Frequent nosebleeds or easy bruising might be more than just a nuisance. Understanding Von Willebrand disease, the most common inherited bleeding disorder, is key to getting a proper diagnosis and managing your symptoms effectively for a full and active life.
What are the main causes of Von Willebrand Disease?
- The primary cause is a genetic mutation that affects the body's ability to produce a crucial blood-clotting protein called the von Willebrand factor (VWF).
- This condition is typically inherited from one or both parents, making von Willebrand genetics a key factor in passing the disorder through family lines.
- There are several types of von Willebrand disease, classified based on whether the VWF protein is deficient in quantity or simply functions improperly.
Key symptoms of Von Willebrand Disease to watch for
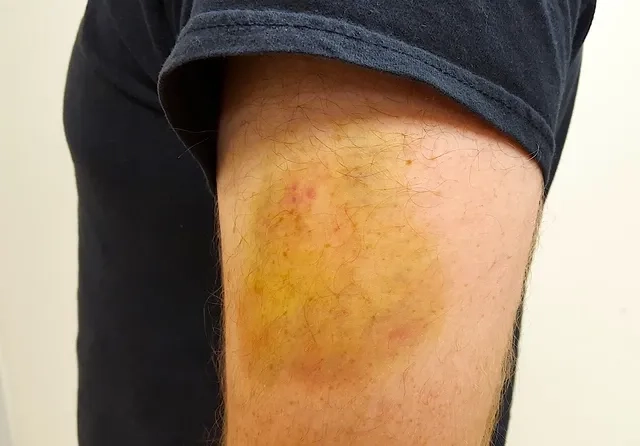
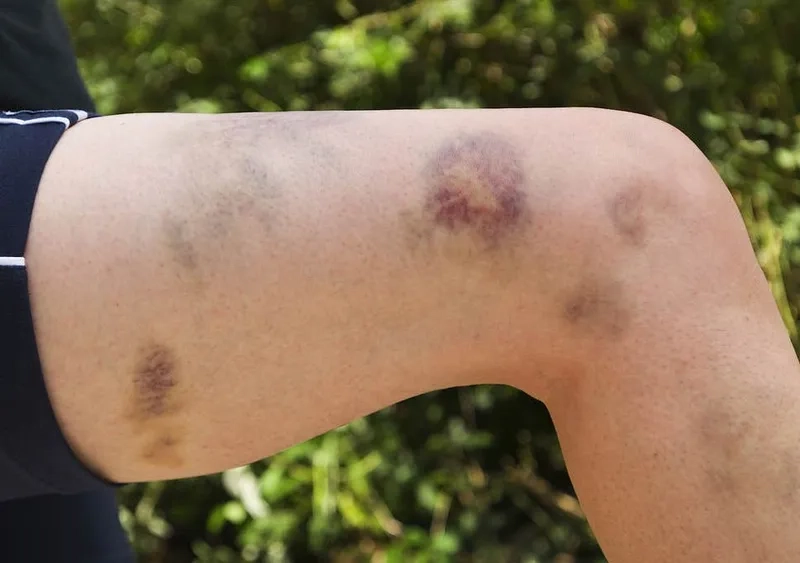
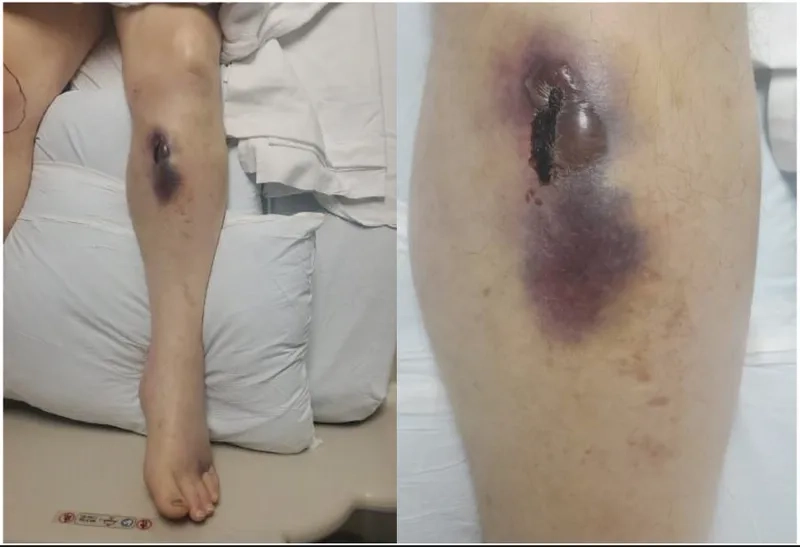
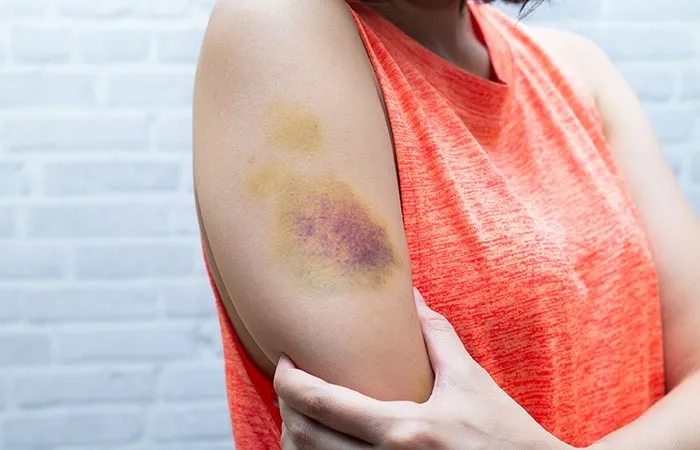
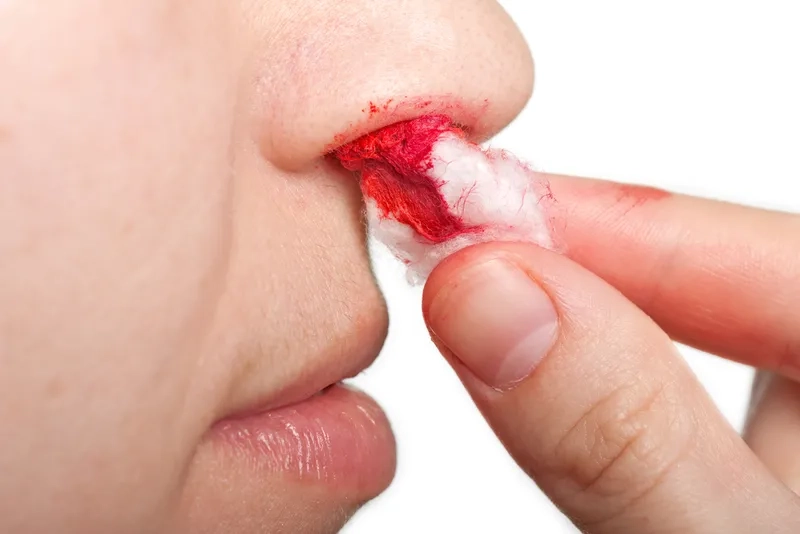
- Common von Willebrand disease symptoms include recurrent and prolonged nosebleeds, easy bruising from minor bumps, and excessive bleeding from the gums.
- Many individuals, particularly women, experience heavy or long-lasting menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia), which is often a key sign leading to a diagnosis.
- Prolonged or excessive bleeding after surgery, dental procedures, or an injury is a significant symptom that warrants investigation by a healthcare professional.
How is Von Willebrand Disease managed and treated?
- Treatment often includes medications like desmopressin (DDAVP), which stimulates the release of stored von Willebrand factor to aid in blood clotting.
- For more severe types, von Willebrand disease treatment may involve replacement therapies that infuse concentrated VWF directly into the bloodstream before procedures.
- Living with von Willebrand disease means avoiding blood-thinning drugs like aspirin and informing all healthcare providers of your condition to ensure safe care.
>>> See more: Ménière's disease - managing dizziness and hearing loss
Image of the disease Von Willebrand Disease


>>> Don't miss: Living with sickle cell anemia - a comprehensive management guide
If you or a family member experience signs of a bleeding disorder, do not wait. Speaking with a haematologist is the first step toward an accurate diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan, empowering you to manage the condition confidently.
>>> See more: Thalassemia - understanding this inherited blood disorder