Kyasanur Forest Disease is a tick-borne viral infection that can cause severe fever and hemorrhagic symptoms. Awareness and preventive measures are key to staying safe.
What are the main causes of Kyasanur Forest Disease?
- Kyasanur Forest Disease is primarily caused by a virus transmitted through tick bites found in forested regions of India.
- Contact with infected animals, especially monkeys, can also spread the Kyasanur Forest Disease virus to humans.
- Handling contaminated blood or tissues from infected animals increases the risk of contracting this disease.
Key symptoms of Kyasanur Forest Disease to watch for
- Sudden high fever accompanied by severe headache and muscle pain are common early signs of Kyasanur Forest Disease.
- Nausea, vomiting, and fatigue often develop as the virus affects multiple organ systems in the body.
- In severe cases, patients may experience bleeding, neurological symptoms, and complications requiring immediate medical attention.

>>>Explore now: Understanding omsk hemorrhagic fever symptoms and risks
How can you prevent Kyasanur Forest Disease effectively?
- Avoid entering tick-infested forest areas and use protective clothing when exposure is unavoidable.
- Apply insect repellents containing DEET or permethrin on skin and clothing to reduce tick bites.
- Vaccination is available in endemic regions and can significantly lower the risk of contracting Kyasanur Forest Disease.
>>>Explore now: Understanding hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome HFRS
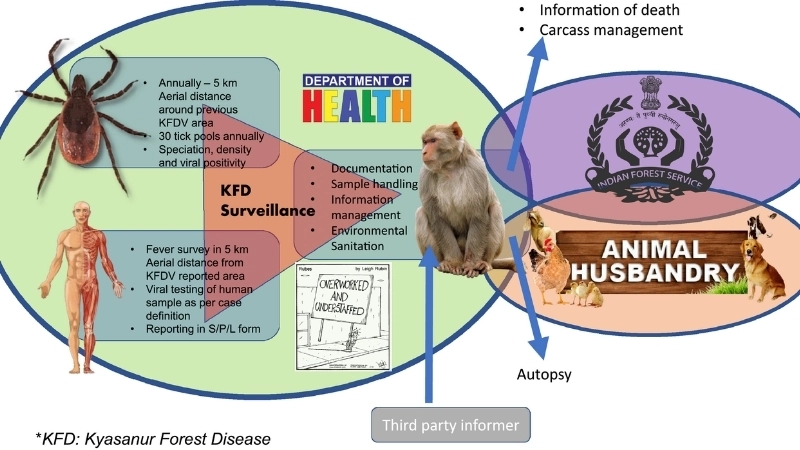
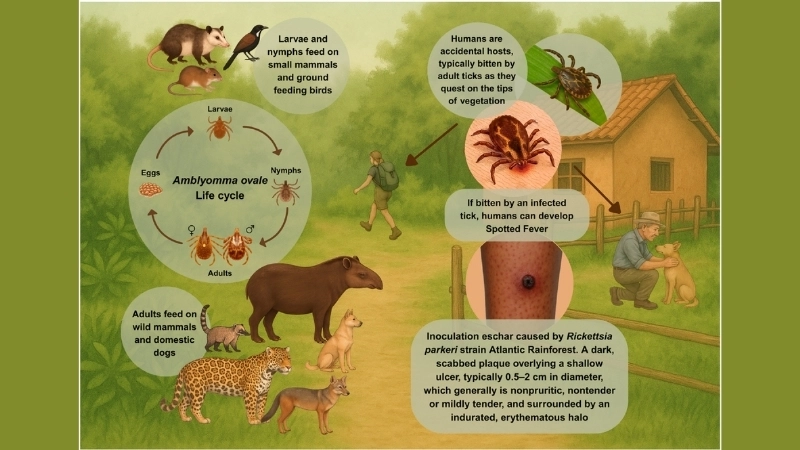
Image description of Kyasanur Forest Disease
Kyasanur Forest Disease is a viral illness transmitted mainly by ticks. It affects humans and monkeys in forested areas, causing fever, body aches, and in severe cases, bleeding and neurological complications.






>>>Explore now: Understanding rift valley fever symptoms and prevention
By understanding Kyasanur Forest Disease and following expert prevention tips, individuals can reduce their risk and respond promptly to symptoms for better health outcomes.