Experiencing sudden joint pain and a rash after visiting Australia? It could be more than just a bug bite. Understanding Barmah Forest virus disease is vital to manage symptoms and avoid potential long-term effects like chronic fatigue. Know the facts now.
What are the main causes of Barmah Forest Virus Disease?
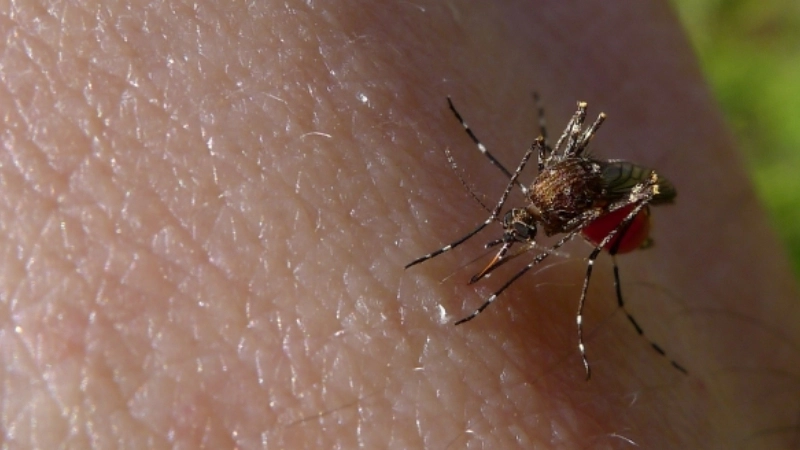
- The disease is caused by the Barmah Forest virus, an arbovirus transmitted to humans exclusively through the bite of an infected mosquito.
- Various mosquito species, primarily in coastal and inland waterway regions of Australia, act as vectors, carrying the virus from infected animals to people.
- Barmah Forest virus disease is not contagious from person to person; you can only acquire the infection through an infected mosquito bite.

Key symptoms of Barmah Forest Virus Disease to watch for
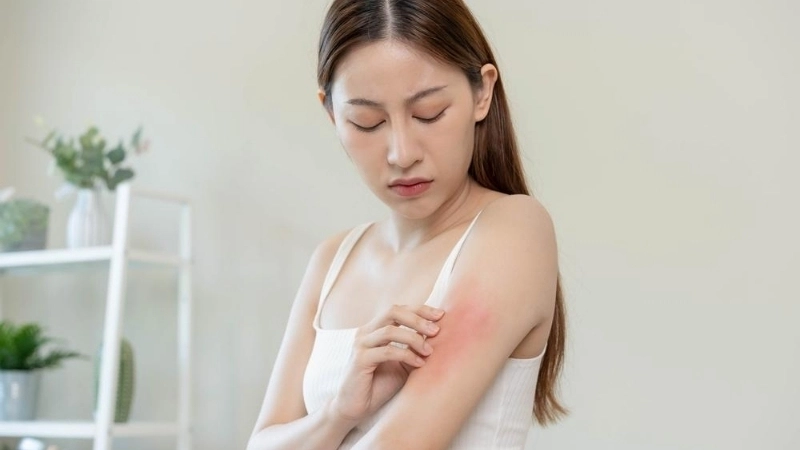
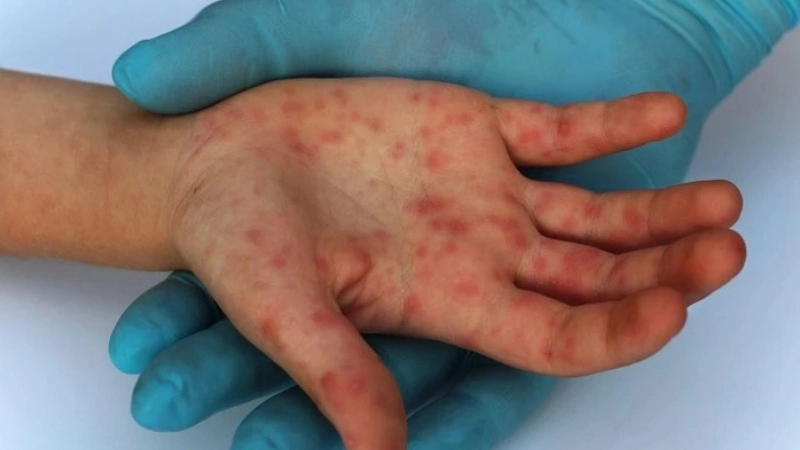
- The most common symptoms of Barmah Forest virus are debilitating joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, often accompanied by a distinctive red rash.
- Many people also experience fever, headaches, muscle aches (myalgia), and a general feeling of being unwell, which is very similar to the flu.
- Lethargy and chronic fatigue are significant symptoms that can persist for several weeks or even months after the initial infection has resolved.
How can you prevent Barmah Forest Virus Disease effectively?
- Effective mosquito bite prevention includes using an insect repellent containing DEET or picaridin on all exposed skin, especially around dawn and dusk.
- Wear long, loose-fitting, and light-colored clothing to cover as much of your body as possible when you are spending time outdoors.
- Avoid areas with high mosquito activity, like wetlands, and ensure your accommodation has intact insect screens on all windows and doors.
>>> Learn now: Salmonellosis - A bacterial infection from contaminated food
Image of the disease Barmah Forest Virus Disease


>>> See more: Typhoid fever - A guide to vaccination, symptoms, and prevention
While Barmah Forest virus recovery can be slow, understanding the illness is key. If you suspect you have it, see a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment to manage symptoms and potential long-term effects. Protect yourself and travel smart.
>>> Don't miss: Yersiniosis - A bacterial infection often mistaken for appendicitis






