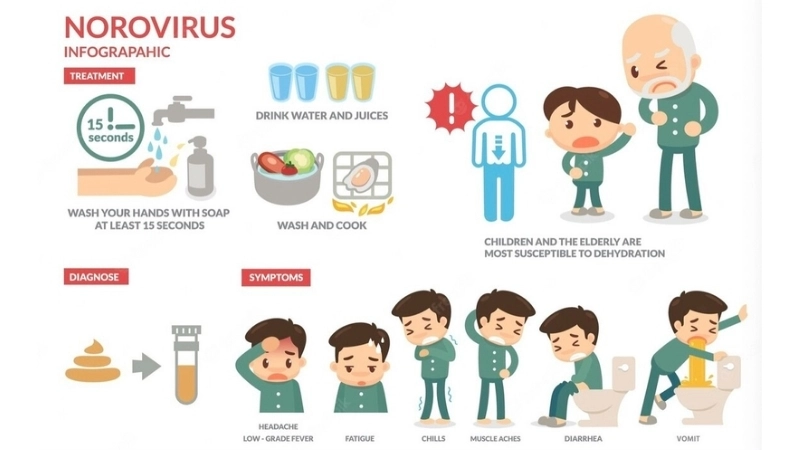
Norovirus Infection is a highly contagious stomach virus causing nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Understanding its symptoms and prevention is key to staying safe.
What are the main causes of Norovirus Infection?
- Consuming contaminated food or water is a leading cause, often including raw shellfish, unwashed vegetables, or improperly handled meals.
- Close contact with an infected person spreads the virus easily, especially in crowded places like schools, nursing homes, and cruise ships.
- Touching contaminated surfaces and then touching your mouth or face allows the virus to enter the body and trigger infection.
Key symptoms of Norovirus Infection to watch for
- Sudden onset of nausea and vomiting is a hallmark symptom, which can lead to dehydration if not managed promptly.
- Watery diarrhea often occurs within 12–48 hours of exposure and may be accompanied by abdominal cramps and discomfort.
- Low-grade fever, fatigue, and muscle aches commonly develop as the immune system reacts to the viral infection.
>>>Explore now: Understanding Viral Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu) symptoms
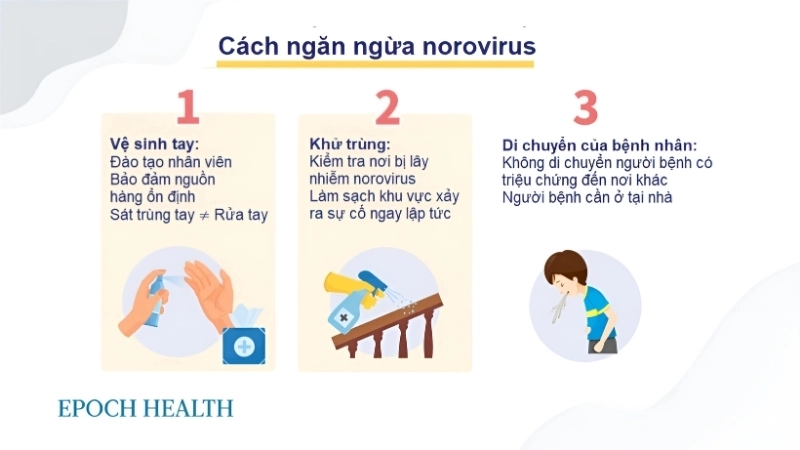
How can you prevent Norovirus Infection effectively?
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water after using the bathroom or before handling food to remove potential viral particles.
- Disinfect frequently touched surfaces with bleach-based cleaners, especially in kitchens, bathrooms, and communal spaces.
- Avoid sharing utensils, towels, or food with someone who is showing symptoms of Norovirus Infection to reduce transmission risk.
>>>Explore now: Understanding cowpox causes symptoms and treatment guide
Image description of Norovirus Infection
Norovirus Infection is a highly contagious viral illness affecting the stomach and intestines. It spreads through contaminated food, water, and surfaces, causing vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach cramps.



>>>Explore now: Understanding Orf (Contagious Ecthyma) symptoms and care
Early recognition and proper hygiene are essential in controlling Norovirus Infection. Stay informed, take precautions, and consult healthcare professionals if symptoms persist.