Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) is a common heart defect. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can help patients and families manage it safely.
What are the main causes of Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)?
- Congenital defects during fetal heart development can result in a hole in the ventricular septum, disrupting normal blood flow between heart chambers.
- Genetic factors may increase the risk, as certain inherited mutations affect heart structure and can lead to the development of VSD in newborns.
- Maternal health issues such as uncontrolled diabetes, infections, or exposure to harmful substances during pregnancy can contribute to VSD formation.
Ventricular septal defect symptoms early warning signs in babies
>>> Discover more: Understanding Danon Disease symptoms and early signs
Key symptoms of Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) to watch for
- Shortness of breath and rapid breathing, especially during feeding or physical activity, are common signs of VSD in infants and children.
- Fatigue, poor growth, and difficulty gaining weight may occur due to inefficient oxygen delivery caused by the heart defect.
- Heart murmurs detected during medical examinations are often the first indication of a VSD, prompting further diagnostic testing.
How can you prevent Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) effectively?
- Maintaining proper prenatal care with routine checkups helps monitor fetal development and detect potential heart abnormalities early.
- Managing chronic conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure before and during pregnancy reduces the likelihood of congenital heart defects.
- Avoiding harmful substances such as alcohol, tobacco, and certain medications during pregnancy can significantly lower the risk of VSD in newborns.
Ventricular septal defect in adults risks of late detection
>>> Discover more: Causes and risk factors of Restrictive Cardiomyopathy (RCM)
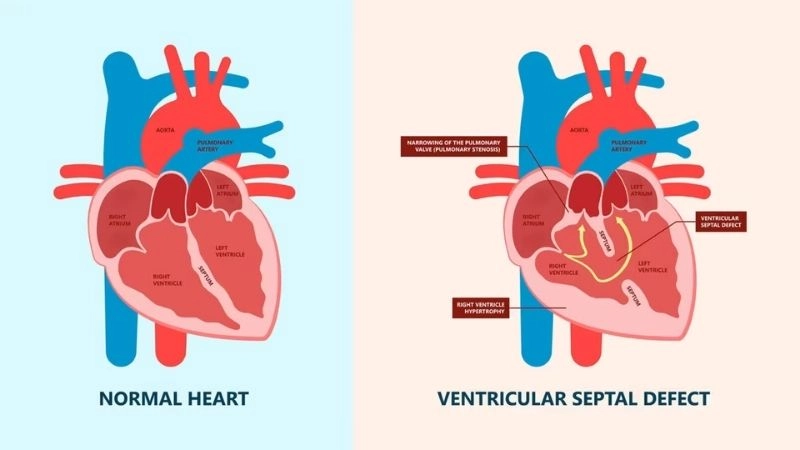
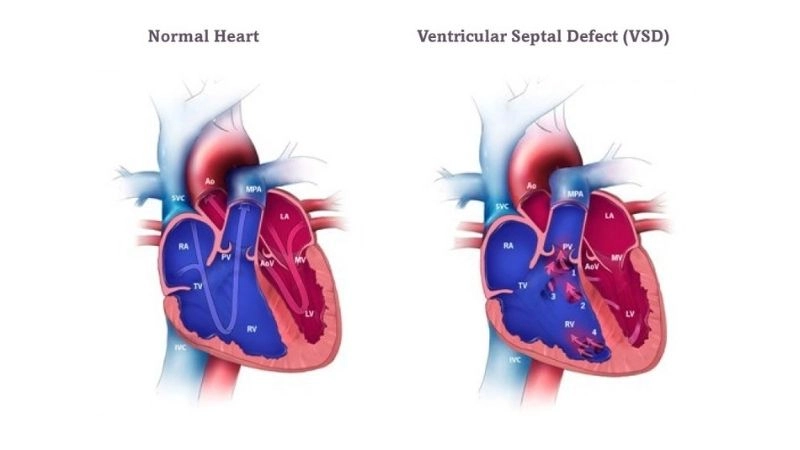
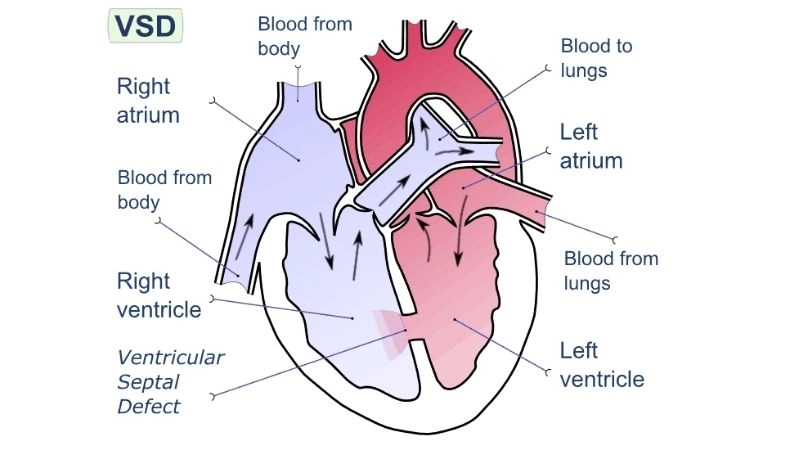
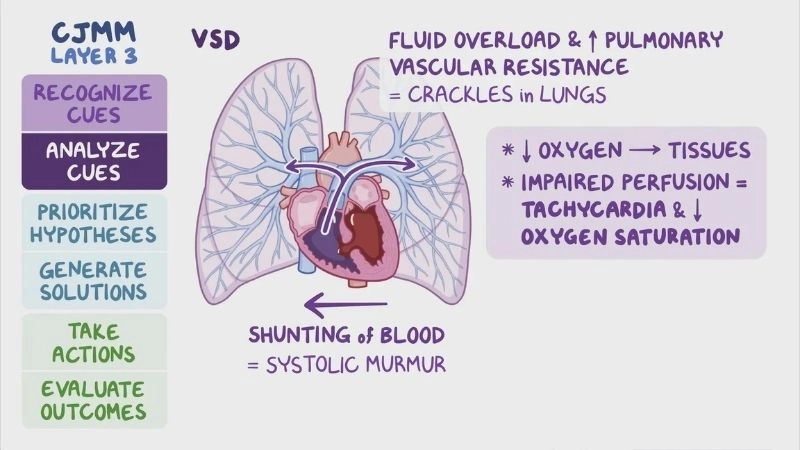
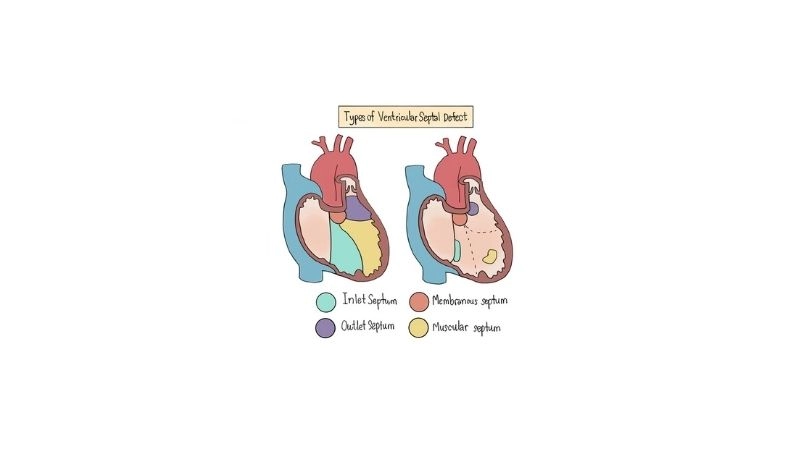
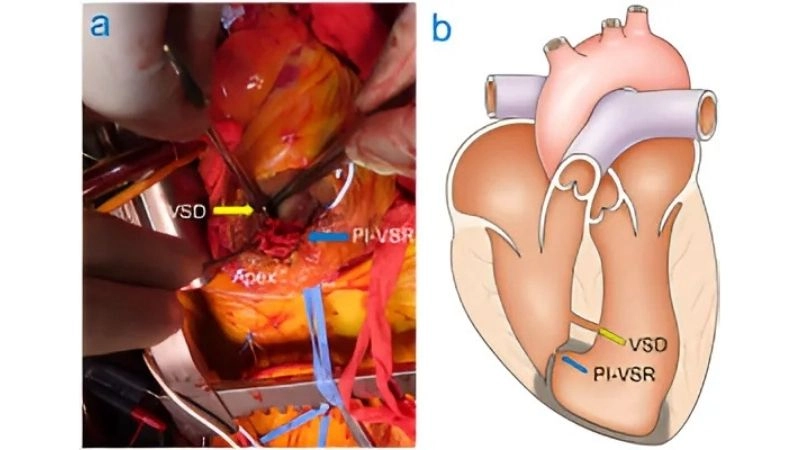
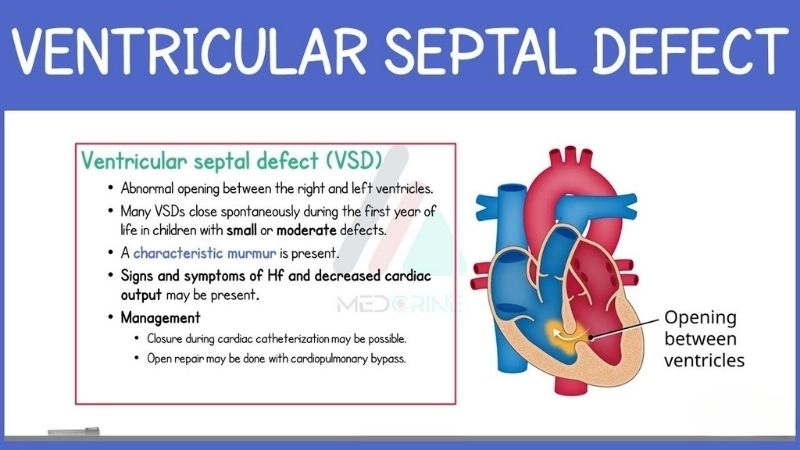
Images visual examples of Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
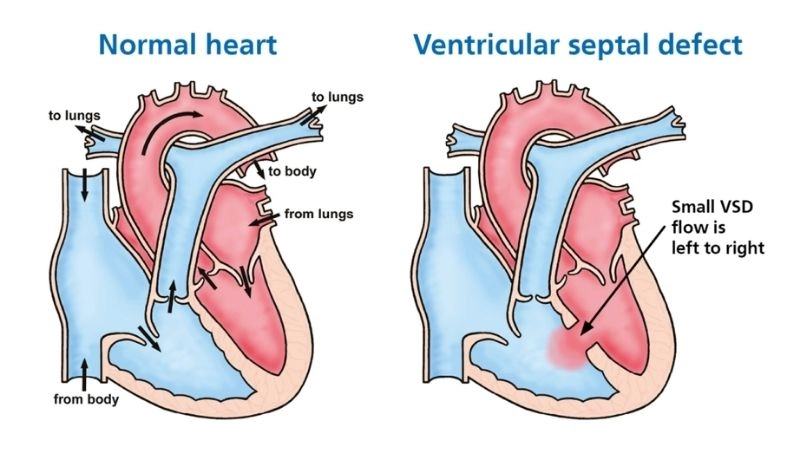
Visual examples of Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) typically show a hole in the septum between the left and right ventricles, causing abnormal blood flow and increased heart workload.
>>> Discover more: Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) Causes And Risk Factors Explained
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) requires proper care. Timely diagnosis and treatment improve outcomes, allowing patients to live healthier, more active lives.