Don't ignore the subtle signs your heart is sending you. Understanding Coronary Artery Disease is the first, most crucial step toward protecting your long-term heart health and preventing serious complications.
What are the main causes of Coronary Artery Disease?
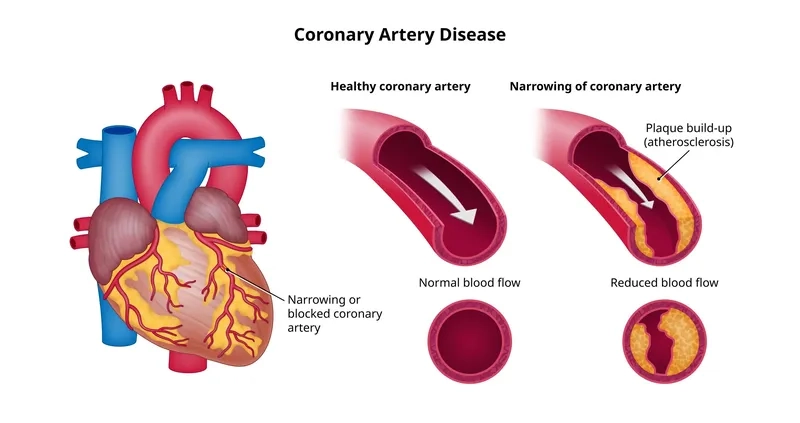
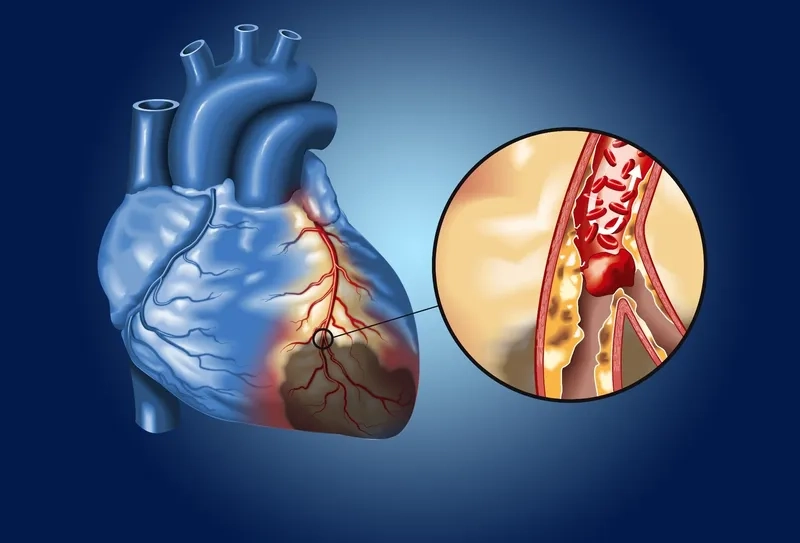
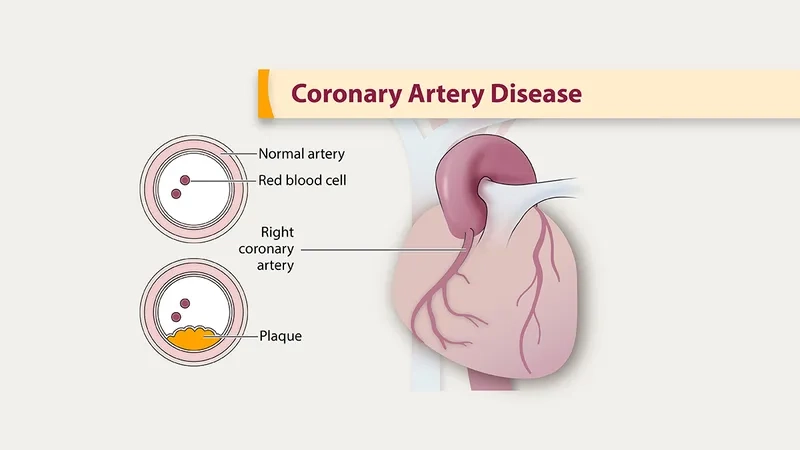
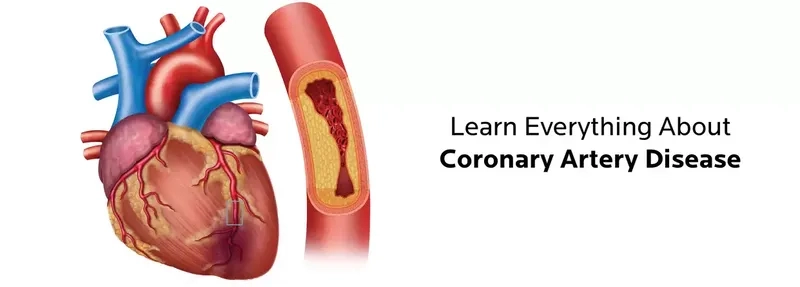
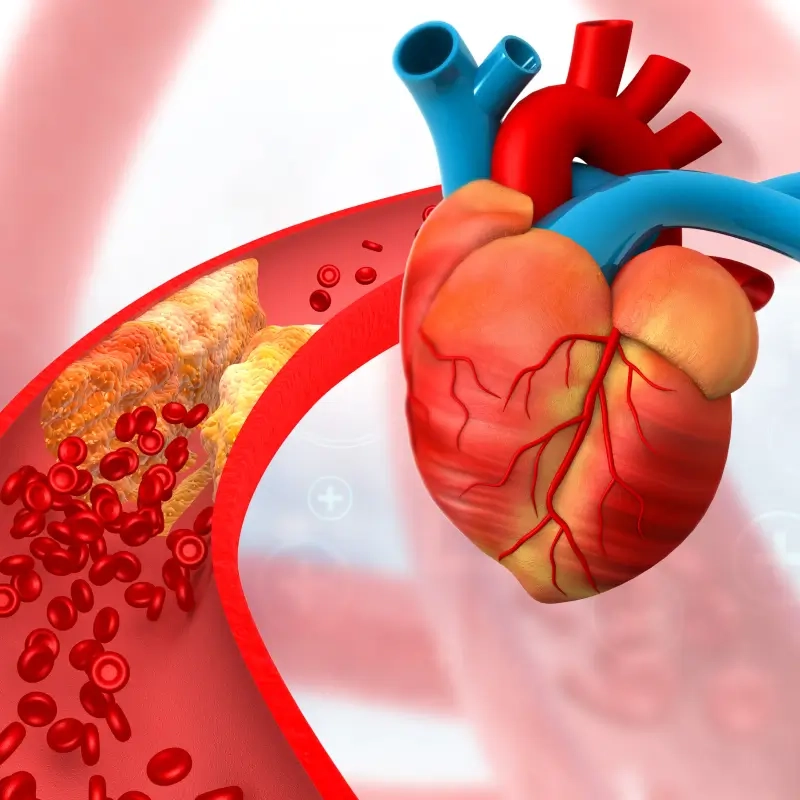
- What is coronary artery disease? It's a condition where plaque builds up in your heart's arteries, a process known as atherosclerosis.
- The primary causes of coronary artery disease include high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes, which all damage the inner artery walls.
- Major risk factors for CAD also include a family history of heart disease, obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and high levels of stress.
Key symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease to watch for
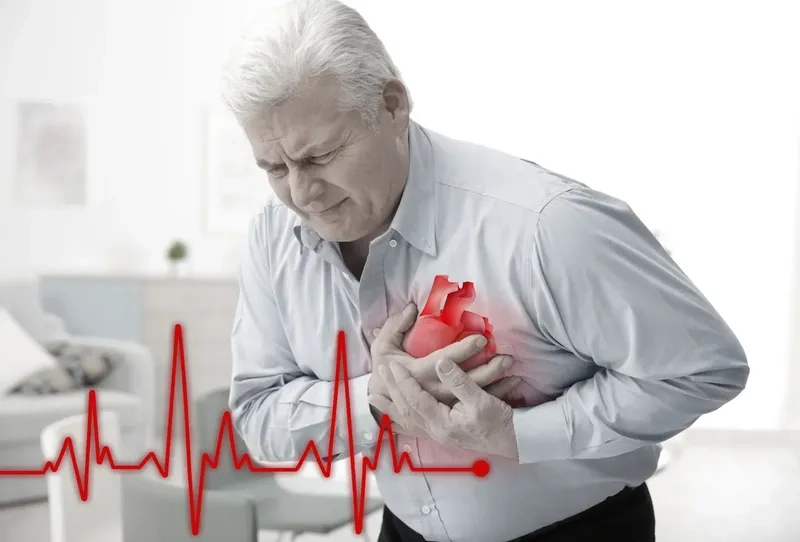
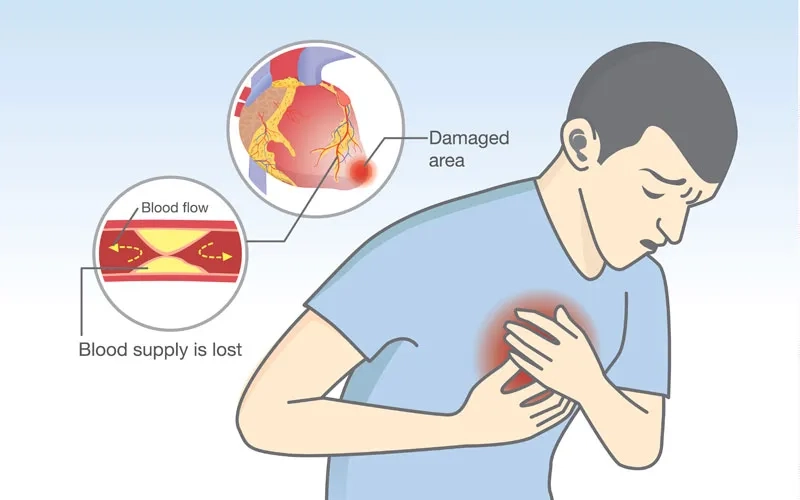
- The most common of all coronary artery disease symptoms is angina, which feels like chest pain, pressure, tightness, or a squeezing sensation.
- Other signs of blocked arteries can include shortness of breath, especially during physical exertion, and overwhelming fatigue with minimal daily activity.
- A heart attack is the most severe symptom, presenting as crushing chest pain that may spread to the shoulder, arm, back, or jaw.
How can you prevent Coronary Artery Disease effectively?
- Effective coronary artery disease prevention involves adopting a heart-healthy CAD diet that is low in saturated fat, salt, and added sugars.
- Modern CAD treatment includes medications to manage cholesterol and blood pressure, combined with lifestyle changes like regular exercise and smoking cessation.
- For severe blockages, a heart stent procedure (angioplasty) may be performed by a doctor to open the narrowed artery and restore blood flow.
>>> Discover more: Epidermolysis bullosa – symptoms, diagnosis and care
Image of the disease Coronary Artery Disease

>>> Learn now: Mast cell activation syndrome – symptoms and treatment
Proactive management is key to living well with this condition. If you have risk factors or are experiencing symptoms, speak with your doctor about a heart health screening.
>>> Details at: Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome – signs and care