Joint pain and stiffness shouldn't control your life. Understanding rheumatoid arthritis is the first step to managing symptoms and preventing long-term damage. Don't ignore the early signs; take control of your health today.
What are the main causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
- What is rheumatoid arthritis? It's an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, primarily the lining of the joints.
- A genetic predisposition plays a significant role; having specific genes can make you more susceptible to environmental triggers that activate the disease.
- Environmental factors like smoking, certain infections, and physical or emotional trauma are thought to trigger the condition in genetically susceptible individuals.
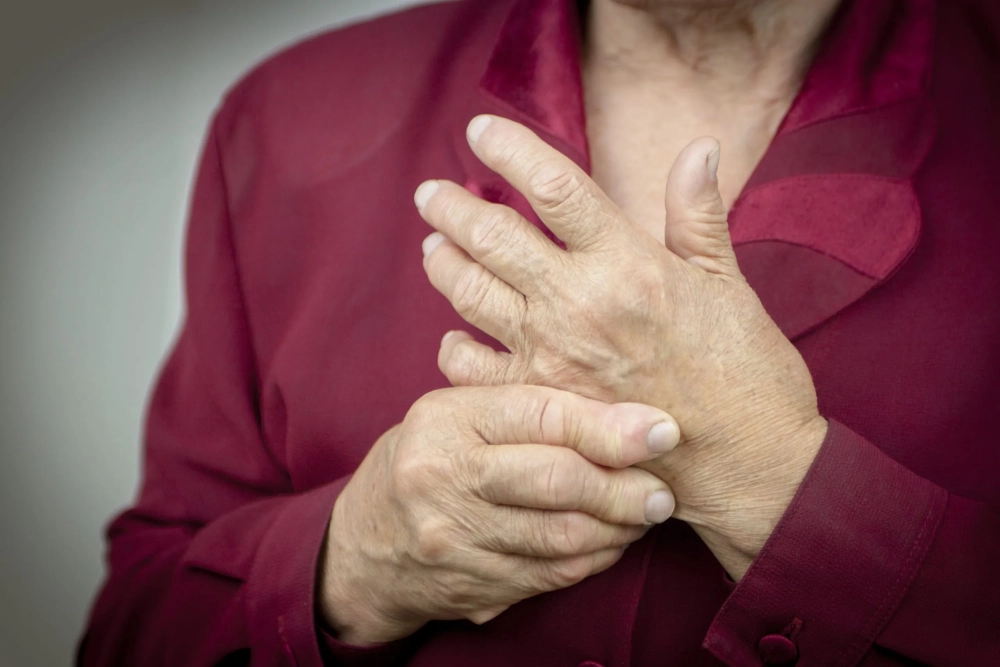
Key symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis to watch for
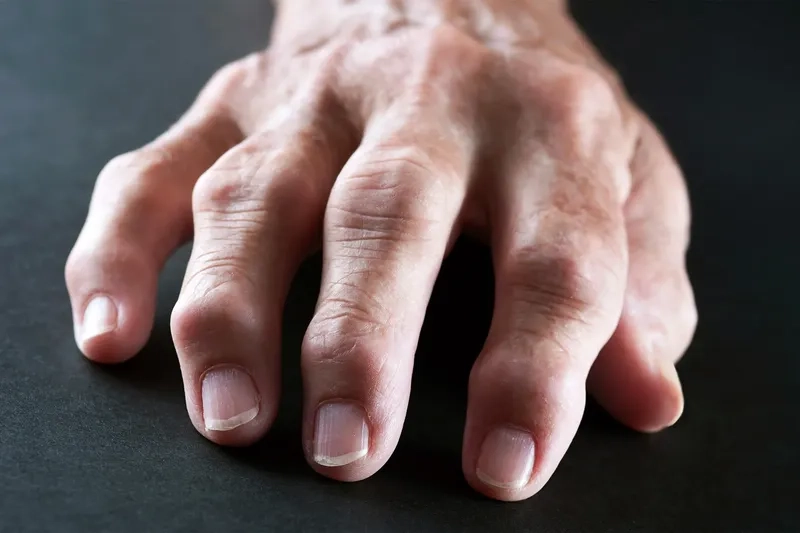
- The most common rheumatoid arthritis symptoms are tender, warm, swollen joints, often affecting smaller joints like those in the hands and feet symmetrically.
- Morning stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes, severe fatigue, and a low-grade fever are classic early signs of RA that should not be ignored.
- Symptoms often occur in periods of increased disease activity known as an RA flare up, followed by periods of remission where symptoms may ease
>>> Understand more: Hashimoto's thyroiditis - The autoimmune cause of hypothyroidism
How can you prevent complications from Rheumatoid Arthritis effectively?
- While you can't prevent RA, early diagnosis through blood tests like the rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP test is crucial to start treatment.
- Following a consistent RA treatment plan with drugs like methotrexate or biologics for RA is the most effective way to prevent joint damage.
- Adopting a balanced RA diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods and engaging in regular, gentle exercise can help manage symptoms and improve overall health.
>>> See more photos: Hemochromatosis - The risks of iron overload in your body
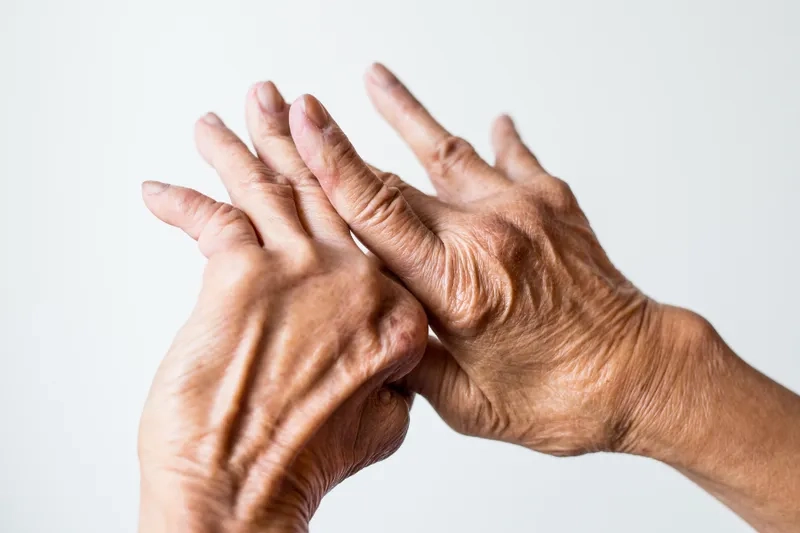
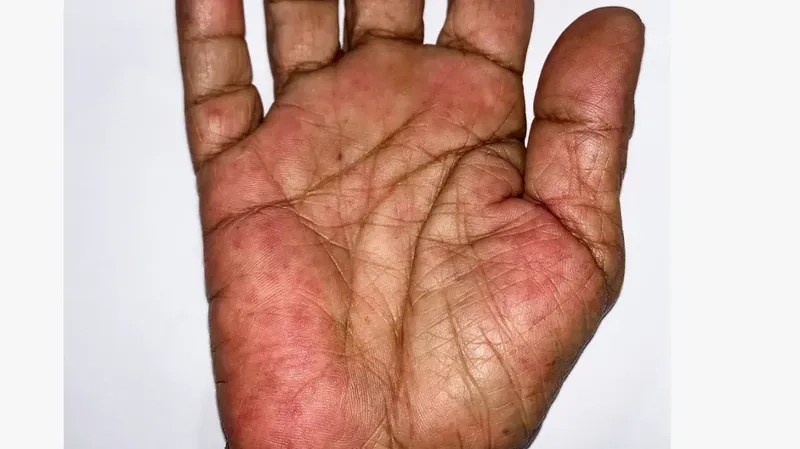
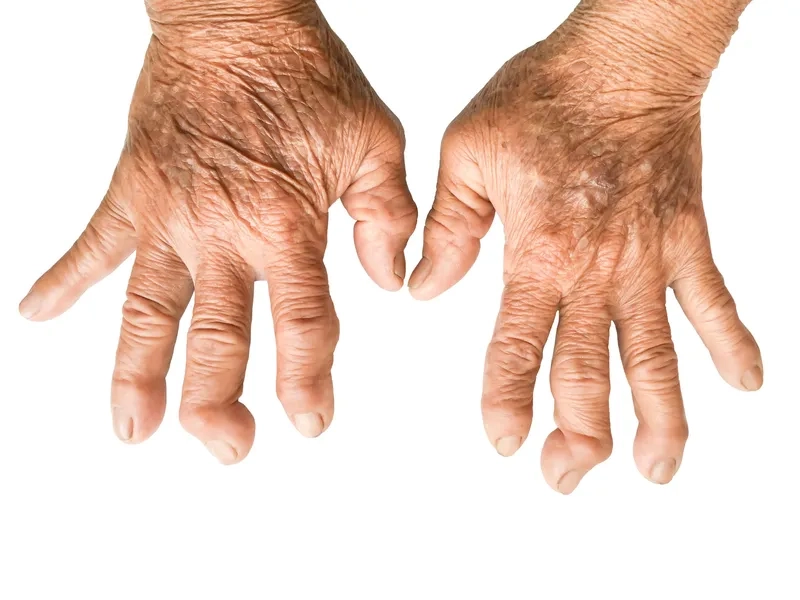
The top Rheumatoid Arthritis images everyone is searching for
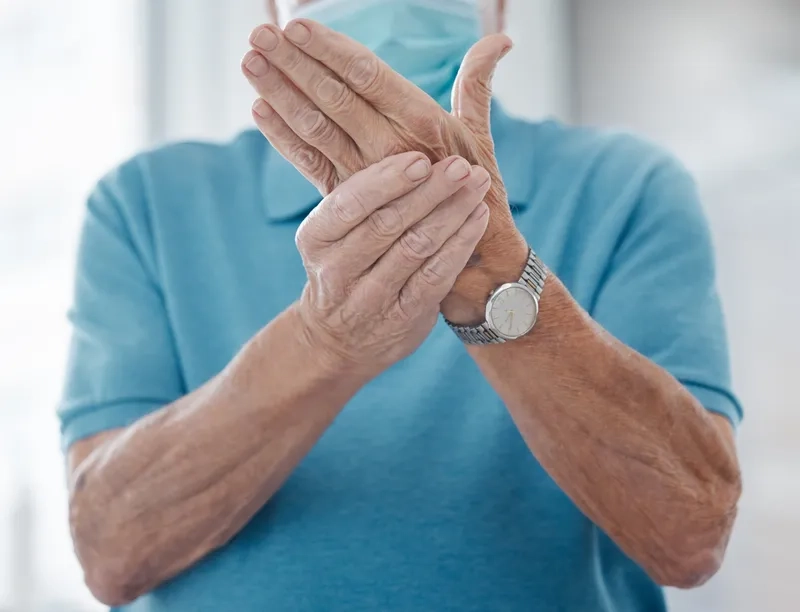



>>> Explore more: Wilson's disease - When copper builds up in the body