Feeling dizzy when you stand up? It might be more than just a head rush. Understanding Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) is the first step toward getting a correct diagnosis, managing your symptoms, and reclaiming your daily life.
What are the main causes of Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome?
- The exact cause is often unknown, but it is a form of dysautonomia, meaning the autonomic nervous system that controls involuntary functions does not work correctly.
- Common POTS syndrome triggers include major surgery, significant trauma, or a preceding viral illness that can disrupt the body's regulation of blood flow.
- The condition involves an abnormal response to gravity, leading to inadequate blood volume returning to the heart and brain when a person stands up.

Key symptoms of Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome to watch for
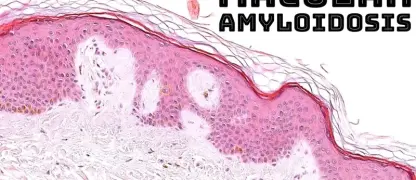
- The defining sign is a heart rate increase of 30+ beats per minute (40+ for teens) within 10 minutes of standing, without a drop in blood pressure.
- Common POTS symptoms include severe lightheadedness, brain fog, fatigue, palpitations, and fainting or near-fainting, especially after standing for a prolonged period.
- Many individuals also experience headaches, nausea, shakiness, and poor sleep, which can significantly interfere with daily functioning, work, and school.
How is Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome managed?
- A cornerstone of POTS treatment is increasing fluid and salt intake according to a specialized POTS diet to help expand blood volume.
- A formal POTS diagnosis is often confirmed with a tilt table test, which carefully measures how your heart rate and blood pressure respond to changes in position.
- Management strategies also include specific exercise protocols to improve conditioning and medications to help stabilize heart rate and blood pressure.
>>> Discover more: Pompe disease – symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Image of the disease Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome




>>> Learn now: Amyloidosis – causes, symptoms and care options
If you suspect you have POTS, don't try to manage it alone. Consulting a cardiologist or neurologist is essential for an accurate diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan. Proper medical guidance can make a significant difference in your quality of life.
>>> Learn now: Mast cell activation syndrome – symptoms and treatment