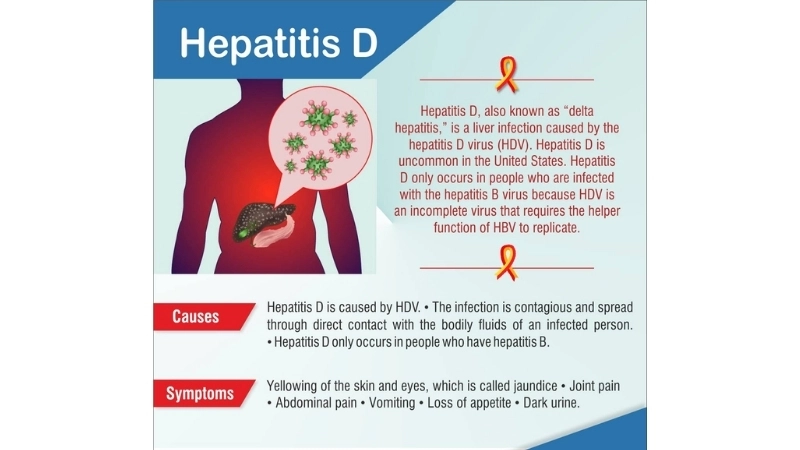
Hepatitis D is a rare but serious liver infection. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for early detection and effective management.
What are the main causes of Hepatitis D?
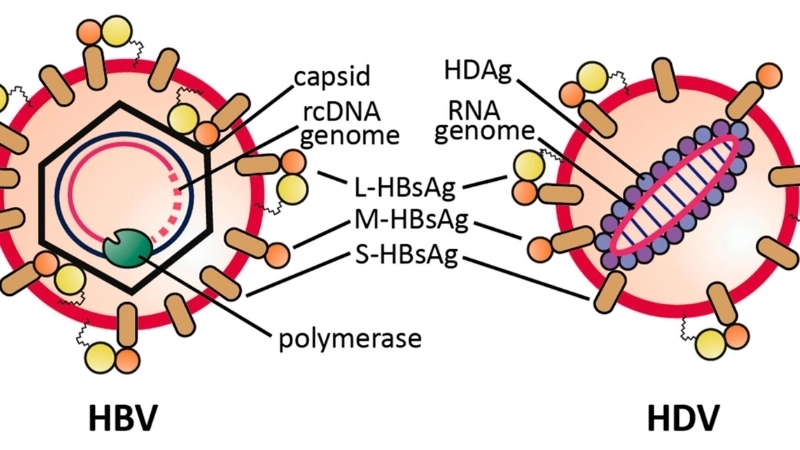
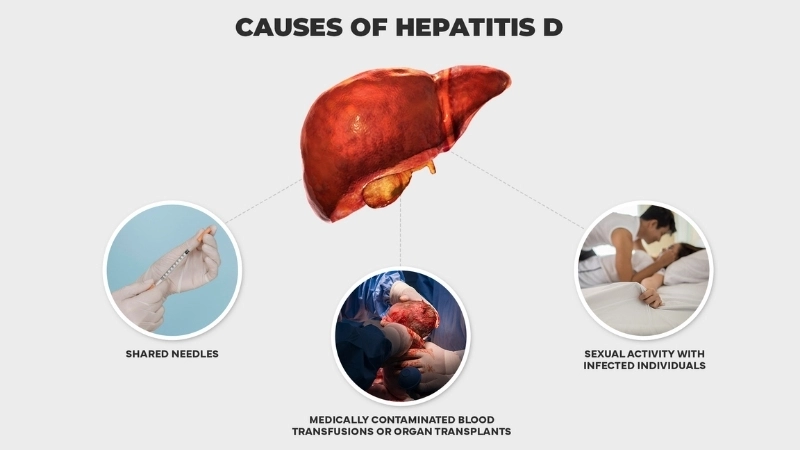
- Hepatitis D occurs when a person is already infected with hepatitis B, as the virus requires hepatitis B to replicate efficiently.
- Exposure to contaminated blood or body fluids, such as through shared needles, increases the risk of contracting hepatitis D.
- Unprotected sexual contact with an infected person can also transmit hepatitis D, especially if hepatitis B infection is present.
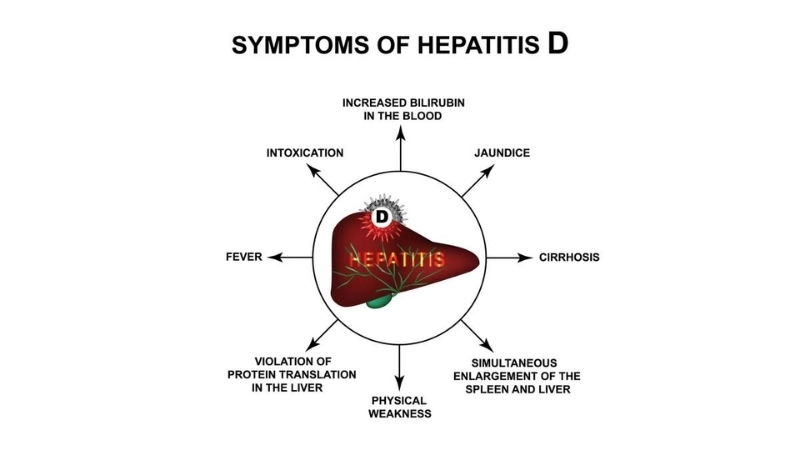
Key symptoms of Hepatitis D to watch for
- Fatigue and weakness are common early signs of hepatitis D, often accompanied by nausea and loss of appetite.
- Jaundice, or yellowing of the skin and eyes, can indicate liver inflammation caused by hepatitis D infection.
- Abdominal pain, particularly in the upper right side, may occur due to liver swelling and inflammation from the virus.
>>>Refer to more: Understanding Hepatitis C symptoms causes and risks
How can you prevent Hepatitis D effectively?
- Vaccination against hepatitis B is the most effective way to prevent hepatitis D infection, as the virus cannot exist without hepatitis B.
- Avoid sharing needles or personal items like razors or toothbrushes to reduce the risk of bloodborne transmission of hepatitis D.
- Practice safe sexual behaviors, including using condoms, especially if you or your partner have a history of hepatitis B.
>>>Refer to more: Understanding Hepatitis B symptoms and early warning signs
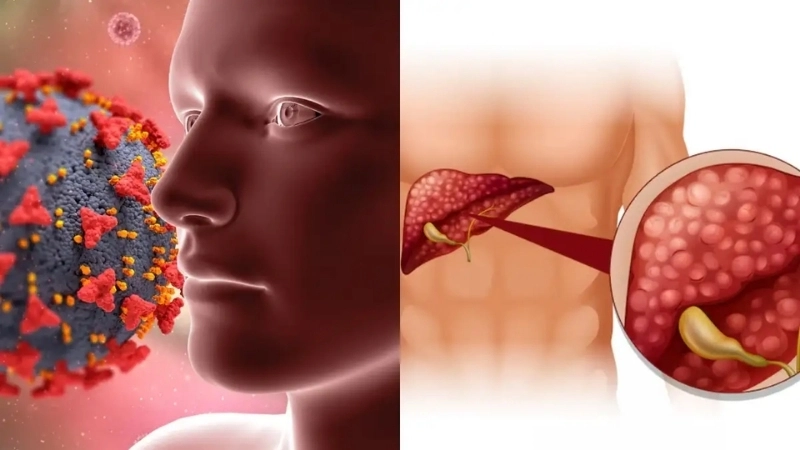
Image description of Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis D virus, which can only infect individuals who already have hepatitis B. It can lead to liver inflammation, fatigue, jaundice, and severe complications if untreated.



>>>Refer to more: Understanding Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / AIDS
Proper knowledge and medical care can help manage Hepatitis D effectively. Staying informed about symptoms, risks, and prevention is key to protecting liver health.