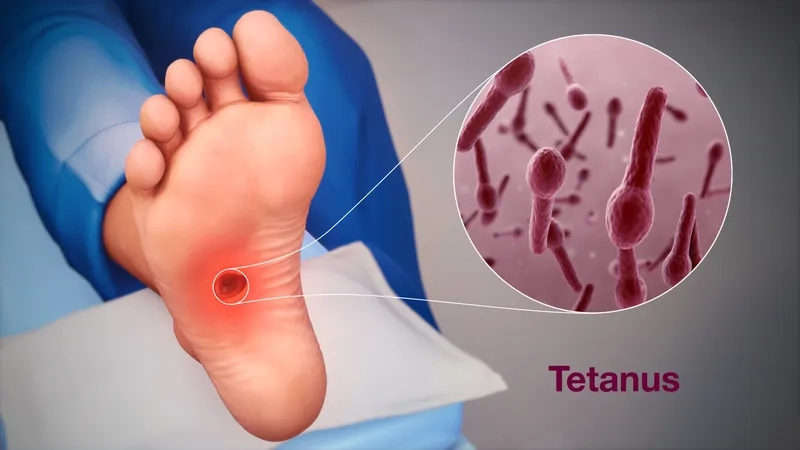
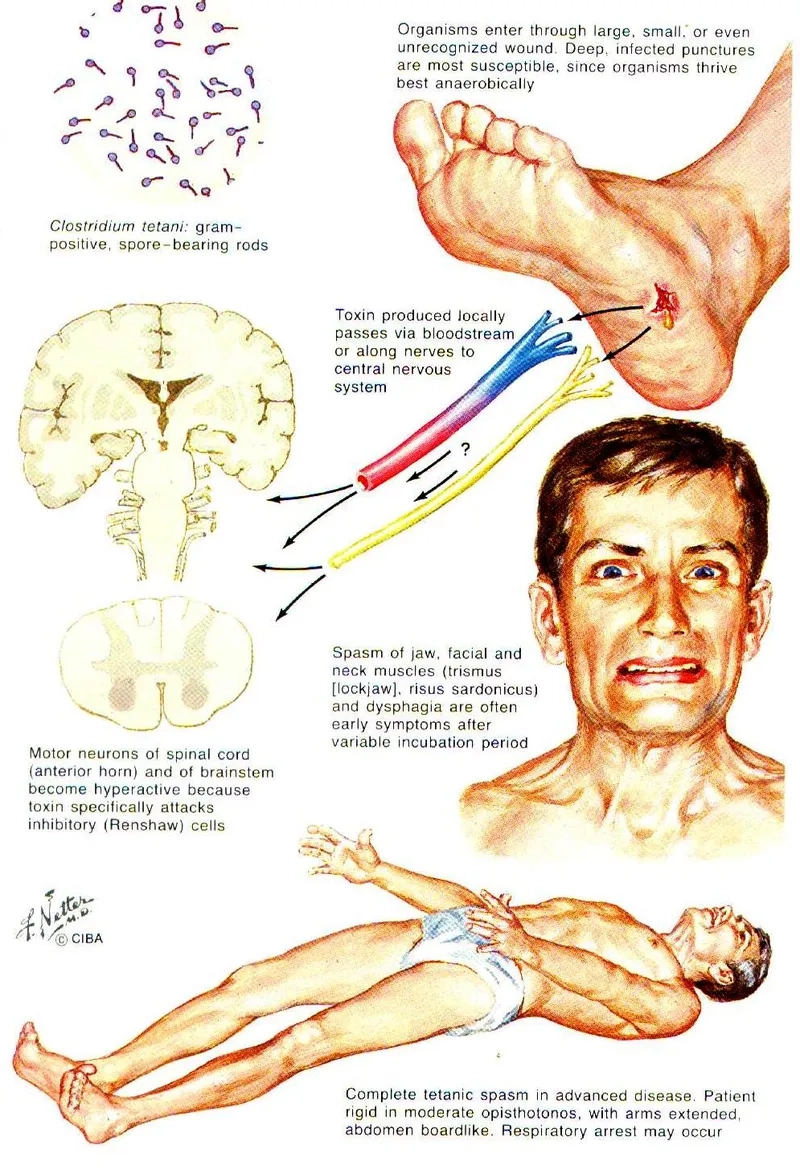
- The infection is caused by spores of the bacterium Clostridium tetani, which are commonly found in soil, dust, and animal manure worldwide.
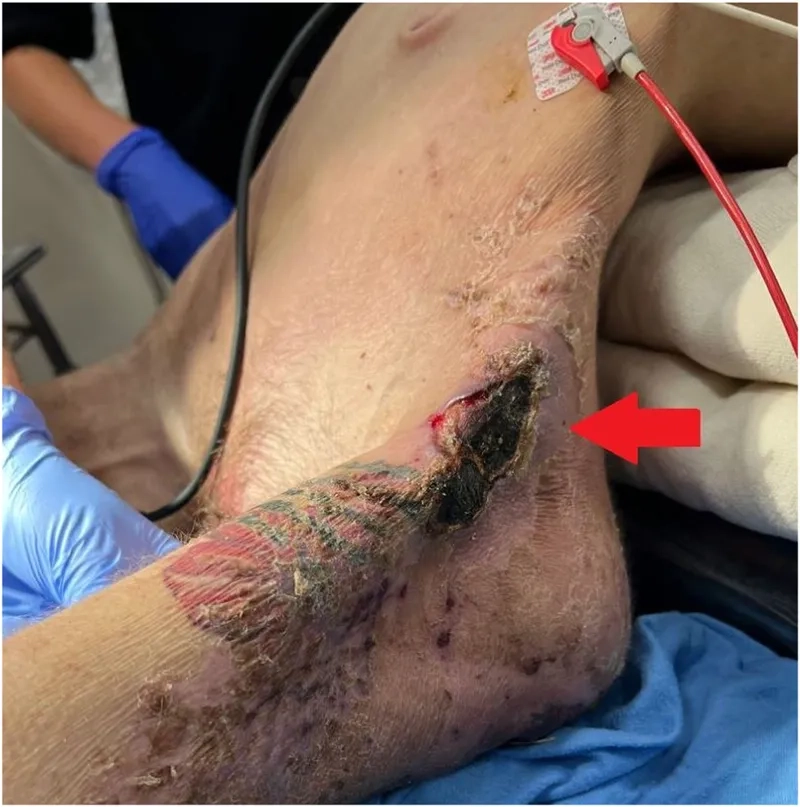
- These spores enter the body through breaks in the skin, often from puncture wounds, burns, or crush injuries, not just a rusty nail tetanus injury.
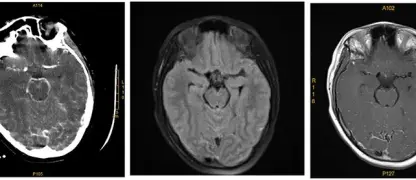
- Once inside, the spores develop into bacteria that produce a powerful toxin, which directly attacks the body’s central nervous system and causes symptoms.
Key symptoms of tetanus to watch for
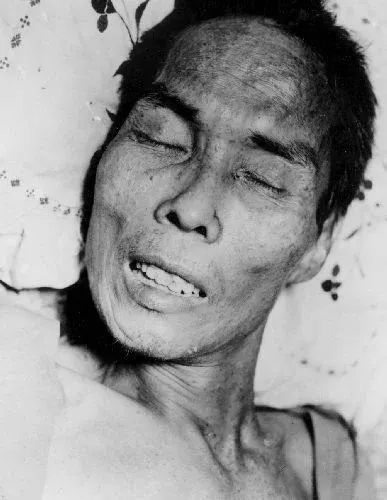
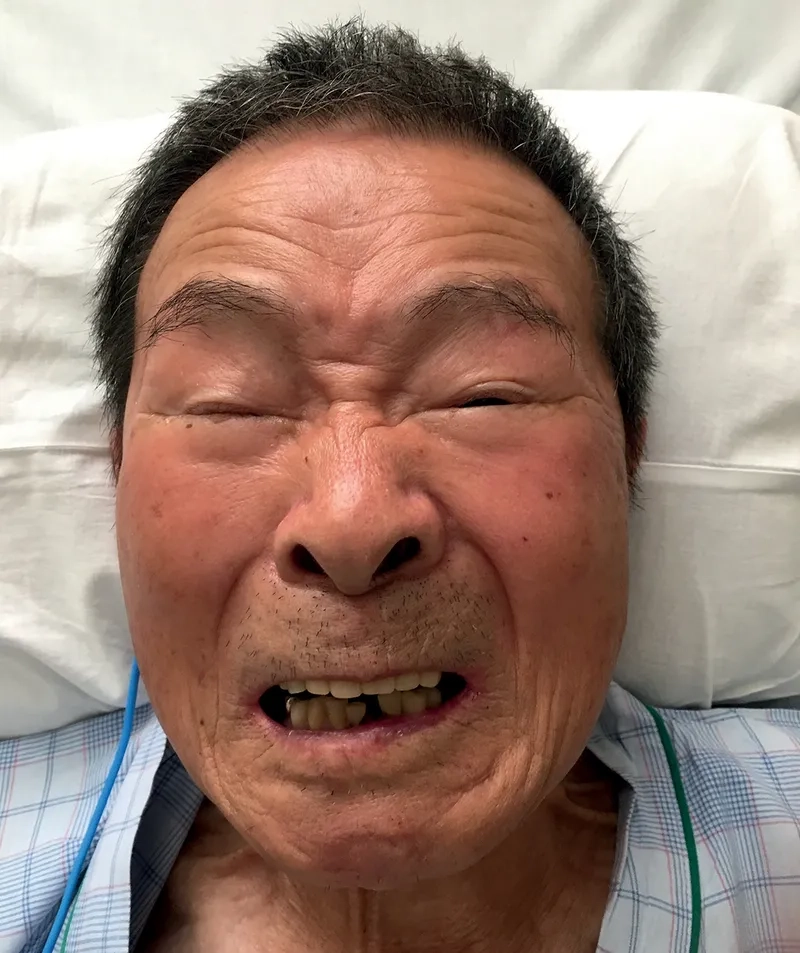
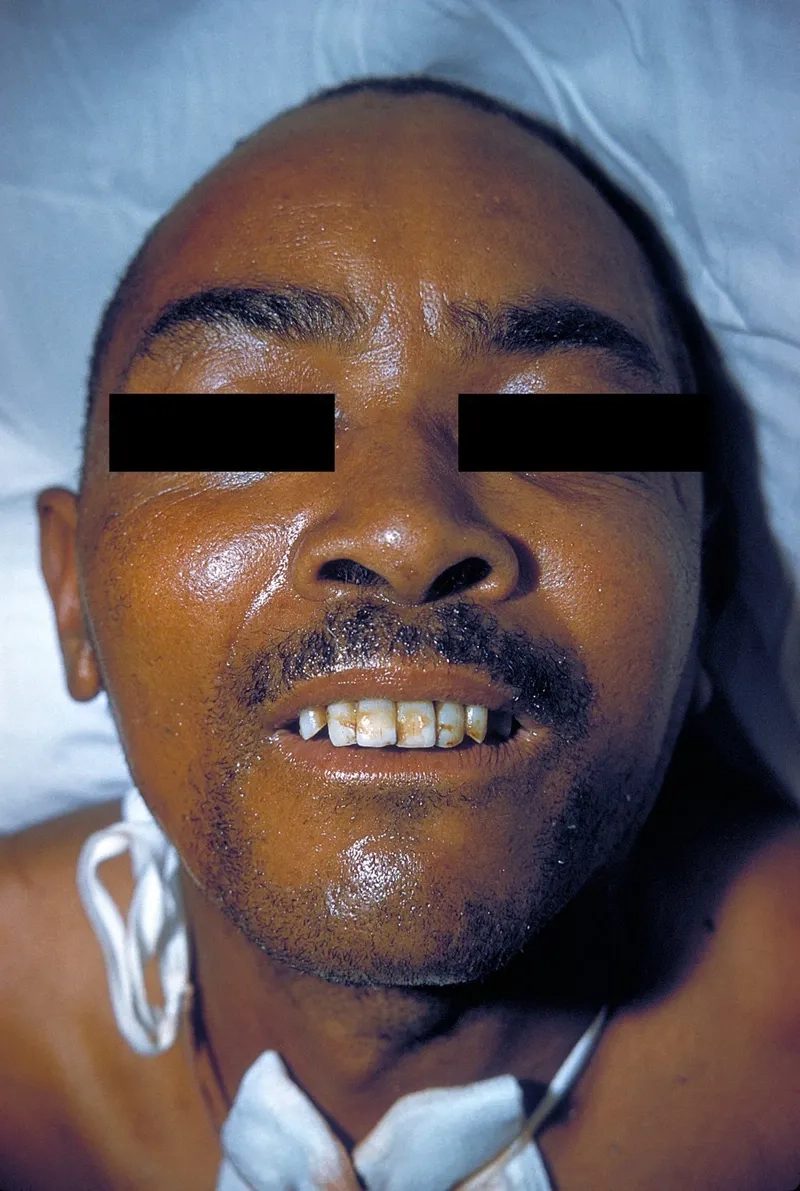
- The most common of tetanus symptoms is stiffness in the jaw muscles, famously known as lockjaw, which can make opening the mouth difficult.
- This is often followed by painful muscle spasms tetanus, stiffness in the neck and abdomen, difficulty swallowing, and sometimes fever.
- Severe cases can lead to spasms so intense they cause bone fractures and breathing problems, making immediate medical attention an absolute necessity.
How can you prevent tetanus effectively?
- The most effective tetanus prevention is immunisation with the tetanus vaccine (DTaP, Tdap), which protects against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis.
- To the question of how often do you need a tetanus shot, adults should receive a booster dose every 10 years to maintain immunity.
- Proper and immediate puncture wound care is also crucial; thoroughly clean any cut or wound to help prevent bacterial spores from growing.
>>> Don't miss: Mycoplasma pneumoniae - The cause of walking pneumonia
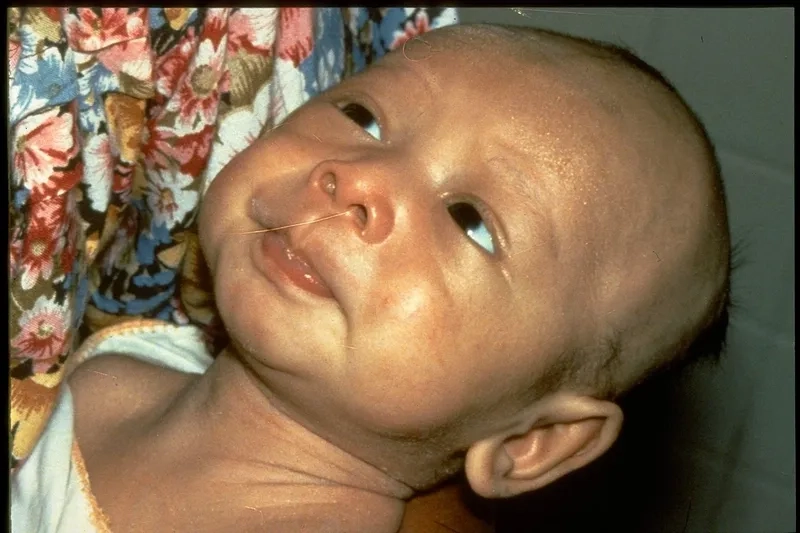
Illustrated Images of the Tetanus
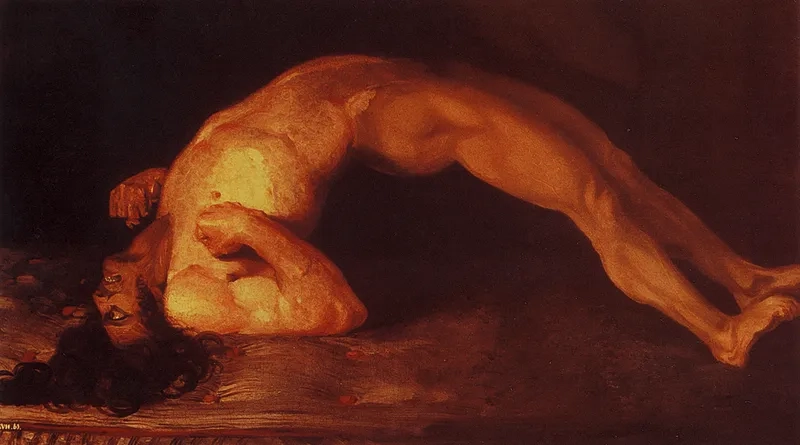
>>> Discover more: Primary amebic meningoencephalitis - The brain-eating amoeba
Is tetanus contagious? No, but it can be deadly. Immediate treatment for tetanus, which may include tetanus immunoglobulin, is vital. Always consult a doctor after a deep wound to ensure your tetanus shot is current.
>>> See details: Scabies - How to treat this intensely itchy skin condition