Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection / AIDS affects millions worldwide. Learn its causes, early symptoms, and essential prevention tips to stay informed and protected.
What are the main causes of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection / AIDS?
- HIV spreads primarily through unprotected sexual contact, allowing the virus to enter the bloodstream and attack the immune system rapidly.
- Sharing contaminated needles or syringes significantly increases the risk of contracting HIV among users of injectable substances.
- Transmission from mother to child can occur during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding if the mother is HIV positive.
Key symptoms of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection / AIDS to watch for
- Persistent fever, night sweats, and unexplained weight loss are common early indicators of HIV infection.
- Swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, and prolonged diarrhea may signal the weakening of the immune system due to HIV.
- Opportunistic infections such as pneumonia or tuberculosis often emerge as the immune system becomes severely compromised.
>>>Refer to this immediately: Key facts about Brazilian Hemorrhagic Fever you should know
How can you prevent Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection / AIDS effectively?
- Consistently using condoms during sexual activity dramatically reduces the risk of HIV transmission.
- Avoid sharing needles, syringes, or any instruments that may be contaminated with bloodborne viruses.
- Pregnant women with HIV should seek medical treatment to lower the chance of transmitting the virus to their child.
>>>Refer to this immediately: Understanding venezuelan hemorrhagic fever and risks
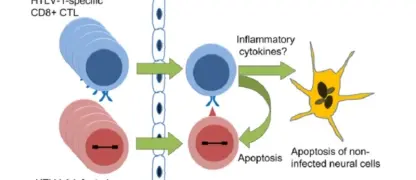
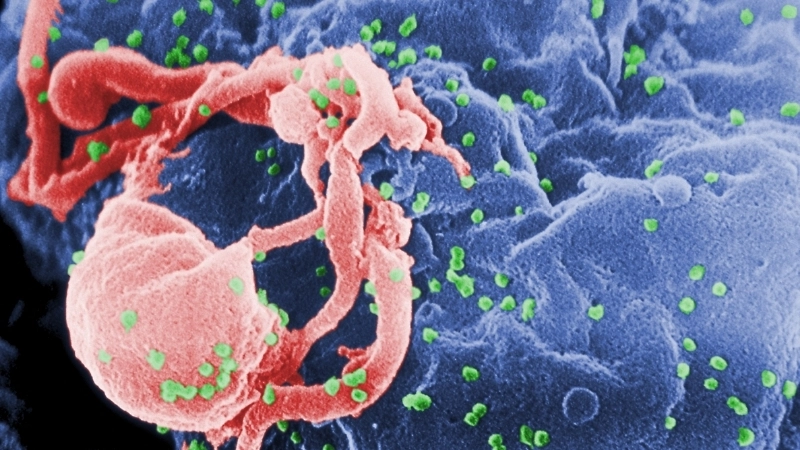
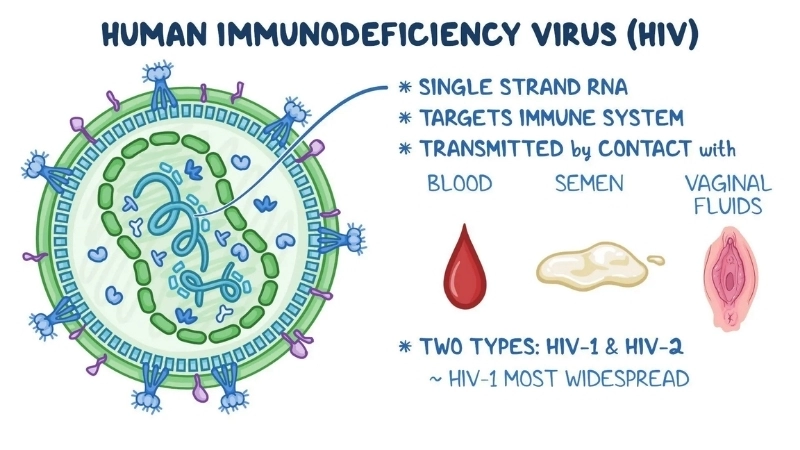
Image description of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection / AIDS
A microscopic view of the HIV virus attacking immune cells, illustrating how it weakens the body’s defense system and leads to AIDS.


>>>Refer to this immediately: Symptoms and warning signs of Bolivian Hemorrhagic Fever
Awareness and timely care are crucial in managing Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection / AIDS. Stay informed, follow medical guidance, and reduce risks effectively.