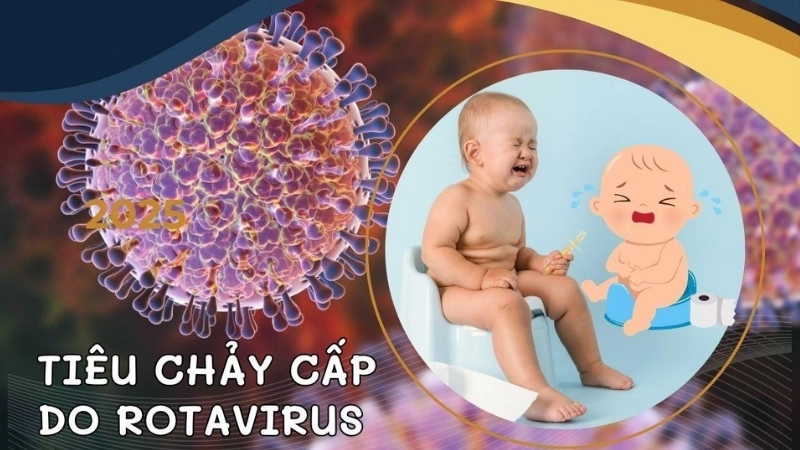
Rotavirus Infection is a highly contagious virus affecting children and adults. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and prevention methods is crucial for protecting your family’s health.
What are the main causes of rotavirus infection?
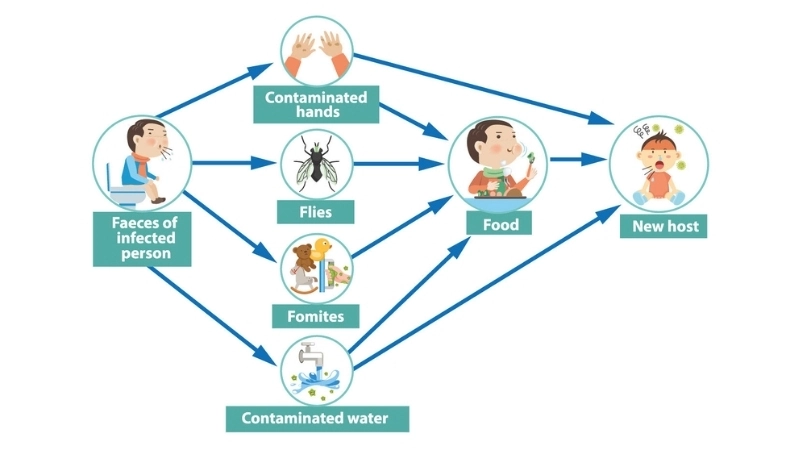
- Rotavirus spreads through the fecal-oral route, often via contaminated hands, surfaces, or objects touched by infected individuals.
- Consuming food or water contaminated with rotavirus can lead to rapid infection, especially in infants and young children.
- Close contact in childcare or crowded environments increases the risk of rotavirus transmission among children.
Key symptoms of rotavirus infection to watch for
- Severe watery diarrhea is a common symptom, often lasting three to eight days and leading to dehydration if untreated.
- Vomiting and nausea frequently accompany infection, causing discomfort and worsening fluid loss in affected individuals.
- Fever and abdominal pain are typical signs, alerting caregivers to possible rotavirus infection in children and adults.

>>>Explore now: Understanding norovirus infection and its common symptoms
How can you prevent rotavirus infection effectively?
- Vaccination is the most effective preventive measure, recommended for infants in multiple doses to reduce the risk of severe disease.
- Maintaining good hand hygiene and sanitizing surfaces regularly can significantly limit the spread of rotavirus in homes and public spaces.
- Avoid sharing eating utensils, cups, or personal items, especially in childcare centers, to minimize exposure to infected individuals.
>>>Explore now: Understanding Viral Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu) symptoms
Image description of rotavirus infection
Rotavirus infection is a contagious viral illness primarily affecting children, causing diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and dehydration. It spreads easily through contaminated surfaces and close contact.


>>>Explore now: Understanding cowpox causes symptoms and treatment guide
Preventing Rotavirus Infection requires vaccination, proper hygiene, and awareness of early symptoms. Acting promptly reduces complications and ensures better health outcomes for all.