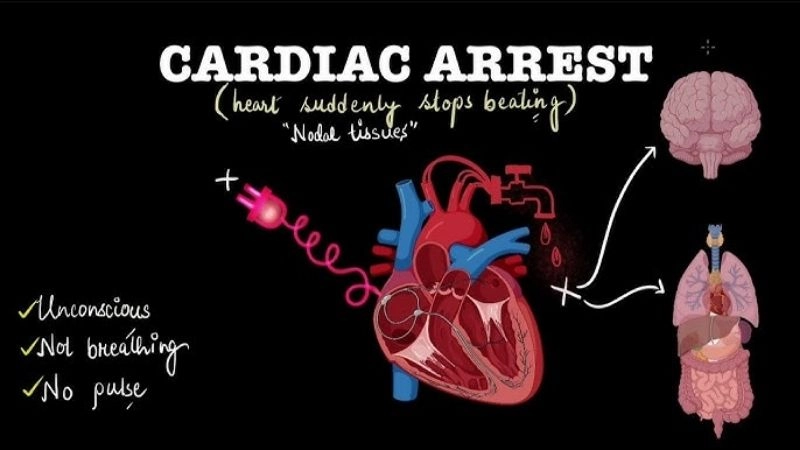
Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating, cutting off blood flow. It is a critical emergency that requires rapid diagnosis and treatment.
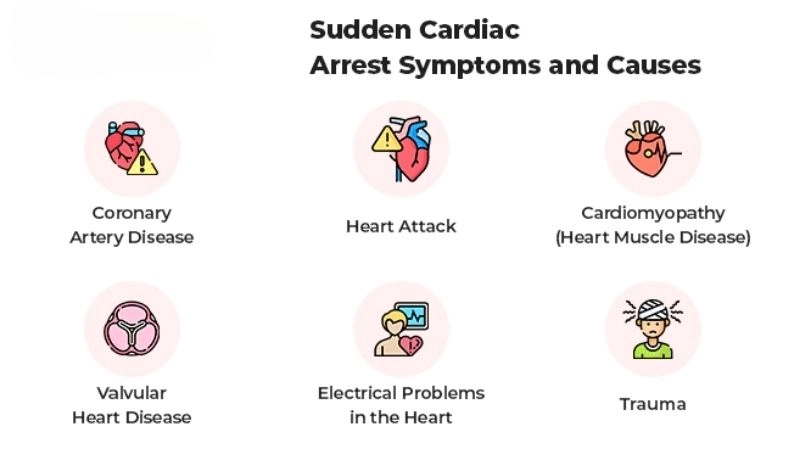
What are the main causes of cardiac arrest?
- Sudden arrhythmias can disrupt the heart's normal rhythm, leading to cardiac arrest within minutes if not treated immediately.
- Coronary artery disease blocks blood flow to the heart, significantly increasing the risk of sudden cardiac arrest.
- Severe heart attacks damage heart muscles, making the heart unable to pump blood efficiently and triggering cardiac arrest.

Early warning of cardiac arrest symptoms
>>> Discover more: Understanding symptoms and causes of Noonan Syndrome
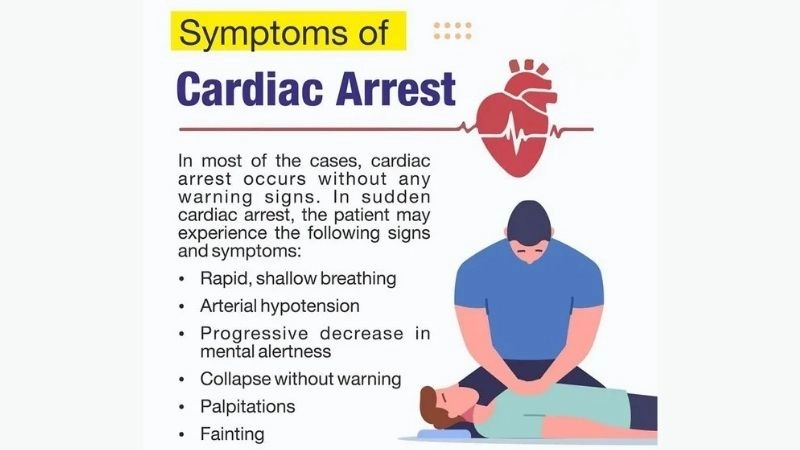
Key symptoms of cardiac arrest to watch for
- Sudden loss of consciousness occurs within seconds, often accompanied by no detectable pulse or breathing.
- Chest pain, dizziness, or palpitations may precede cardiac arrest, signaling urgent heart dysfunction that requires immediate attention.
- Shortness of breath or extreme fatigue can indicate the heart is failing and may precede a cardiac arrest event.
How can you prevent cardiac arrest effectively?
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoidance of smoking to reduce heart disease risks.
- Regular cardiovascular checkups and monitoring blood pressure, cholesterol, and heart rhythm help detect early warning signs.
- Manage chronic conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and obesity to minimize factors that contribute to cardiac arrest.
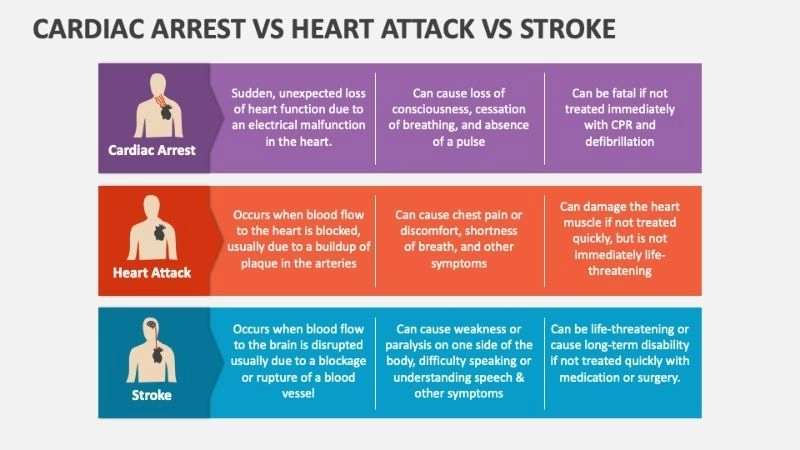
Truth behind cardiac arrest vs heart attack
>>> Discover more: Pompe disease progression and how it impacts the body
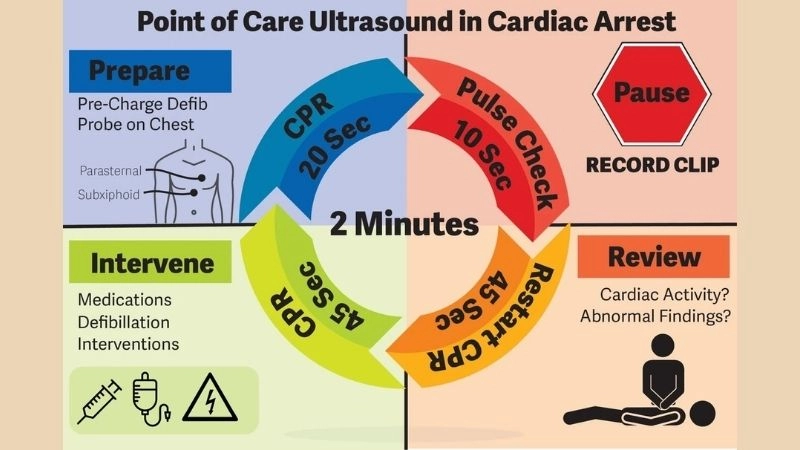
Images visual examples of cardiac arrest
Visual examples may include diagrams showing heart rhythm abnormalities, blocked coronary arteries, or heart failure scenarios.

>>> Discover more: Cardiogenic shock symptoms causes and medical management
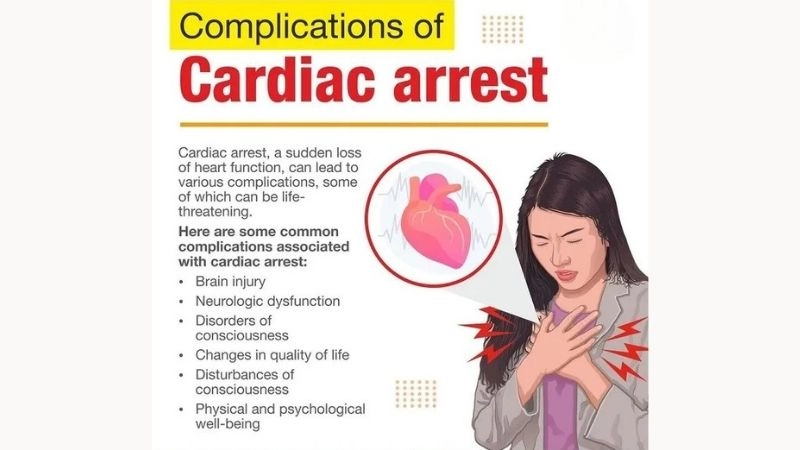
Cardiac arrest remains a serious global emergency. Recognizing symptoms, causes, and treatment options is vital to improve survival and reduce complications.