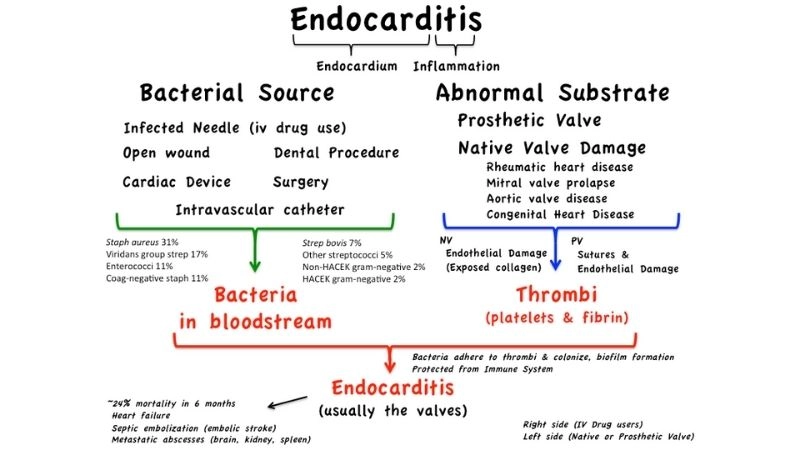
Infective Endocarditis is a dangerous infection of the heart’s inner lining. Understanding causes, symptoms, and treatments is vital to protect long-term health.
What are the main causes of infective endocarditis?
- Bacterial infection from oral, skin, or urinary tract sources can spread into the bloodstream and infect damaged heart valves.
- Risk increases with pre-existing heart defects, artificial valves, or a history of rheumatic heart disease.
- Intravenous drug use or invasive medical procedures can introduce harmful microbes directly into the bloodstream.

Infective endocarditis symptoms warning signs of valve infection
>>> Understand more about: Understanding Pericarditis (Acute & Chronic) in depth
Key symptoms of infective endocarditis to watch for
- Persistent fever with chills and fatigue is often the earliest warning sign of the infection.
- Shortness of breath, chest pain, or heart murmurs may develop as the heart function becomes impaired.
- Skin changes such as tiny red spots or painful nodes on fingers and toes may appear.
How can you prevent infective endocarditis effectively?
- Maintain excellent oral hygiene and regular dental care to minimize bacterial entry.
- Use antibiotics before certain dental or surgical procedures if you have high-risk heart conditions.
- Avoid IV drug use and ensure sterile medical practices during treatments.
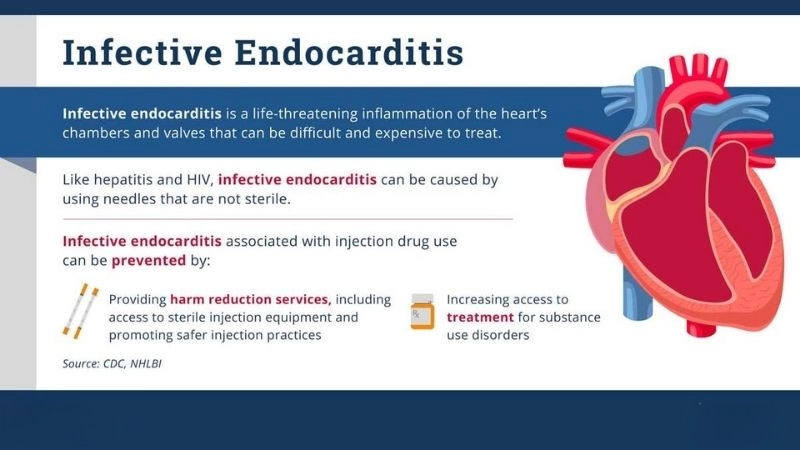
Infective endocarditis treatment medical and surgical management
>>> Understand more about: Constrictive pericarditis causes symptoms and care
Images visual examples of infective endocarditis
Visual examples often show infected heart valves with vegetations, highlighting bacterial growth and damage that disrupts normal valve function.
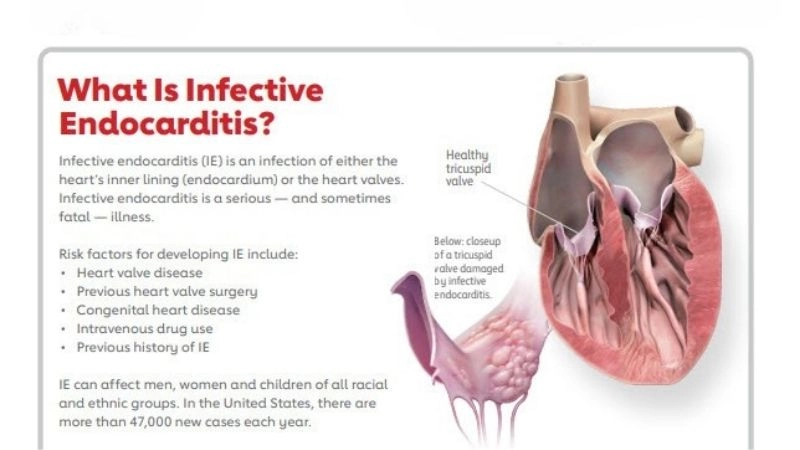

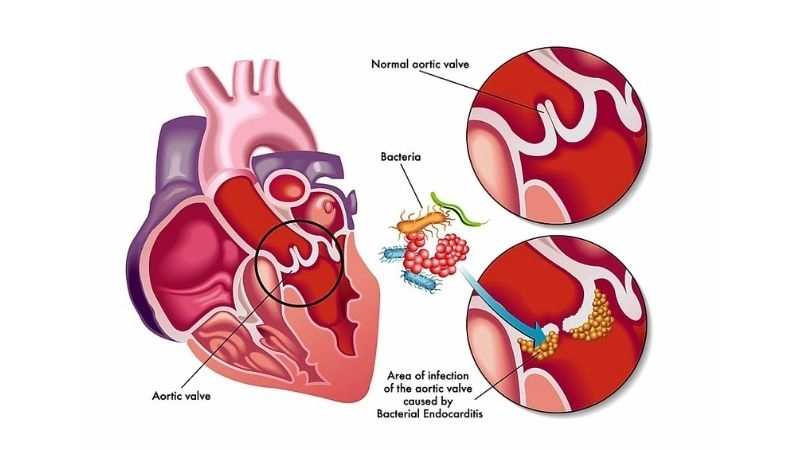



>>> Understand more about: How myocarditis impacts the heart and overall health
Managing Infective Endocarditis requires timely diagnosis and proper treatment. Awareness of prevention and early care is crucial for long-term heart health.