Orf (Contagious Ecthyma) is a viral infection affecting sheep and goats. Learn about its symptoms, prevention, and treatment to protect both animals and humans effectively.
What are the main causes of Orf (Contagious Ecthyma)?
- Orf is caused by a Parapoxvirus primarily transmitted from infected sheep or goats through direct contact with lesions or contaminated materials.
- Broken skin or cuts on hands or fingers increase susceptibility to contracting Orf from animals carrying the virus.
- Contaminated farm equipment, wool, or clothing can act as a source for the virus, leading to human infections when hygiene measures are insufficient.
Key symptoms of Orf (Contagious Ecthyma) to watch for
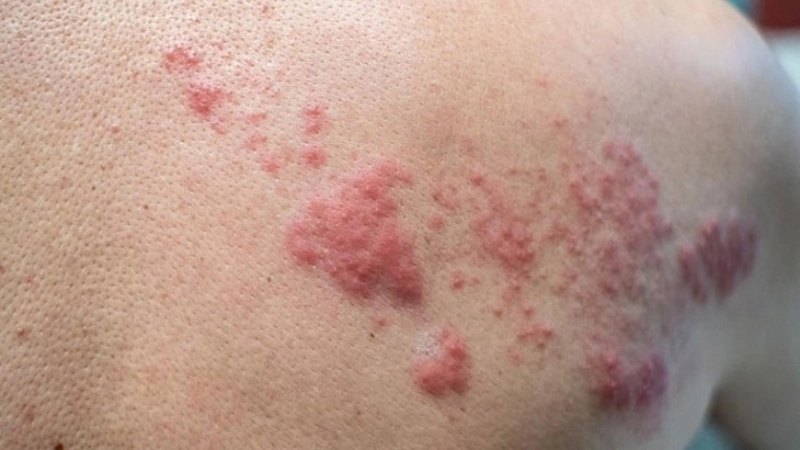
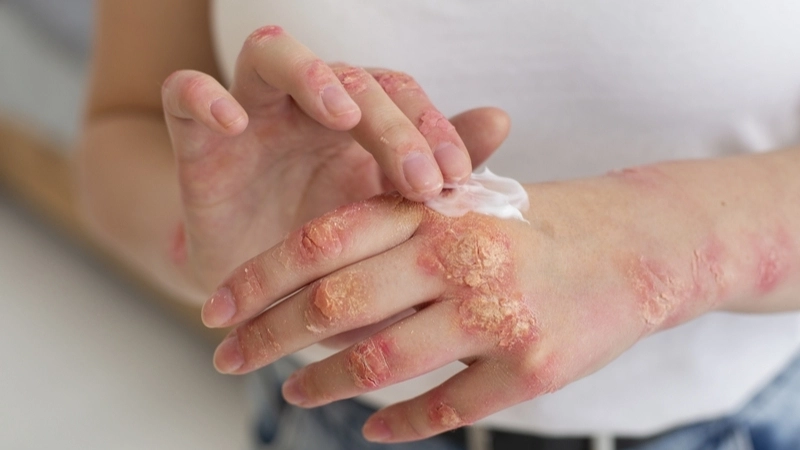
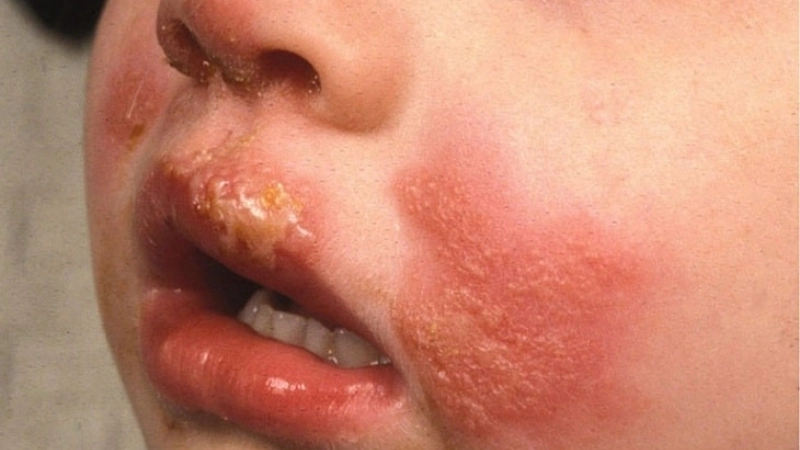
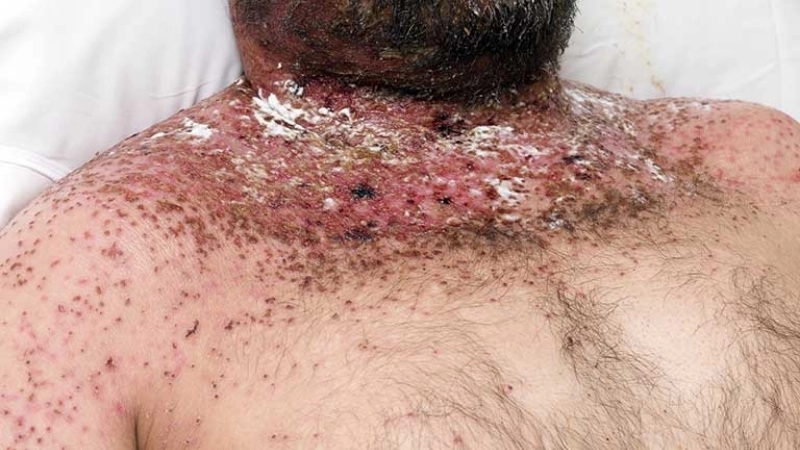
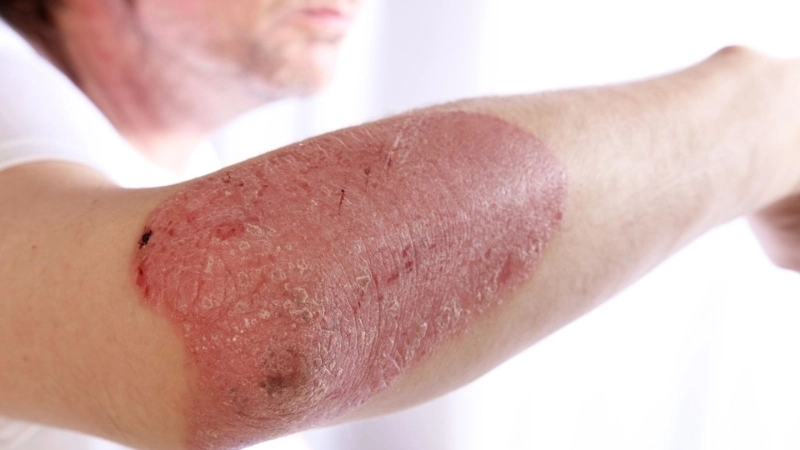
- Painful, red pustules or nodules usually appear on the hands, fingers, or arms after 3–7 days of exposure to the virus.
- Swelling, itchiness, and sometimes mild fever accompany the lesions, signaling the body’s immune response to the infection.
- Lesions may crust over and heal within 3–6 weeks, though secondary bacterial infections can prolong discomfort or cause complications.

>>>Explore now: Understanding kaposi's sarcoma symptoms and treatments
How can you prevent Orf (Contagious Ecthyma) effectively?
- Wear protective gloves and clothing when handling sheep, goats, or contaminated materials to reduce direct skin exposure.
- Maintain strict hygiene, including washing hands thoroughly and disinfecting tools or surfaces that contact infected animals.
- Vaccinate livestock if possible, as immunizing sheep and goats reduces virus prevalence and lowers human infection risk.
>>>Explore now: Warts (Common, Plantar, Genital) causes and treatments
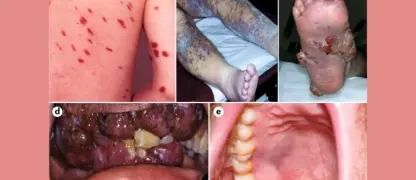
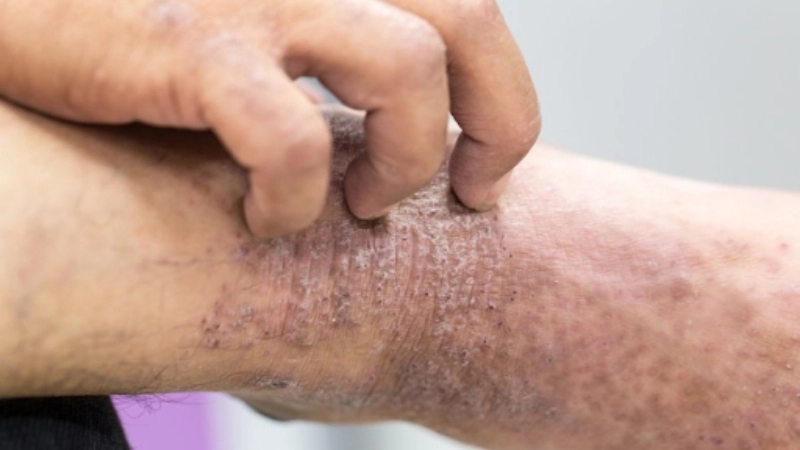
Image description of Orf (Contagious Ecthyma)
Orf (Contagious Ecthyma) is a viral skin disease affecting both animals and humans. It causes painful, scabby lesions, primarily on hands, fingers, and areas exposed to infected sheep or goats.


>>>Explore now: Understanding molluscum contagiosum causes and symptoms
Understanding Orf (Contagious Ecthyma) helps farmers and caregivers reduce spread. Timely prevention, proper hygiene, and vaccination are key to managing this contagious disease.