Murray Valley Encephalitis is a rare but serious viral infection affecting the brain. Learn about its symptoms, causes, and steps to prevent infection effectively.
What are the main causes of Murray Valley Encephalitis?
- Murray Valley Encephalitis is primarily caused by infection with a mosquito-borne virus that spreads quickly in rural and wetland areas.
- Seasonal flooding increases mosquito populations, raising the risk of virus transmission to humans in affected regions.
- People with prolonged outdoor exposure in endemic areas are more likely to encounter infected mosquitoes carrying the virus.
Key symptoms of Murray Valley Encephalitis to watch for
- High fever, severe headache, and fatigue are early indicators that the virus has entered the body.
- Nausea, vomiting, and muscle stiffness often develop as the infection progresses, signaling potential neurological involvement.
- Confusion, seizures, and altered consciousness can occur in severe cases, highlighting the risk of encephalitis complications.
>>>Explore now: Understanding Barmah Forest Virus Disease symptoms today
How can you prevent Murray Valley Encephalitis effectively?
- Avoid mosquito bites by wearing long sleeves, pants, and using insect repellents when visiting endemic areas.
- Reduce exposure to mosquito habitats, including wetlands and stagnant water, especially during peak mosquito activity.
- Follow public health alerts and vaccination recommendations in areas prone to Murray Valley Encephalitis outbreaks.
>>>Explore now: Ross River Fever causes symptoms and prevention tips
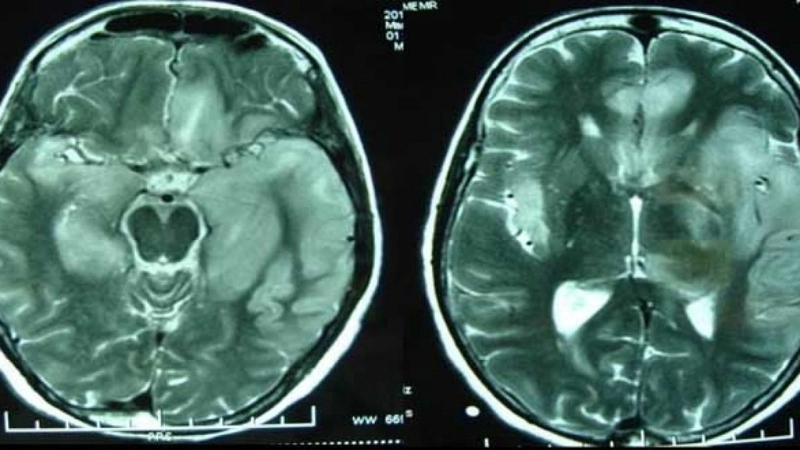
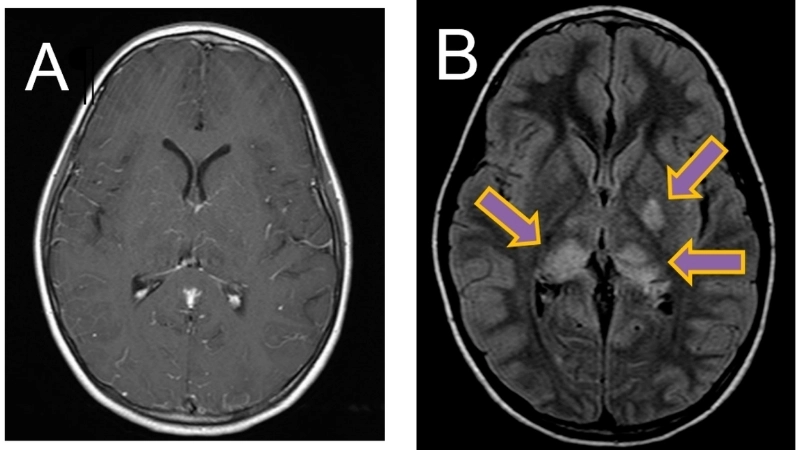
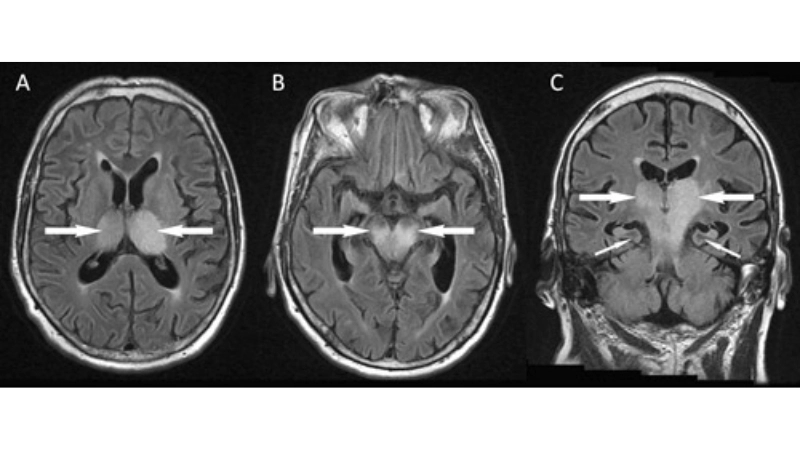
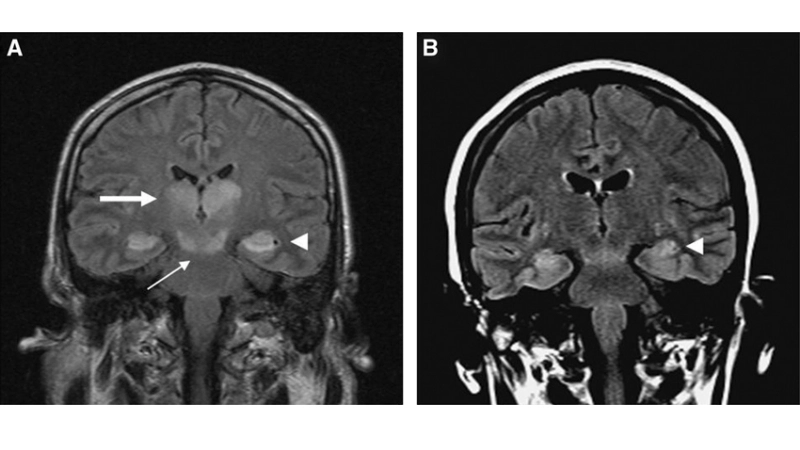
Image description of Murray Valley Encephalitis
Murray Valley Encephalitis is a rare but serious viral infection transmitted by mosquitoes, primarily affecting the brain and nervous system, with potential life-threatening complications.
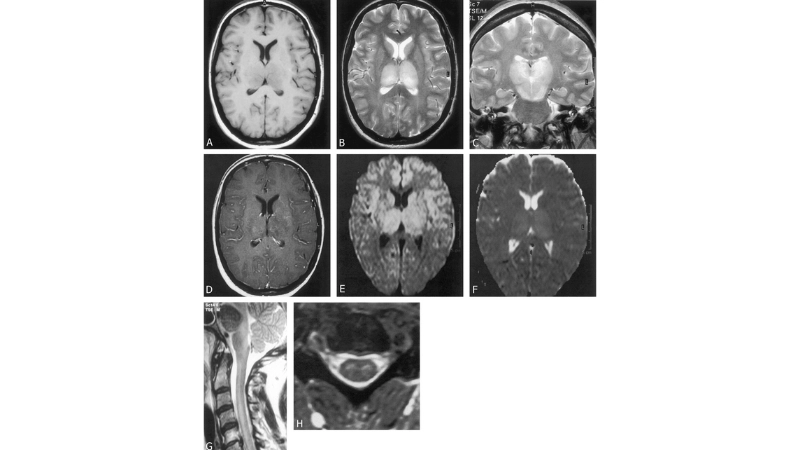
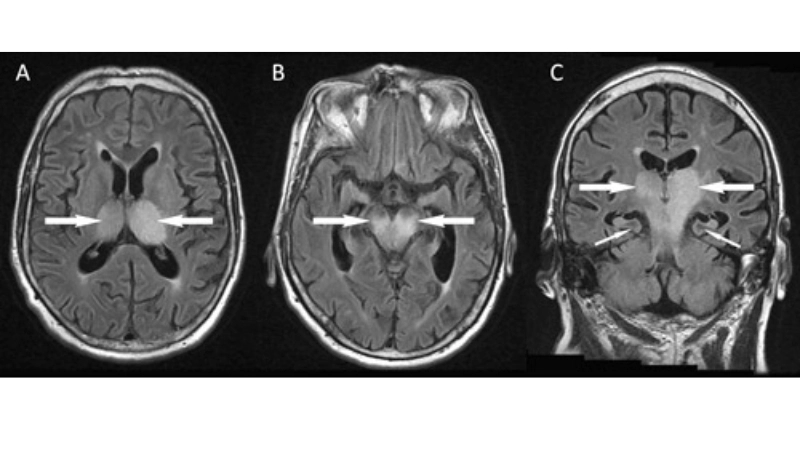
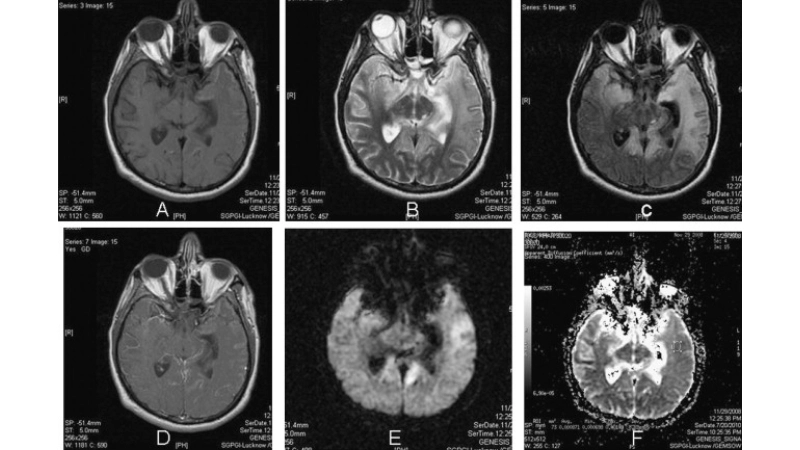
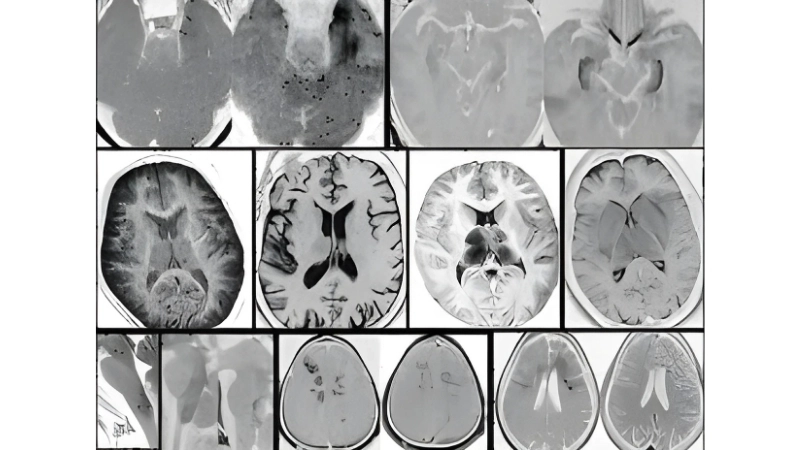
>>>Explore now: Understanding oropouche fever and how it spreads fast
Early detection and preventive measures are crucial for Murray Valley Encephalitis. Stay informed and seek medical attention immediately if symptoms appear.