Down Syndrome (associated heart defects) is a critical health concern, influencing growth, cardiac function, and quality of life. Awareness ensures better care.
What are the main causes of Down Syndrome (associated heart defects)?
- Genetic abnormalities such as an extra chromosome 21 increase the risk of congenital heart defects in children with Down Syndrome.
- Abnormal fetal heart development during early pregnancy often leads to atrioventricular septal defects in affected infants.
- Family history and maternal factors may contribute to a higher risk of heart complications associated with Down Syndrome.

Understanding Down syndrome heart defects
>>> Understand more about: Key facts about marfan syndrome symptoms and complications
Key symptoms of Down Syndrome (associated heart defects) to watch for
- Shortness of breath during feeding or activity is a common symptom indicating heart defects in children with Down Syndrome.
- Poor growth and delayed weight gain often occur due to the heart’s inability to pump blood effectively.
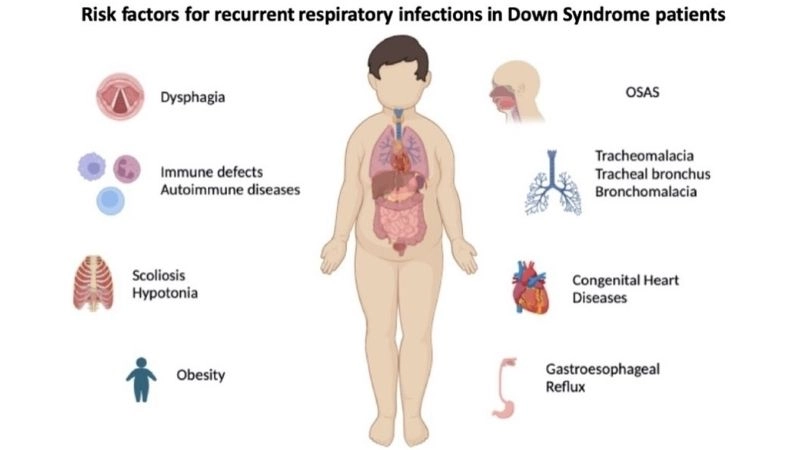
- Frequent respiratory infections may signal underlying congenital heart problems associated with Down Syndrome.
How can you prevent Down Syndrome (associated heart defects) effectively?
- Prenatal screening and genetic counseling help detect risk factors early, allowing timely medical interventions.
- Regular echocardiograms and pediatric checkups ensure early detection and treatment of congenital heart defects.
- Maintaining maternal health with proper nutrition and avoiding harmful exposures reduces pregnancy-related risks.
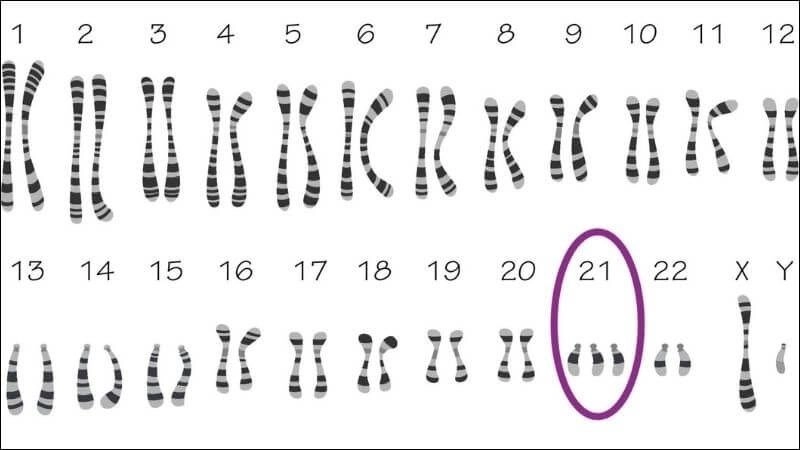
Atrioventricular septal defect in Down syndrome
>>> Understand more about: Loeys-Dietz syndrome overview causes and prevention tips
Images visual examples of Down Syndrome
Visual examples of Down Syndrome (associated heart defects) often show cardiac imaging, including echocardiograms, that highlight structural abnormalities in the heart commonly linked with the condition.
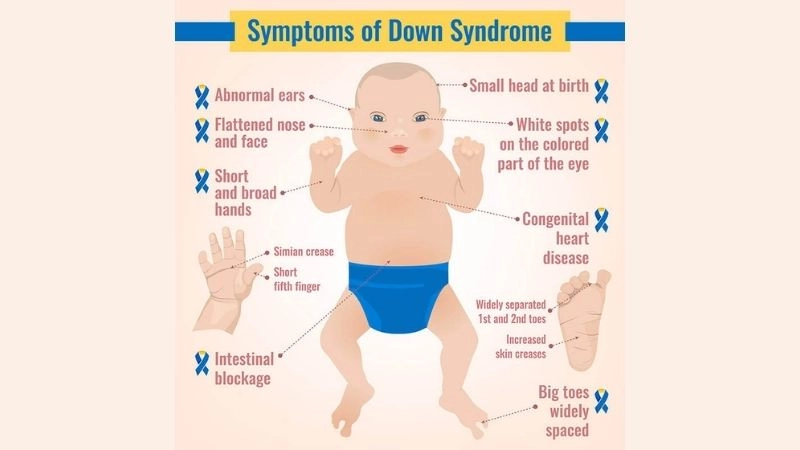





>>> Understand more about: Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (Vascular Type) key symptoms
Understanding Down Syndrome (associated heart defects) helps improve treatment, provide timely support, and enhance overall health and life expectancy.





