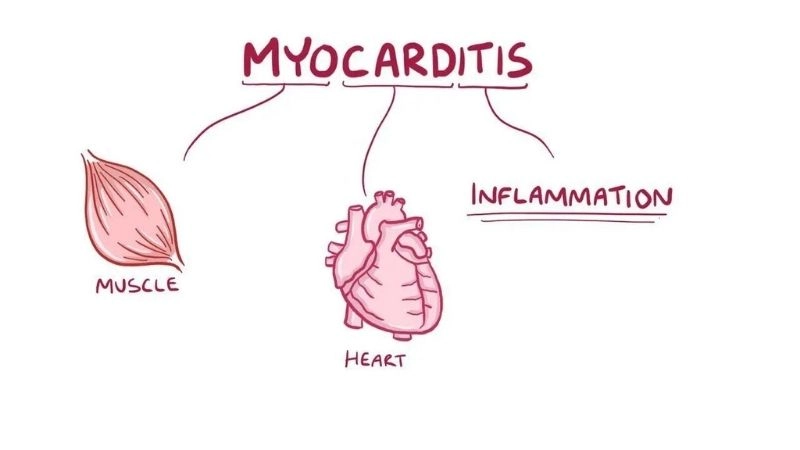
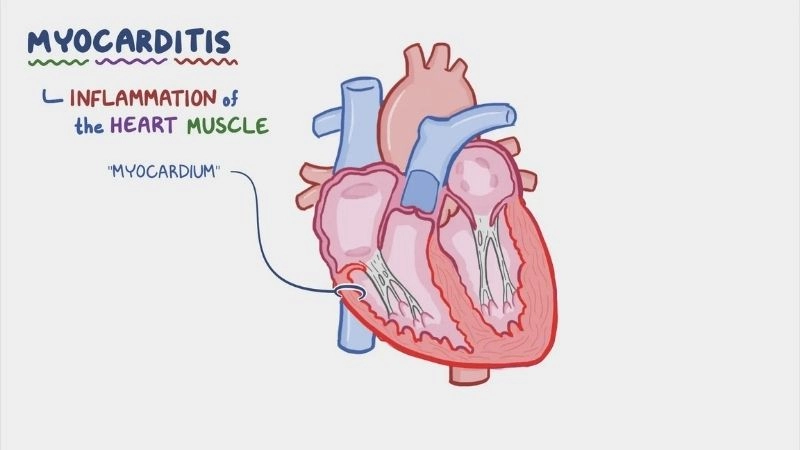
Myocarditis is an inflammatory heart disease that weakens muscle tissue and impacts circulation. Explore symptoms, causes, and treatments for myocarditis.
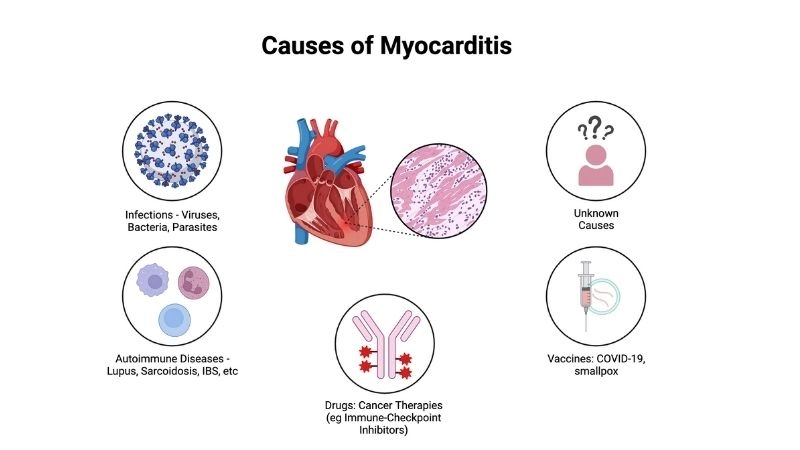
What are the main causes of myocarditis?
- Viral infections like influenza, adenovirus, or COVID-19 directly attack heart muscle cells and cause inflammation.
- Autoimmune disorders can target heart tissue, leading to chronic myocarditis in some cases.
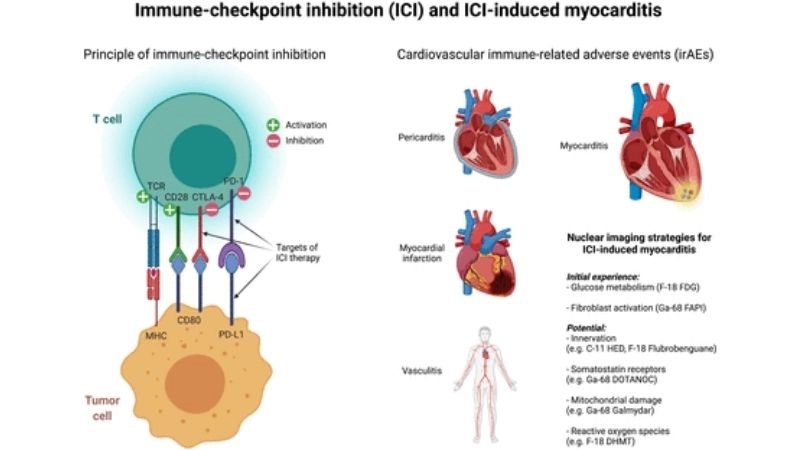
- Certain drugs, toxins, or chemotherapy may trigger heart inflammation through toxic effects.
Myocarditis symptoms warning signs of heart muscle inflammation
>>> Discover more: Atrioventricular Canal Defect (Endocardial Cushion Defect)
key symptoms of myocarditis to watch for
- Chest pain or tightness that feels similar to a heart attack.
- Shortness of breath with fatigue or swelling in the legs.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat, palpitations, or fainting.
How can you prevent myocarditis effectively?
- Strengthen immunity with vaccines, hygiene, and healthy habits.
- Control chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension.
- Avoid alcohol abuse, drugs, or unregulated medications.
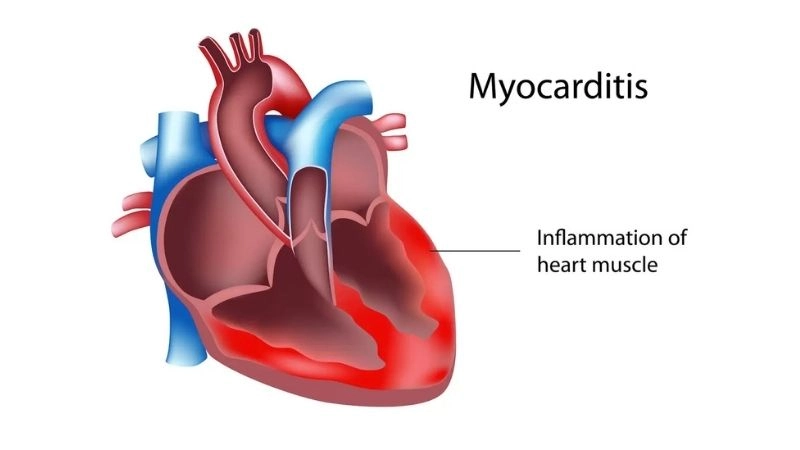
Myocarditis causes underlying triggers of this cardiac condition
>>> Discover more: Understanding Pericarditis (Acute & Chronic) in depth
Images visual examples of myocarditis
Images show inflamed heart tissue and scans highlighting heart muscle damage that reduces function and may cause severe complications.



>>> Discover more: Constrictive pericarditis causes symptoms and care
Myocarditis poses serious risks if untreated but early diagnosis and treatment can ensure recovery. Stay informed about myocarditis to protect your heart.