Don't ignore chest pain or shortness of breath after an illness. Understanding Myocarditis is crucial for a safe recovery and preventing potential long-term heart damage. This guide covers what you need to know.
What are the main causes of Myocarditis?
- What is myocarditis? It is an inflammation of the myocardium, or heart muscle, which weakens the heart and reduces its ability to pump blood effectively.
- The most common causes of myocarditis are infections, leading to viral myocarditis, but bacteria, fungi, and certain autoimmune diseases can also be triggers.
- In some instances, exposure to environmental toxins or severe allergic reactions to drugs can also cause the heart muscle to become inflamed.

Key symptoms of Myocarditis to watch for
- Key myocarditis symptoms include chest pain, rapid or abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias), severe fatigue, and shortness of breath, even while at rest.
- Other signs can include swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet due to fluid retention, alongside flu-like symptoms like fever and body aches.
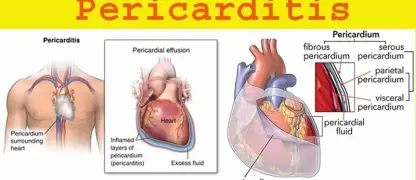
- When considering myocarditis vs pericarditis, the chest pain in myocarditis is often a dull ache, unlike the sharp, stabbing pain of pericarditis.
How can you prevent Myocarditis effectively?
- Since infections are a primary cause, prevention involves practicing good hygiene, staying current on vaccinations, and avoiding close contact with sick individuals.
- A timely myocarditis diagnosis is vital for proper myocarditis treatment, which aims to support heart function and address the underlying cause of inflammation.
- A supervised myocarditis recovery is essential to prevent chronic myocarditis and reduce the risk of other myocarditis long term effects like heart failure.
>>> Learn fully at: Pulmonary embolism – causes, symptoms and treatment
Image of the disease Myocarditis




>>> Don't miss: Valvular heart disease – symptoms and management
Never dismiss chest pain or severe fatigue, especially after a viral illness. Seek immediate medical attention to ensure a proper diagnosis and protect your long-term heart health.
>>> Learn now: Aortic aneurysm – signs, risks and treatment