Athlete's heart is a benign condition often seen in individuals engaged in intense training. Recognizing symptoms and understanding treatment ensures safe exercise.
What are the main causes of Athlete's Heart?
- Intense physical training over months or years can lead to an enlarged heart, causing Athlete's Heart as the heart adapts to increased demands.
- Genetic factors may predispose some athletes to structural changes in the heart, making them more susceptible to Athlete's Heart during rigorous training.
- High endurance sports, such as marathon running or competitive swimming, create chronic stress on the cardiovascular system, promoting heart adaptations typical of Athlete's Heart.

Key warning signs of athlete's heart symptoms
>>> See more: Key warning signs of cardiac amyloidosis you should know
Key symptoms of Athlete's Heart to watch for
- Mild fatigue during or after exercise may occur as the heart becomes more efficient, yet some athletes might notice shortness of breath or unusual tiredness.
- Occasional palpitations or irregular heartbeats can develop due to structural changes in the heart muscle associated with prolonged athletic activity.
- Lower resting heart rate is common, sometimes below 50 beats per minute, reflecting the heart’s adaptation but potentially alarming if sudden symptoms arise.
How can you prevent Athlete's Heart effectively?
- Schedule regular cardiovascular check-ups, including ECG and echocardiography, to monitor heart size and rhythm, particularly for athletes engaged in high-intensity training.
- Gradually increase training intensity and duration to allow the heart to adapt safely without developing abnormal enlargement or rhythm disturbances.
- Maintain a balanced lifestyle with proper nutrition, hydration, and adequate rest to reduce stress on the cardiovascular system and support healthy heart function.
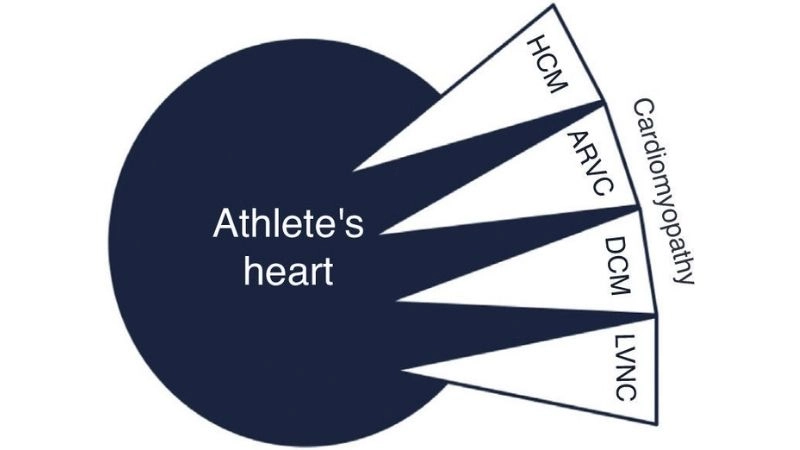
Common athlete's heart EKG changes explained
>>> See more: Hemochromatosis (Iron Overload Heart Disease) overview
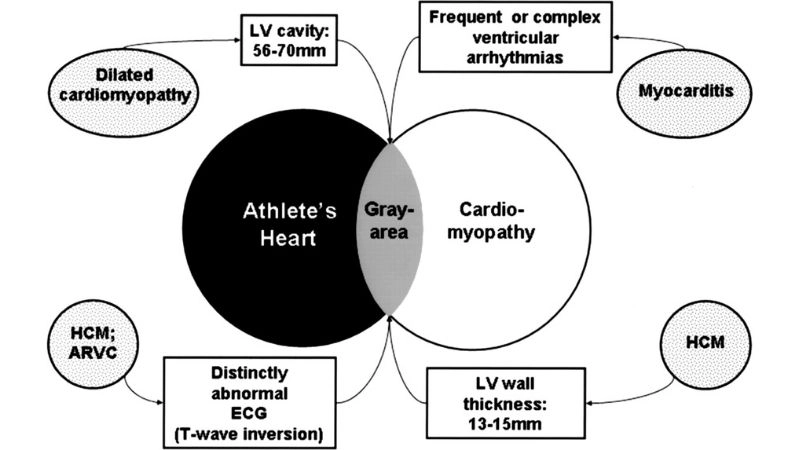
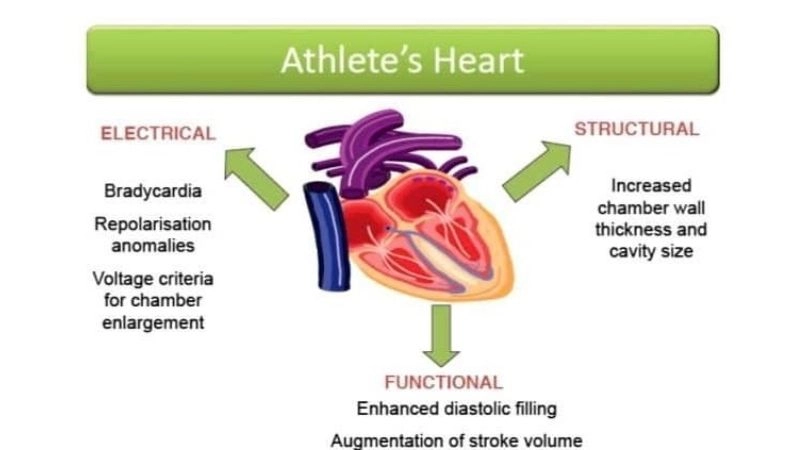
Images visual examples of Athlete's Heart
A healthy athletic heart shows mild enlargement with thicker heart walls and lower resting heart rate. Diagnostic imaging like echocardiograms can visualize structural adaptations.

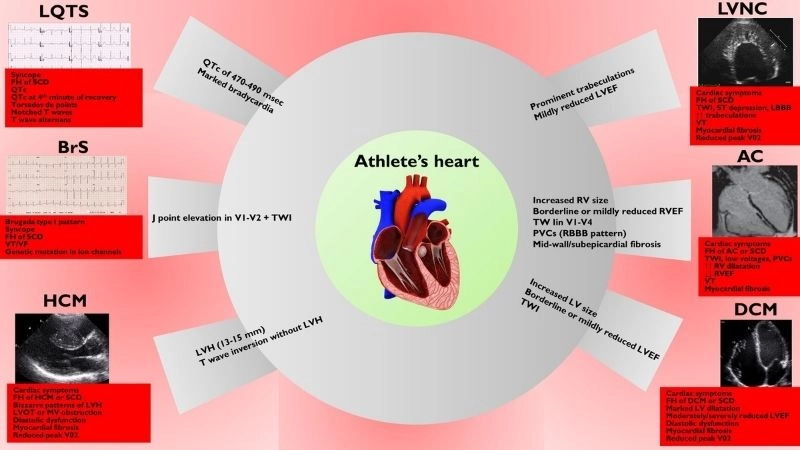
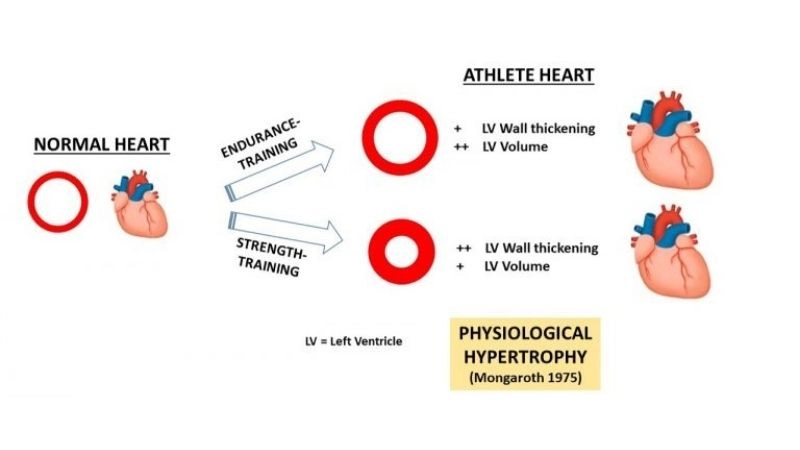


>>> See more: Carcinoid heart disease signs diagnosis and management
Athlete's heart highlights the impact of intense exercise on the body. With proper diagnosis and management, athletes can maintain peak performance and safety.