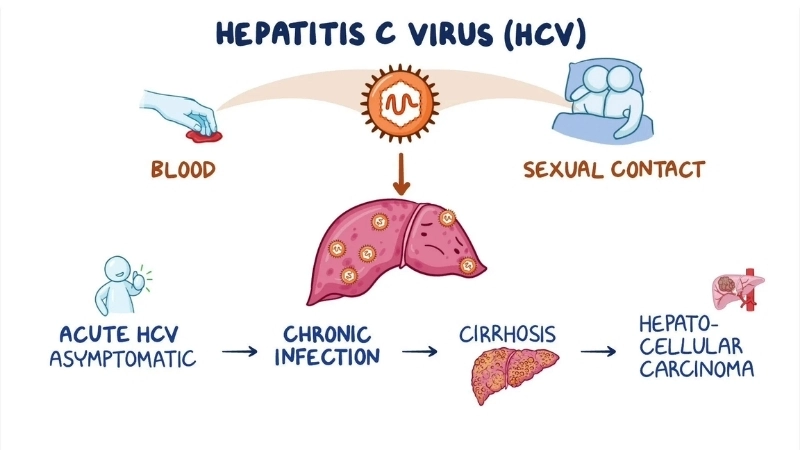
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that affects the liver, causing inflammation and potential long-term damage. Early detection and proper care are vital for better outcomes.
What are the main causes of Hepatitis C?
- Hepatitis C is primarily caused by exposure to infected blood through contaminated needles, medical equipment, or transfusions.
- Sharing personal items like razors, toothbrushes, or nail clippers with an infected person can transmit the virus.
- Unprotected sexual contact with someone infected or from mother to child during birth increases the risk of infection.
Key symptoms of Hepatitis C to watch for
- Persistent fatigue, weakness, or lack of energy may indicate a chronic Hepatitis C infection affecting liver function.
- Jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes, is a common sign of liver damage due to Hepatitis C.
- Abdominal pain, swelling, or discomfort in the upper right side may signal inflammation or liver enlargement.
>>>Refer to more: Understanding Hepatitis B symptoms and early warning signs
How can you prevent Hepatitis C effectively?
- Avoid sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment to reduce the risk of contracting Hepatitis C.
- Ensure all blood products and medical procedures are safe and screened to prevent accidental infection.
- Practice safe sex and avoid sharing personal hygiene items to minimize the chances of virus transmission.
>>>Refer to more: Understanding Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / AIDS
Image description of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that attacks the liver, often leading to inflammation, liver scarring, or cirrhosis. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of complications.





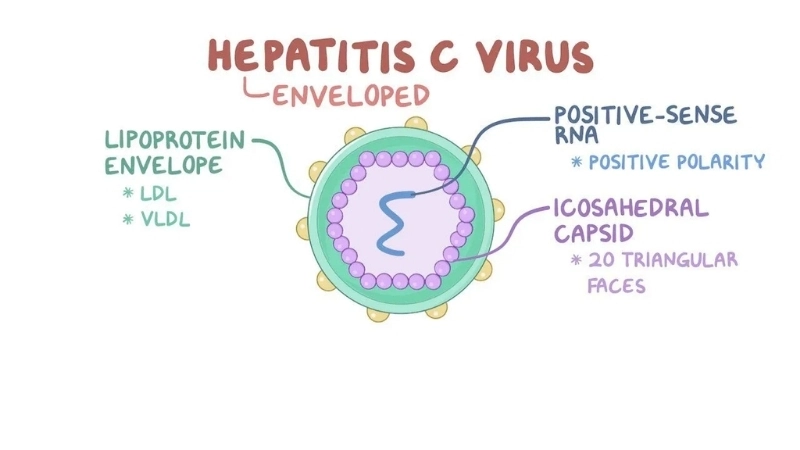


>>>Refer to more: Key facts about Brazilian Hemorrhagic Fever you should know
By understanding Hepatitis C symptoms, treatments, and prevention methods, individuals can take control of their health and reduce risks of severe liver complications.