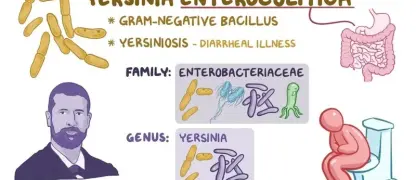
Don't let Salmonellosis disrupt your health. This common foodborne illness is preventable with the right knowledge. This guide provides essential facts on how to protect yourself and your family from this widespread bacterial infection.
What are the main causes of Salmonellosis?
- Salmonellosis is a bacterial infection caused by Salmonella, often contracted by eating contaminated food, which is how you get salmonella.
- Common salmonella infection sources include raw or undercooked poultry, making salmonella from chicken a primary concern for food safety in everyday meals.
- Contaminated raw salmonella from eggs, unpasteurized milk, and cross-contamination from kitchen surfaces can also easily spread the harmful bacteria.

Key symptoms of Salmonellosis to watch for
- The main salmonella symptoms include diarrhea, fever, and stomach cramps, which typically begin 6 hours to 6 days after infection.
- While most people ask how long does salmonella last (usually 4-7 days), severe infections can cause bloody stool salmonella and dehydration.
- The illness is salmonella contagious; the bacteria can spread from person to person through poor hygiene, especially if hands are not washed thoroughly.
How can you prevent Salmonellosis effectively?
- A key salmonella prevention step is cooking food thoroughly; using a food thermometer ensures you reach the correct cooking temperatures to kill salmonella.
- Always wash your hands, utensils, and cutting boards with soap and hot water after they have been in contact with raw meat or eggs.
- Avoid cross-contamination by keeping raw meats, poultry, and seafood separate from ready-to-eat foods in your kitchen and refrigerator.
>>> See this article: Listeriosis: Risks in Pregnancy and Food Safety Tips
Recognizing the warning signs of Salmonellosis through images





>>> Find out together: Gastrointestinal Anthrax: Causes and Symptoms
Proper salmonella treatment focuses on hydration, though some severe cases may require antibiotics for salmonella. If symptoms are severe or persistent, consult a healthcare professional immediately for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate care.
>>> See more: Botulism: A Guide to Symptoms and Food Safety