While incredibly rare, this devastating brain infection is nearly always fatal. Understanding the risks of Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis before you enter warm freshwater is critical for protecting yourself and your family. Awareness is your most powerful tool.
What are the main causes of Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis?
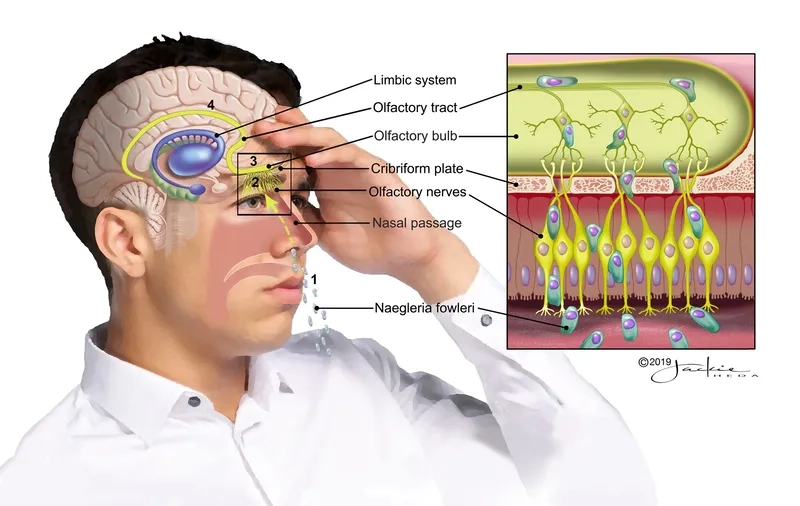
- The sole cause is the brain-eating amoeba, Naegleria fowleri, a single-celled organism that thrives in bodies of warm freshwater amoeba like lakes and rivers.
- How do you get Naegleria fowleri? The amoeba enters the body when contaminated water is forcefully pushed up the nose during swimming or diving.
- A significant neti pot amoeba risk exists if you use untreated tap water for nasal rinsing, allowing the amoeba direct access to the brain.
Key symptoms of Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis to watch for
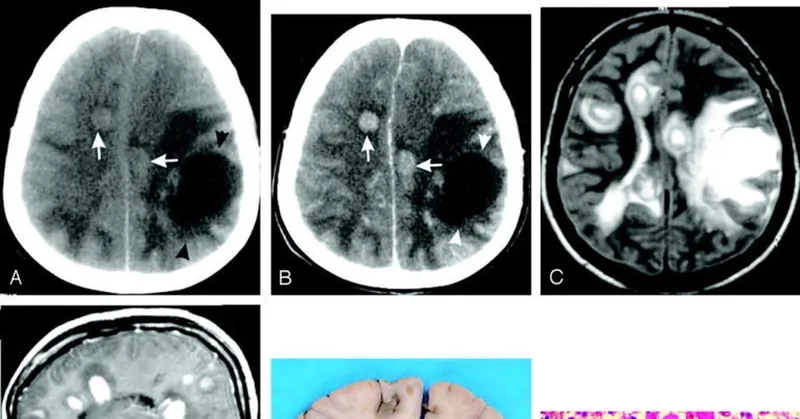
- Initial symptoms of brain-eating amoeba mimic meningitis, including severe headache, fever, nausea, and vomiting, starting one to twelve days after exposure.
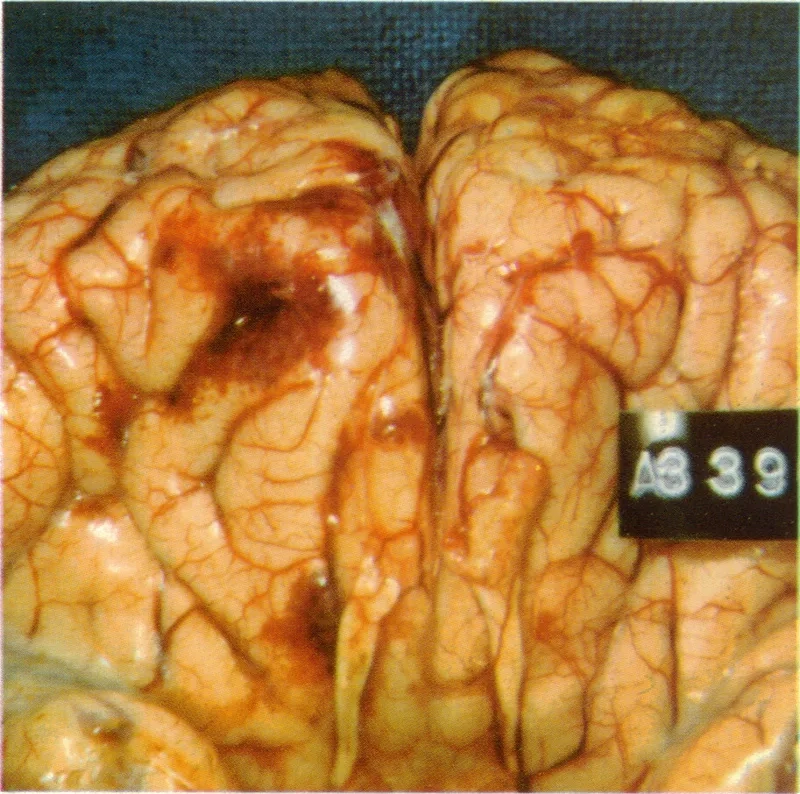
- The disease progresses rapidly to include a stiff neck, confusion, loss of balance, seizures, and hallucinations as the amoeba destroys brain tissue.
- It is important to know is Naegleria fowleri contagious? No, the infection cannot be spread from one person to another.
How can you prevent Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis effectively?
- The most effective prevention of PAM is to avoid submerging your head or stirring up sediment while in warm, stagnant freshwater bodies.
- Always use nose clips when swimming in high-risk water or use only sterile, distilled, or previously boiled water for all nasal rinsing devices.
- A rapid diagnosis of PAM is critical for any chance of survival; PAM treatment may include the drug miltefosine, but the brain-eating amoeba survival rate is tragically low.
>>> Find out together: Hookworm infection - Causes, symptoms, and modern treatment
Image of the disease Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis


>>> Discover more: Helminthiasis - A guide to parasitic worm infections
Due to the rapid progression of this infection, immediate emergency medical attention is essential if symptoms appear after freshwater exposure. Awareness and prevention are the best defenses against this rare but tragic disease.
>>> See more: Head lice (pediculosis) - A complete guide to treatment





