Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) is a genetic arrhythmia that triggers dangerous heart rhythms during stress or exercise, requiring urgent care.
What are the main causes of catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT)?
- Genetic mutations in heart proteins disrupt calcium regulation, triggering abnormal electrical signals that lead to dangerous arrhythmias under physical or emotional stress.
- Inherited from family history, CPVT often passes through generations, requiring careful genetic testing for early detection and effective preventive management.
- Excessive adrenaline release during exercise or stress increases the risk of CPVT episodes, as the heart’s electrical activity becomes unstable under intense conditions.
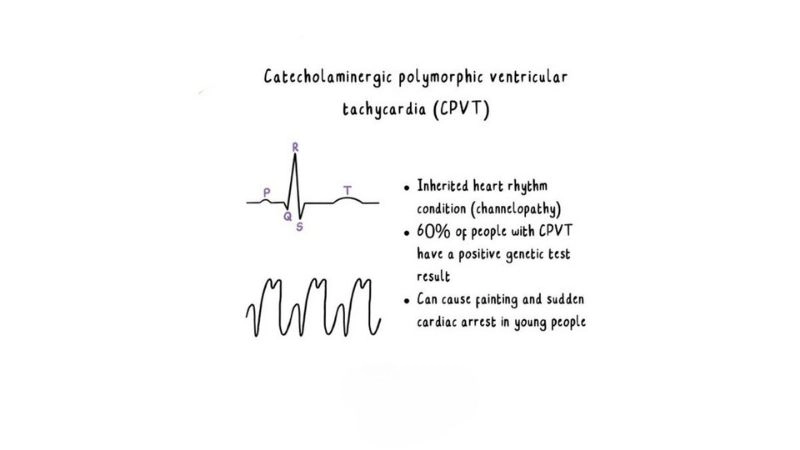
CPVT rare heart rhythm disorder with hidden danger
>>> See more: Understanding Short QT Syndrome (SQTS) and its impact
Key symptoms of catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) to watch for
- Sudden fainting episodes during exercise or strong emotions may signal CPVT, requiring urgent medical evaluation to rule out life-threatening heart rhythm disturbances.
- Palpitations or a racing heartbeat often occur unexpectedly in CPVT patients, especially during physical exertion or stressful moments in daily life.
- Seizure-like episodes can develop in severe CPVT cases, often mistaken for neurological disorders but actually caused by dangerous cardiac arrhythmias.
How can you prevent catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) effectively?
- Regular medical checkups and genetic testing help identify CPVT early, ensuring timely management before severe heart rhythm complications develop.
- Beta-blocker medications prescribed by cardiologists significantly reduce CPVT risk by stabilizing the heart rate and controlling adrenaline sensitivity.
- Lifestyle adjustments like avoiding extreme exercise, managing stress, and monitoring heart activity lower the chance of CPVT-related complications.
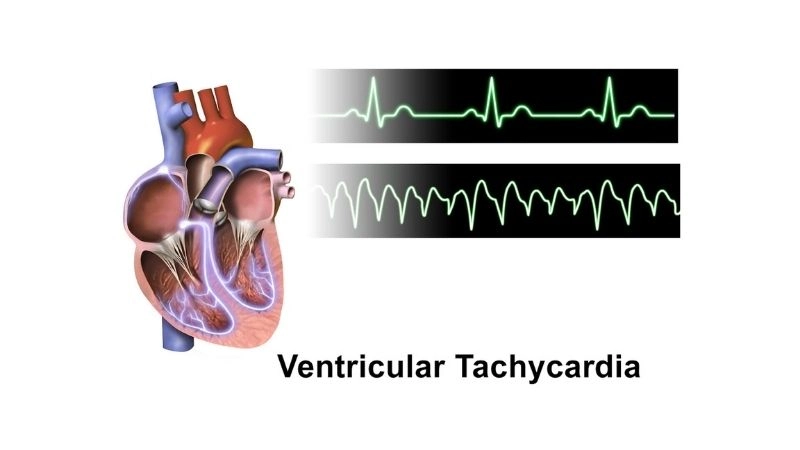
Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia Symptoms show sudden risk
>>> See more: Brugada Syndrome risk factors you must know right now
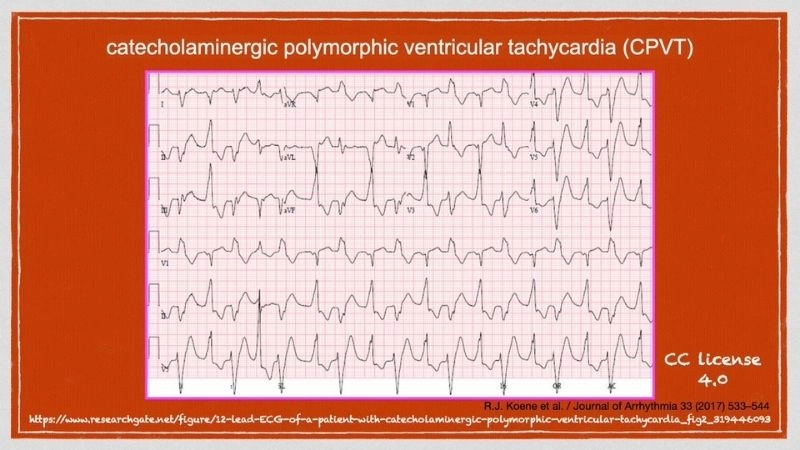
Images visual examples of catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT)
Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia CPVT is a rare genetic heart rhythm disorder. It causes fainting, palpitations, or sudden cardiac arrest triggered by exercise or stress.
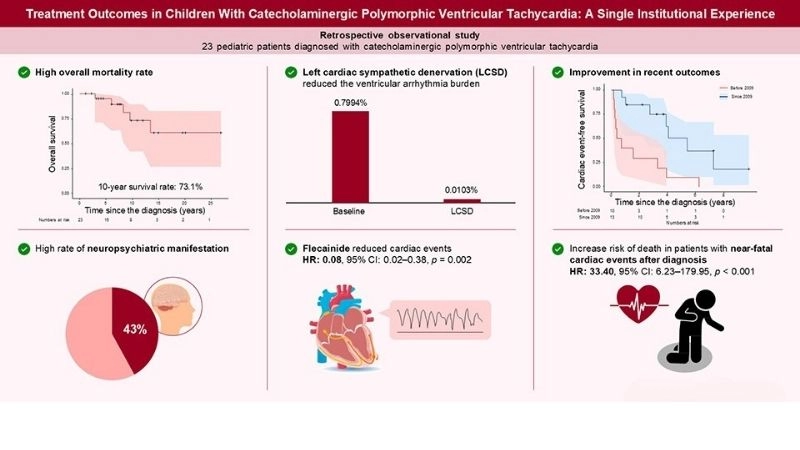
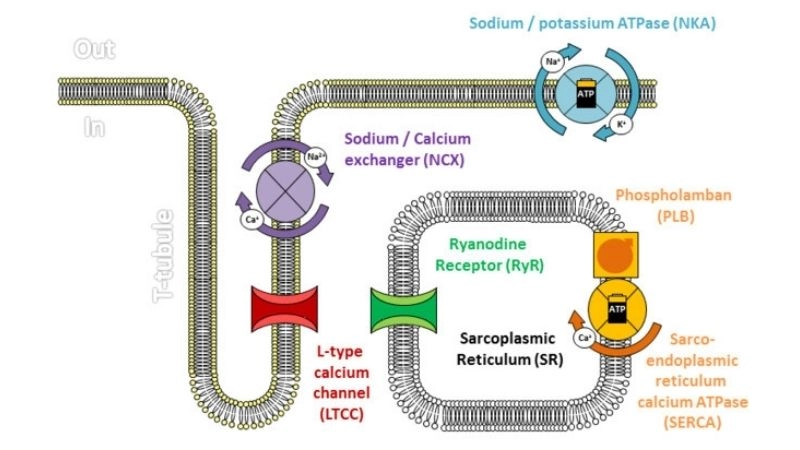
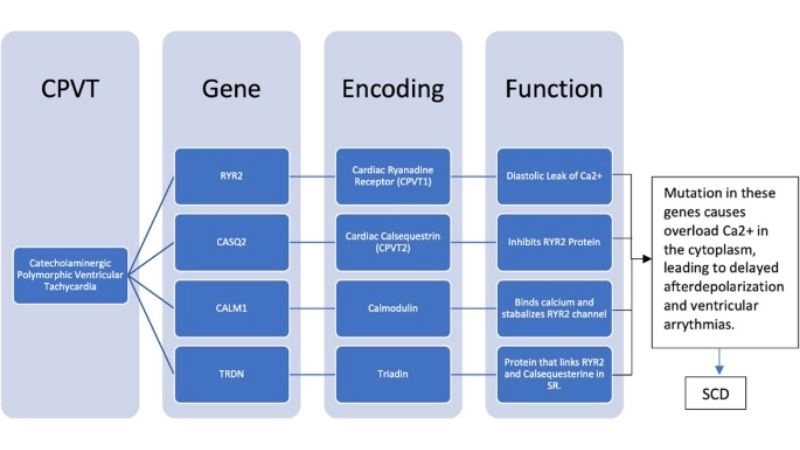
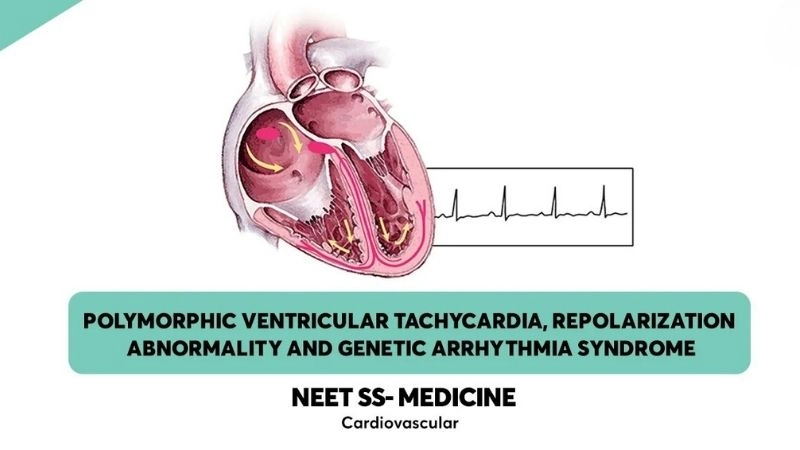
>>> See more: Understanding atrial flutter symptoms and prevention
Understanding catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) helps early diagnosis and treatment, reducing risks and improving long-term heart health outcomes.





