Advances in medicine have transformed the outlook on HIV/AIDS. Understanding the facts is more important than ever for protecting your health, dispelling outdated myths, and knowing the difference between HIV vs AIDS.
What are the main causes of HIV/AIDS?
- To understand how is hiv transmitted, know it spreads through contact with specific body fluids, most commonly during unprotected sexual intercourse.
- Sharing contaminated needles, syringes, or other drug injection equipment is another major route of transmission for the human immunodeficiency virus.
- The virus can also be passed from an infected mother to her child during pregnancy, childbirth, or through breastfeeding without medical intervention.
Key symptoms of HIV/AIDS to watch for
- The early signs of hiv can appear two to four weeks after exposure and often mimic the flu, with symptoms like fever, rash, and fatigue.
- Following the initial phase, a person may experience a long period without any hiv symptoms, though the virus is still active in the body.
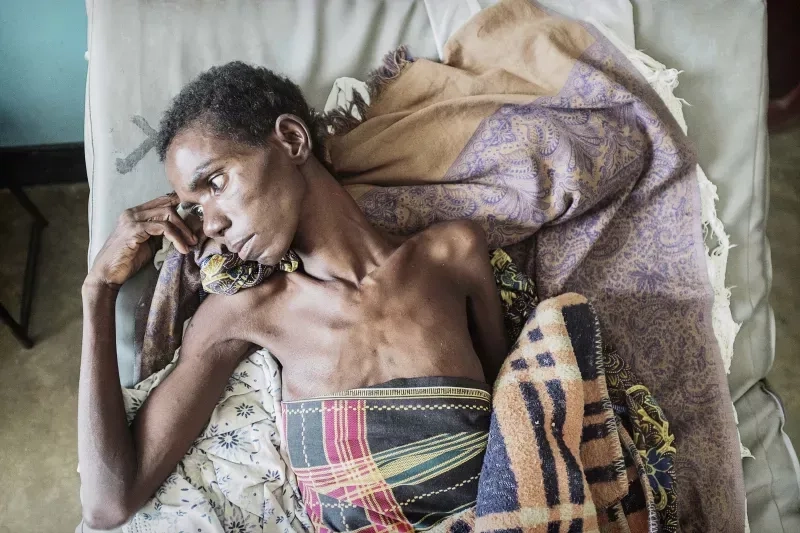
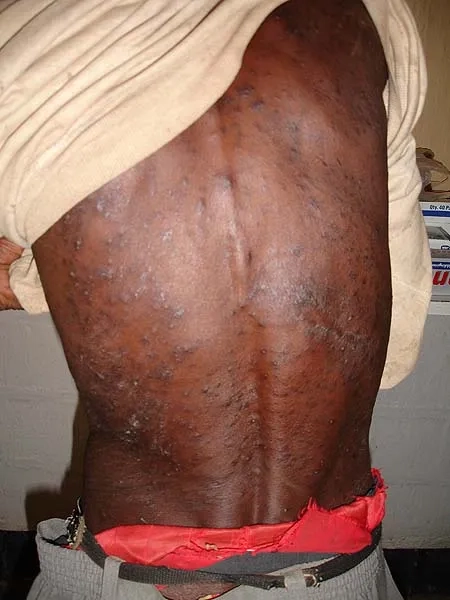
- Without treatment, the immune system weakens, leading to AIDS, with severe aids symptoms like opportunistic infections, significant weight loss, and extreme fatigue.
How can you prevent HIV/AIDS effectively?
- The most effective hiv prevention method during sexual activity is the consistent and correct use of condoms to create a protective barrier.
- For those at high risk, medications like PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis) can significantly reduce the chance of acquiring HIV if taken as prescribed.
- Getting a regular hiv test is crucial for knowing your status and seeking care early, which also helps prevent further transmission.
>>> See more: Pasteurellosis - A bacterial infection from animal bites
Image of the disease HIV/AIDS
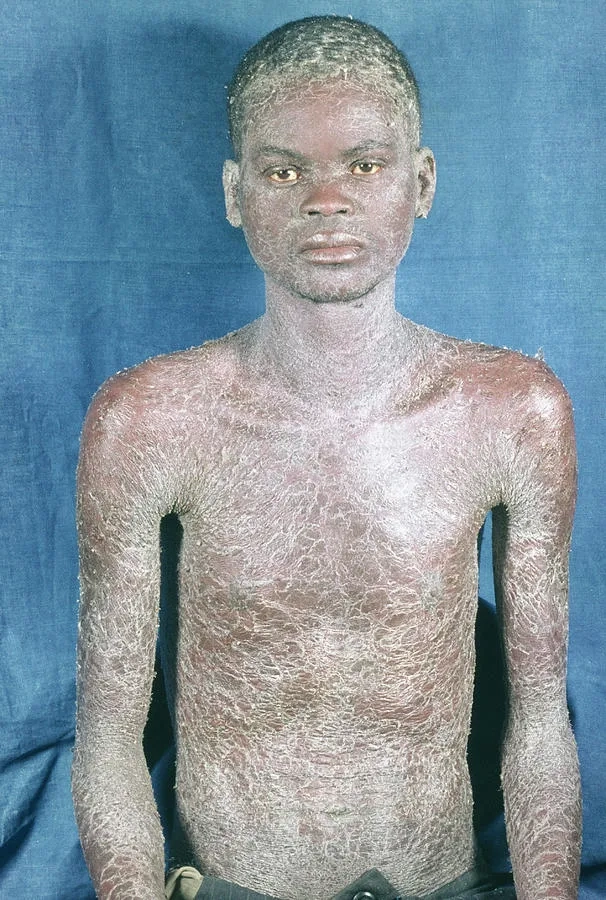
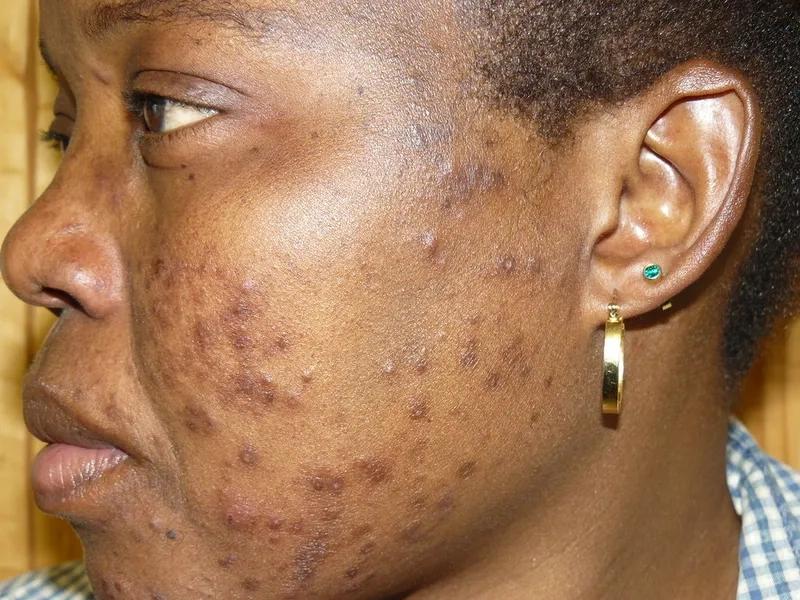
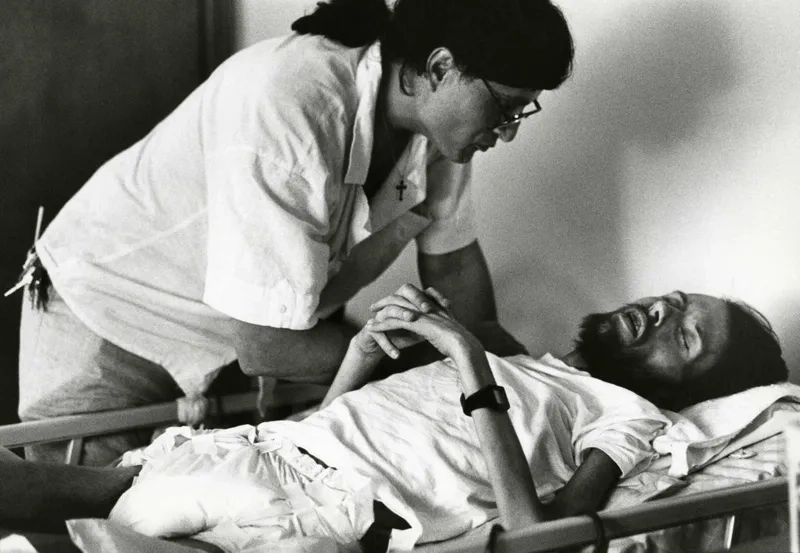
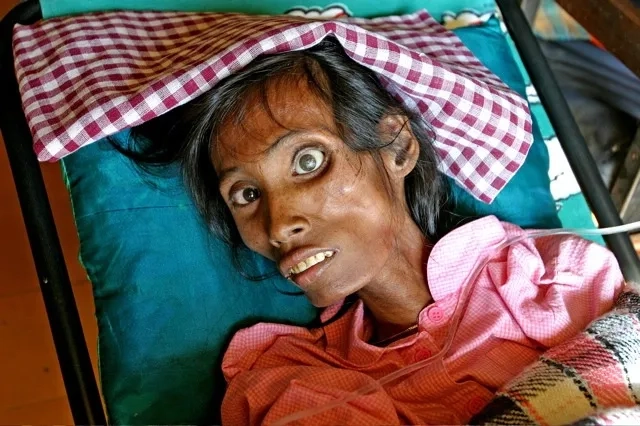
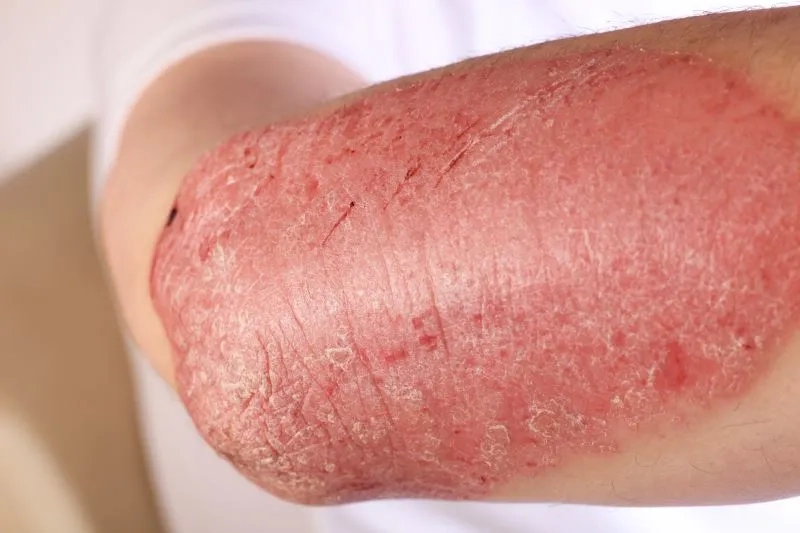
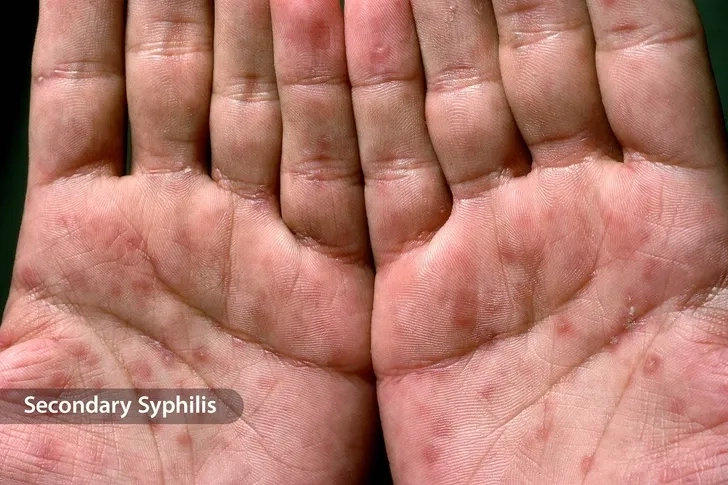
>>> See details: Pityriasis versicolor - A common fungal skin condition
While the answer to is hiv curable is still no, modern hiv treatment can control the virus effectively. With proper care, hiv life expectancy is now close to normal, underscoring the importance of testing and treatment.
>>> Don't miss: Rhinosporidiosis - A chronic fungal infection of the nose