Liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma) is a serious condition affecting millions. Early detection, understanding risk factors, and proper treatment are key to improving survival outcomes.
What are the main causes of Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular carcinoma)?
- Chronic hepatitis B or C infection significantly increases the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma over time.
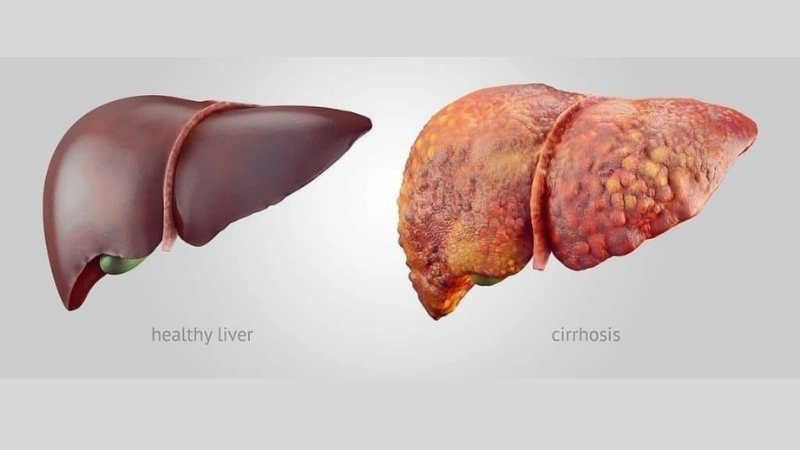
- Long-term alcohol abuse can lead to cirrhosis, which often progresses into liver cancer in high-risk patients.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and obesity contribute to liver inflammation, promoting conditions favorable for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Key symptoms of Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular carcinoma) to watch for
- Unexplained weight loss, loss of appetite, and fatigue may signal early stages of liver cancer.
- Persistent abdominal pain or swelling on the right side can indicate tumor growth in the liver.
- Jaundice, or yellowing of the skin and eyes, often develops in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma cases.
>>>Refer to this immediately: Cervical cancer symptoms every woman should never ignore
How can you prevent Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular carcinoma) effectively?
- Vaccination against hepatitis B and regular screening for hepatitis C reduces liver cancer risk dramatically.
- Limiting alcohol consumption and maintaining a healthy lifestyle lowers the chance of liver cirrhosis and subsequent cancer.
- Eating a balanced diet, managing weight, and controlling metabolic conditions like diabetes help protect liver health.
>>>Refer to this immediately: Understanding nasopharyngeal carcinoma causes and risks
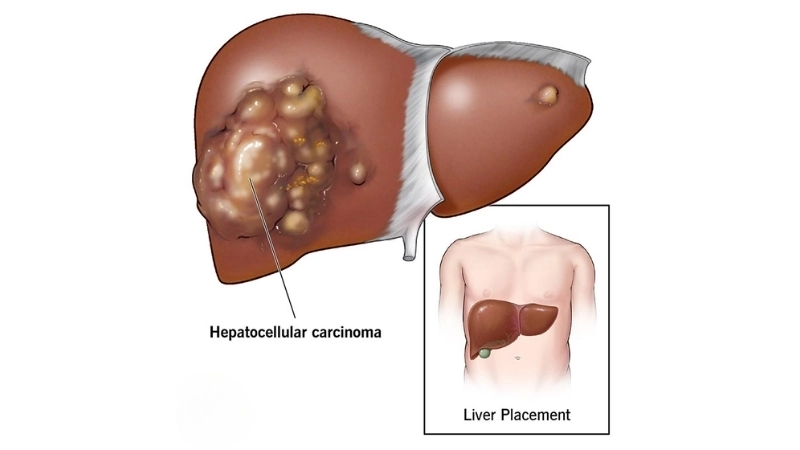
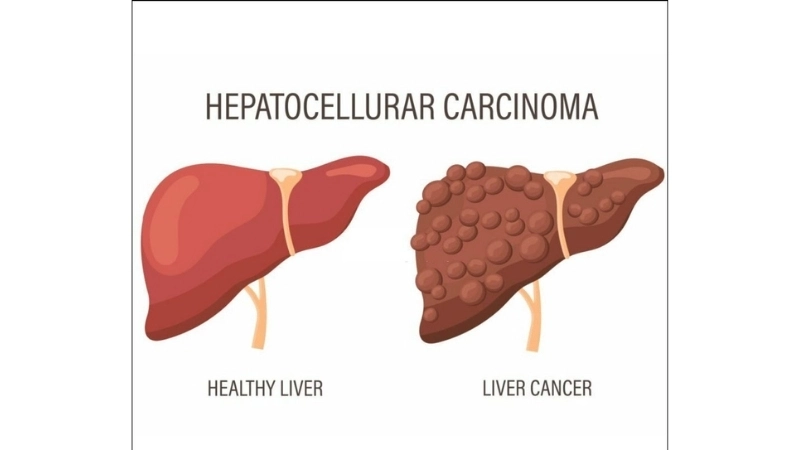
Image description of Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular carcinoma)
Liver cancer, or hepatocellular carcinoma, is a serious disease where malignant cells form in liver tissues. Early detection and lifestyle management improve prognosis and treatment outcomes.






>>>Refer to this immediately: Understanding burkitt's lymphoma symptoms and causes
Awareness of liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma) symptoms, preventive measures, and available treatments can help patients and families take proactive steps toward better health outcomes.