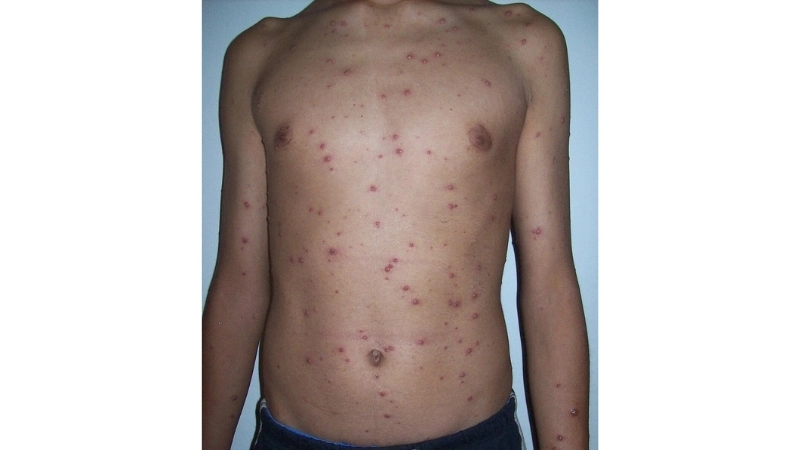
Chickenpox is a highly contagious viral infection that causes itchy rashes and fever. Understanding its symptoms and preventive measures is crucial for adults and children alike.
What are the main causes of Chickenpox?
- Chickenpox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which spreads easily through direct contact or airborne droplets from an infected person.
- A weakened immune system increases susceptibility, making children, pregnant women, and individuals with chronic illnesses more vulnerable to infection.
- Exposure to contaminated surfaces or objects, like toys or utensils used by an infected person, can also transmit the virus.
Key symptoms of Chickenpox to watch for
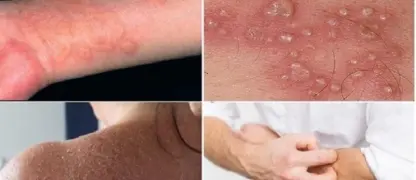
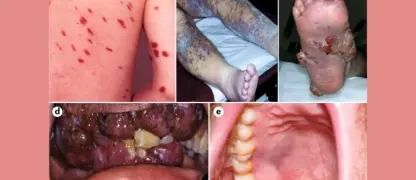
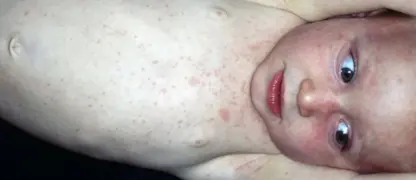
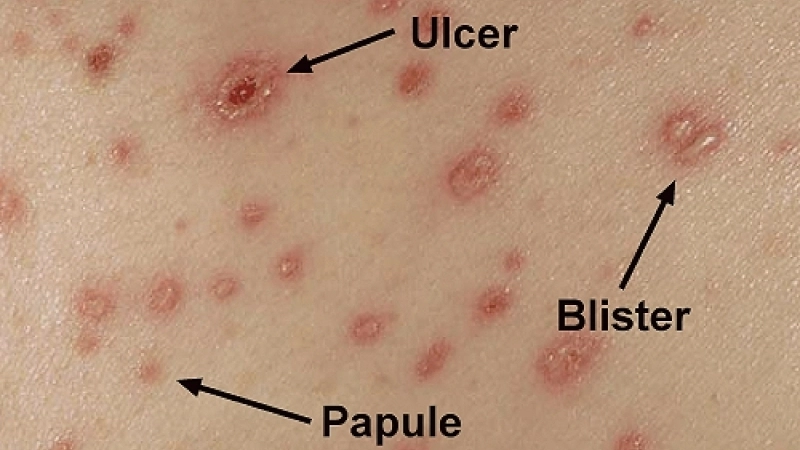
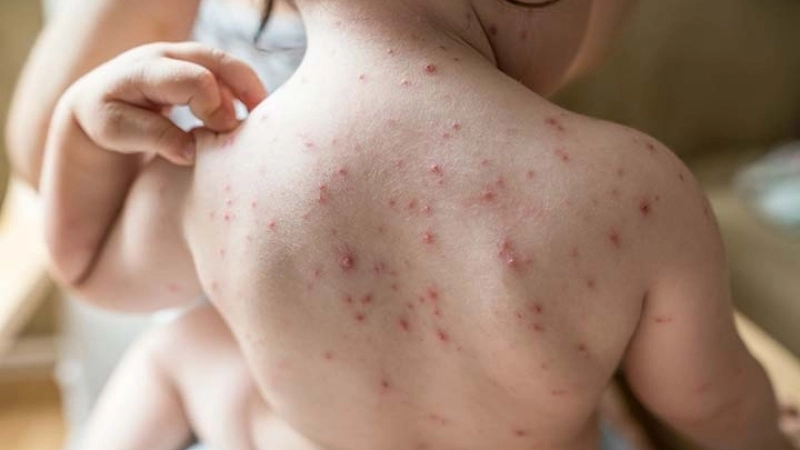
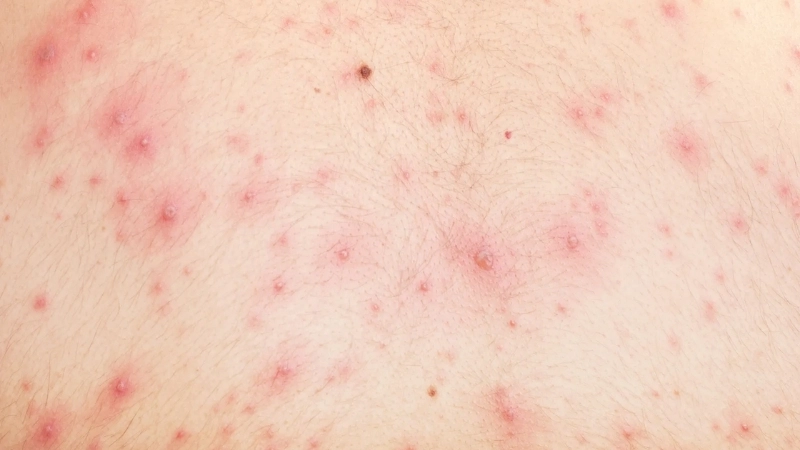
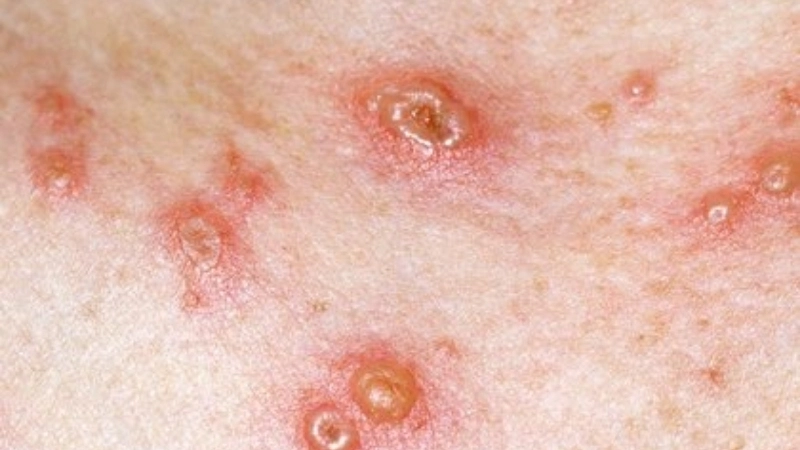
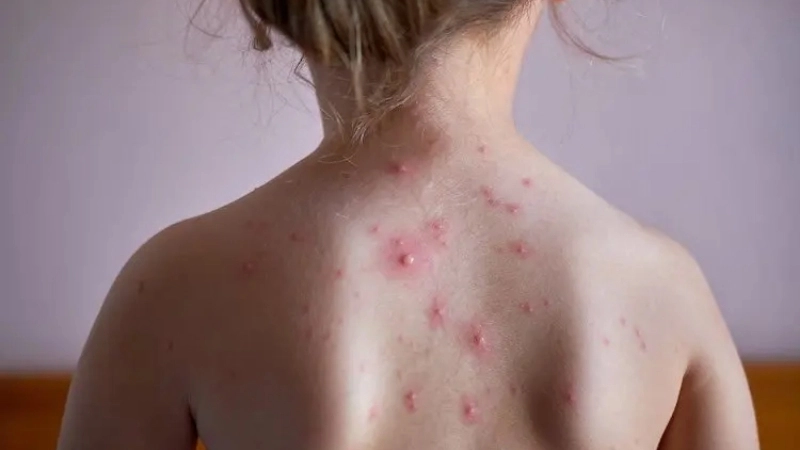
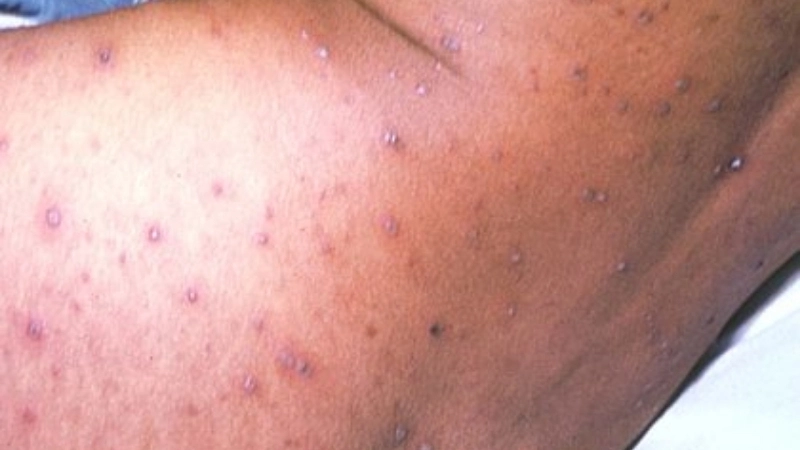
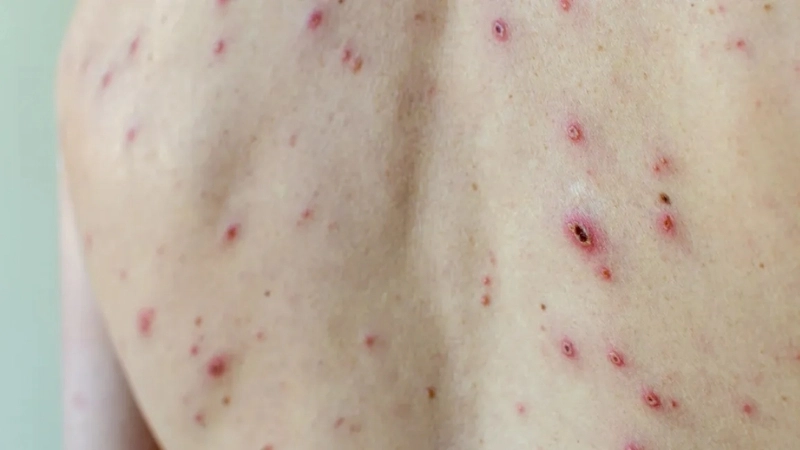
- Red, itchy rashes appear first on the face, chest, and back, progressing to small fluid-filled blisters that can spread across the body.
- Fever, fatigue, and general malaise often accompany the rash, signaling the body’s immune response to the viral infection.
- Loss of appetite, headache, and mild muscle aches may also occur, providing early warning signs before the rash fully develops.
>>>Refer to more: Rubella (German Measles) causes symptoms and prevention
How can you prevent Chickenpox effectively?
- Vaccination is the most reliable prevention, with the varicella vaccine providing strong immunity against future infections.
- Avoid close contact with individuals known to have chickenpox, especially for unvaccinated children and people with weakened immune systems.
- Maintain strict hygiene by washing hands regularly, disinfecting surfaces, and avoiding sharing personal items to reduce the risk of transmission.
>>>Refer to more: Measles (Rubeola) symptoms causes and prevention tips
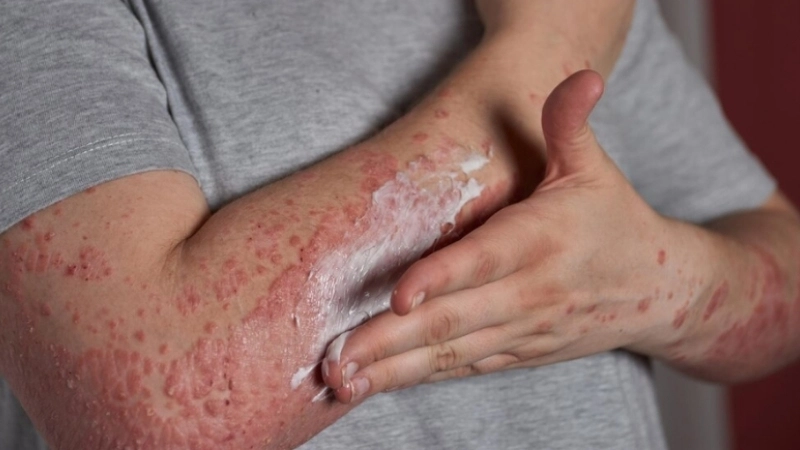
Image description of Chickenpox
Chickenpox is a highly contagious viral infection marked by itchy red rashes and fluid-filled blisters. It primarily affects children but can also impact adults, requiring careful care and preventive measures.
>>>Refer to more: Understanding human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV) infection
By recognizing chickenpox symptoms early and following proper care, you can reduce discomfort and prevent complications. Awareness and vaccination remain key to protection.